Abstract
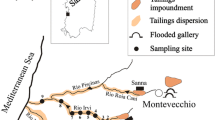
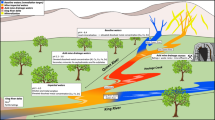
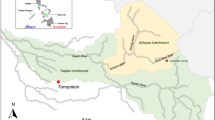
Cu–Pb deposits at Funtana Raminosa in Central Sardinia were intensively exploited, mostly underground, from 1917 until 1983. Flotation tailings were dumped near the mine plant. A hydrogeochemical survey carried out in 2004 showed that mine drainage collected from several galleries was circumneutral, due to the availability of carbonate minerals that buffer the acidity produced by the oxidation of Fe-bearing sulphides. The mine waters contained higher concentrations of dissolved SO4, F, Zn, Cd, Pb, Mn, and Mo than was observed in uncontaminated spring and stream waters in the area. Drainage from the oldest flotation tailings showed much lower concentrations of Zn, Cd, and Pb than those generally observed in mine waters. In contrast, drainage from the recent flotation tailings had the highest levels of dissolved SO4, Zn, and Cd (1,600, 30, and 0.8 mg/L, respectively) when sampled in the dry season; these were two orders of magnitude lower in the rainy season under high flow condition. Pb was ≈ 5 μg/L under different flow conditions. Water in the Rio Saraxinus, a stream that drains the entire mining area, had a relatively low level of contamination (170 μg/L Zn, 7 μg/L Cd, and 0.9 μg/L Pb).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertorino G, Caboi R, Caredda AM, Fanfani L, Gradoli MG, Massoli-Novelli R, Zanzari AR, Zuddas P (1981) Studi di prospezione idrogeochimica per metalli non ferrosi. Commission European Communities, Final Report Contract 113-79-7 MPP I, p 128 (in Italian)
Bertorino G, Caboi R, Caredda AM, Fanfani L, Gradoli MG, Zuddas P (1987) Prospezione idrogeochimica mineraria nell’aria di Gadoni-Seulo (Sardegna Centrale): il significato di solfati e fluoruri disciolti. Rend Soc It Miner Petrol 42:47–58 (in Italian)
Carmignani L, Barca S, Oggiano G, Pertusati PC, Salvadori I, Conti P, Eltrudis A, Funedda A, Pasci S (2001) Geological map of Sardinia. Scale 1:200000. Litografia Artistica Cartografica, Firenze
Chester R (1990) Marine geochemistry. Unwin Hyman, London, p 698
Cidu R, Frau F (2007) Influence of fine particles on the concentration of trace elements in river waters. In: Bullen TD, Wang Y (eds) Proc, WRI-12, July 31-Aug 5, 2007. Kunming/Taylor & Francis, PR China/London, pp 1471–1474
Cidu R, Mereu L (2007) The abandoned copper-mine of Funtana Raminosa (Sardinia): preliminary evaluation of its impact on the aquatic system. In: Cidu R, Frau F (eds) Proc, IMWA 2007: water in mining environment. MAKO Edizioni, Cagliari, pp 53–57
Frau F, Rizzo R, Sabelli C (1998) Creedite from Sardina, Italy: the first European occurrence. N Jb Miner Mh 11:495–504
Garbarino C, Grillo SM, Marini C, Mazzella A, Melis F, Padalino G, Tocco S, Violo M, Maccioni M, Fiori M (1984) The Paleozoic metallogenic epochs of the Sardinian microplate (Western Mediterranean): an attempt of synthesis on geodynamic evolution and mineralizing processes. Rend Soc It Miner Petrol 39:193–228
Haxel GB, Hedrick JB, Orris GJ (2002) Rare earth elements, Critical resources for high technology. US Geological Survey, http://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2002/fs087–02/ (accessed July 2006)
Lee S-G, Lee D-H, Kim Y, Chae B-G, Kim W-Y, Woo N-C (2003) Rare earth elements indicators of groundwater environment changes in fractured rock system: evidence from fracture-filling calcite. Appl Geochem 18:135–143
Leybourne MI, Goodfellow WD, Boyle DR, Hall GM (2000) Rapid development of negative Ce anomalies in surface waters and contrasting REE patterns in groundwaters associated with Zn–Pb massive sulphide deposits. Appl Geochem 15:695–723
McLennan SM (1989) Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. In: Lipin BR, McKay GA (eds) Geochemistry and mineralogy of rare earth elements. Mineral Soc America, Rev Mineralogy 21:169–199
Merten D, Kothe E, Buchel G (2004) Studies on microbial heavy metal retention from uranium mine drainage water with special emphasis on rare earth elements. Mine Water Environ 23:34–43
Mezzolani S, Simoncini A (1993) Sardegna da salvare: paesaggi e architetture delle miniere. Archivio Fotografico Sardo, Nuoro (in Italian)
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) PHREEQC (version 2) a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. Water Res Investig Rep 99–4559
Peplow D, Edmonds R (2006) Cell pathology and development effects of mine waste contamination on invertebrates and fish in the Methow river, Okanogan County, Washington (USA). Mine Water Environ 25:190–203
Protano G, Riccobono F, Sabatini G (1996) Magmatism and hydrothermal processes in the Funtana Raminosa ore district (Central Sardinia, Italy): petrographic and geochemical features. Miner Petrogr Acta 39:135–158
RAS (1998a) Il Parco geominerario della Sardegna: sintesi del progetto. Regione Autonoma della Sardegna (Assessorato della Difesa dell’Ambiente). Grafiche Sainas, Cagliari (in Italian)
RAS (1998b) Nuovo studio dell’idrologia superficiale della Sardegna. Regione Autonoma della Sardegna, (Assessorato della Programmazione, Bilancio ed Assetto del Territorio), Ente Autonomo del Flumendosa, Cagliari (in Italian)
Stara P, Rizzo R, Sabelli C, Ibba A (1999) I minerali di Funtana Raminosa (Gadoni, Sardegna centrale). Riv Mineral Ital 1:10–27 (in Italian)
Tylecote RF, Balmuth MS, Massoli-Novelli R (1984) Copper and bronze metallurgy in Sardinia. In: Balmuth MS, Rowland RJJ (eds) Studies in Sardinian archaeology. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor, pp 115–162
Verplanck PL, Taylor HE, Nordstrom DK, Barber LB (2005) Aqueous stability of gadolinium in surface waters receiving sewage treatment plant effluent, Boulder Creek, Colorado. Environ Sci Technol 39(18):6923–6929
WHO (2006) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by funds from MURST (60% Cidu) and Fondazione Banco di Sardegna. Thanks to IGEA SpA for sampling permission, Orlando Bellè for useful information on the mine history, and Giorgio Contis for IC analyses. Data collected in the 2004 survey were used by Luca Mereu for his thesis degree in Earth Sciences. Thanks to Franco Frau for his useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cidu, R. Influence of Past Mining on the Quality of Surface Waters at Funtana Raminosa (Sardinia). Mine Water Environ 26, 199–208 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-007-0013-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-007-0013-5