Abstract
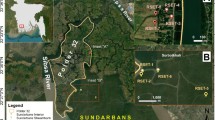
The main objectives of the current work are (1) to determine historic pattern of shoreline changes (erosion and accretion) along the north coast of the Nile Delta, (2) to present a future view on what to be expected regarding climate change impacts, sea-level rise (SLR) scenarios, expected land losses and alteration of some soil characteristics (3) to recognize negative impacts of SLR on the Nile Delta coast and (4) to assess and suggest protection measures. The current investigation was conducted using the advanced techniques of remote sensing and geographic information system. The investigated area with 394 measured locations is located along the northern coast of the Nile Delta between Alexandria and ElTina plain in Sinai peninsula exactly between 29°20′ and 32°40′ E and 29°54′ and 31°35′ N with the minimum erosion values of 1.11 m2, maximum of 6,044,951.64 m2 and total of 16.02 km2. On the other hand, 177 sites showed minimum accretion values of 0.05 m2, maximum of 2,876,855.86 m2 and total of 13.19 km2. SLR was determined by applying the quadrant equation for 10-year intervals using 1990 as the base year. Mediterranean SLR along the Nile Delta coast could be estimated considering three different scenarios (low 0.20 m, medium 0.50 m, and high 0.90 m). Impacts of SLR are divided into (1) primary and (2) secondary impacts. Over the coming decades, the Nile Delta will face greater threat due to SLR and land subsidence as well. Regarding climate change and its impacts on soil characteristics, rapid increase in salinity values during the former three decades were found. This increase may be due to the intrusion of salty water of the Mediterranean. On the other hand, organic matter content decreased due to higher temperature, especially during the summer season. Some protection measures were assessed and suggested to combat or tackle SLR.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bijlsma L, Ehler CN, Klein RJT, Kulshrestha SM, McLean RF, Mimura N, Nicholls RJ, Nurse LA, Perez Nieto H, Stakhiv EZ, Turner RK, Warrick RA (1996) Coastal zones and small islands. In: Watson RT, Zinyowera MC, Moss RH (eds) Impacts, adaptations and mitigation of climate change: scientific-technical analyses, the second assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change, Working Group II. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 289–324
Climate Change (2007) http://www.rothamsted.bbsrc.ac.uk/intopractice/Climate Change.pdf
El-Nahry AH (2001) An approach for sustainable land use studies of some areas in Northwest Nile Delta, Egypt. PhD thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, Soil Department, Cairo University, Egypt
ESRI (2007) Arc Map version 9.2. user manual. ESRI, 380 New York Street, Redlands, CA, 92373-8100, USA
Frihy O, Dewidar K (1993) Influence of shoreline erosion and accretion on texture and heavy mineral compositions of beach sands of the Borolous coast, north-central Nile Delta, Egypt. Marine Geol 114(1–2):1–104 (38 ref.)
Frihy O, Lotfy M (1994) Mineralogy and textures of beach sands in relation to erosion and accretion along the Rosetta promontory of the Nile Delta, Egypt. J Coast Res 10(3):588–599 (29 reference)
Frihy O, Debes A, El Sayed W (2003) Processes reshaping the Nile Delta promontories of Egypt: pre- and post-protection. Geomorphology 53(3–4):263–279
IPCC CZMS (1992) Global climate change and the rising challenge of the sea. Workshop, Isla de Margarita, Venezuela, 9–13 March 1992
IPCC (2007) Climate Change 2007: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. contribution of working group II to the third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. In: Parry, Martin L, Canziani, Osvaldo F, Palutikof, Jean P, van der Linden, Paul J, and Hanson, Clair E (eds) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 1000
ITT (2008) ITT corporation ENVI 4.5 software,1133 Westchester Avenue, White Plains, NY 10604, USA
Lillesand TM, Kiefer RW (2000) Remote sensing and image interpretation. Wiley, New York, p 579
MASR (1978) El-Behaira Governorate Soil Fertility, Ministry of Agriculture and Soil Reclamation, Final report, 1978
Maxwell A (2008) FY95 program summaries Nile Delta subsidence and sea level rise.mht process studies-solid earth processes. Smithsonian Institution, Washington DC
Milliman JD (1992) Sea-level response to climate change and tectonics in the Mediterranean Sea. In: Jeftic L, Milliman JD, Sestini G (eds) Climatic change and the Mediterranean. Edward Arnold, London, pp 45–57
Mohsen A (1999) Sustainable development in the light of climate change. In: IIIEE network, the first global environmental experience sharing conference, 24–26 September 1999. http://www.iiiee.lu.se/networkconference/2.4ahmed.htm. Accessed 1 Feb 2004
Nicholls RJ, Leatherman SP (1996) Adapting to sea-level rise: relative sea-level trends to 2100 for the United States. Coast Manage 24:301–324
NRC (1987) Responding to changes in sea level: engineering implications. Report of the National Research Council. National Academy Press, Washington DC
Ranchin T, Wald L (2000) Comparison of different algorithms for the improvement of the spatial resolution of images. In: Proceeding of the third conference “Fusion of Earth data: merging point measurements, raster maps and remotely sensed images”, Sophia Antipolice, France, January 26–28, pp 33–41
Rowell DL (1995) Soil science methods and applications: Library of Congress Cataloging in Publication data, New York
Shalash S (1982) Effects of sedimentation on the storage capacity of the High Aswan Dam reservoir. Hydrobiologia J 91–92(1); Springer, The Netherlands
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (2002) Coastal engineering manual. Engineer Manual 1110-2-1100, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Washington, DC (in 6 volumes)
Van Goor MA, Zitman TJ, Wang ZB, Stive MJF (2003) Impact of sea-level rise on the morphological equilibrium state of tidal inlets. Mar Geol 202:211–227
Wang B, Chen S, Zhang K, Shen J (1995) Potential impacts of sea-level rise on the Shanghai area. J Coast Res Special Issue 14:151–166
Warrick R, Oerlemans J, Woodworth P, Meier M, Le Provost C (1996) Changes in sea level. In: Houghton JT et al (eds) Climate change 1995: the science of climate change. Report of IPCC Working Group I. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 363–405
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Nahry, A.H., Doluschitz, R. Climate change and its impacts on the coastal zone of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ Earth Sci 59, 1497–1506 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0135-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0135-0