Abstract
The present work demonstrates the efficient alkaline pre-treatment method to obtain a cellulose rich fraction from agricultural waste biomass using low cost and biocompatible aqueous choline hydroxide [Ch]OH, a basic ionic liquid (BIL) and the conversion of isolated cellulose into 5-(hydroxymethyl) furfural, catalyzed by various homogeneous acidic deep eutectic solvents (DES).
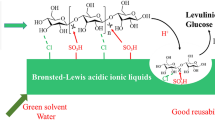
Graphical Abstract

(a) Low cost, mild biodegradable choline hydroxide (basic ionic liquid). (b) White cellulose fibers without bleaching process. (c) Recyclable and recoverable catalysts. And (d) High yield and purity of 5-HMF.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donate, P.M.: Green synthesis from biomass. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-014-0004-2 (2014)
Kumar, A.K., Sharma, S.: Recent updates on different methods of pretreatment of lignocellulosic feedstocks: a review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 4, 1–19 (2017)
Dutta, S., Bhaumik, A., Wu, K.C.W.: Hierarchically porous carbon derived from polymers and biomass: effect of interconnected pores on energy applications. Energy Environ. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EE01075B (2014)
Dutta, S., Wu, K.C.W.: Enzymatic breakdown of biomass: enzyme active sites, immobilization, and biofuel production. Green Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4gc01405g (2014)
Kim, J.S., Lee, Y.Y., Kim, T.H.: A review on alkaline pre-treatment technology for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.085 (2015)
Brodeur, G., Yau, E., Badal, K., Collier, J., Ramachandran, K.B., Ramakrishnan, S.: Chemical and physicochemical pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: a review. Enzyme Res. 1–17. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/787532 (2011)
Guimond, R., Chabot, B., Law, K.N., Daneauld, C.: The use of cellulose nanofibres in paper making. J. Pulp Paper Sci. 36, 55–61 (2010)
Dutta, S., Wu, K.C.W., Saha, B.: Emerging strategies of breaking 3D amorphous network of lignin. Catal. Sci. Technol. 4, 3785–3799 (2014)
Tianjiao, Q.T., Zhang, X., Gu, X., Han, H., Ji, G., Chen, X., Xiao, W.: Ball milling for biomass fractionation and pretreatment with aqueous hydroxide solutions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5, 7733–7742 (2017)
Karp, E.M., Resch, M.G., Donohoe, B.S., Ciesielski, P.N., O’Brien, M.H., Nill, J.E., Mittal, A., Biddy, M.J., Beckham, G.T.: Alkaline pretreatment of switch grass. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 3, 1479–1491 (2015)
Costa Lopes, A.M., Joao, K.G., Morais, A.R.C., Lukasik, E.B., Lukasik, R.B.: Ionic liquids as a tool for lignocellulosic biomass fractionation. Sustain. Chem. Process. 1, 1–31 (2013)
Hou, Q., Ju, M., Li, W., Liu, L., Chen, Y., Yang, Q.: Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass with ionic liquids and ionic liquid-based solvent systems. Molecules. 22, 490 (2017)
Peleteiro, S., Rivas, S., Alonso, J.L., Santos, V., Parajo, J.C.: Utilization of ionic liquids in lignocellulose biorefineries as agents for separation, derivatization, fractionation or pretreatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03461 (2015)
Costa Lopes, A.M., Lukasik, R.B.: Acidic ionic liquids as sustainable approach of cellulose and lignocellulosic biomass conversion without additional catalysts. ChemSusChem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201402950 (2015)
Rashida, T., Kait, C.F., Regupathi, I., Murugesan, T.: Dissolution of kraft lignin using protic ionic liquids and characterization. Ind. Crops Prod. 84, 284–293 (2016)
Sochaa, A.M., Parthasarathia, R., Jian, S., Pattathile, S.K., Whytea, D., Bergerona, M., Georgea, A., Trana, K., Stavilad, V., Venkatachalame, S., Hahne, M.G., Simmonsa, B.A., Singh, S.: Efficient biomass pretreatment using ionic liquids derived from lignin and hemicellulose. PNAS. 3587–3595. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1405685111 (2014)
Matsagar, B.M., Hossain, S.A., Islam, T., Alamri, H.R., Alothman, Z.A., Yamauchi, Y., Dhepe, P.L., Wu, K.C.W.: Direct production of furfural in one-pot fashion from raw biomass using Brønsted acidic ionic liquids. Sci. Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13946-4 (2017)
Ninomiya, K., Inoue, K., Aomori, Y., Ohnishi, A., Ogino, C., Shimizu, N., Takahashi, K.: Characterization of fractionated biomass component and recovered ionic liquid during repeated process of cholinium ionic liquid-assisted pretreatment and fractionation. Chem. Eng. J. 259, 323–329 (2015)
Ren, H., Zong, M.H., Wu, H., Li, N.: Efficient pretreatment of wheat straw using novel renewable cholinium ionic liquids to improve enzymatic saccharification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03729 (2016)
Ninomiya, K., Yamauchi, T., Kobayashi, M., Ogino, C., Shimizua, N., Takahashi, K.: Cholinium carboxylate ionic liquids for pretreatment of lignocellulosic materials to enhance subsequent enzymatic saccharification. Biochem. Eng. J. 71, 25–29 (2013)
Hou, X.D., Smith, T.J., Li, N., Zong, M.H.: Novel renewable ionic liquids as highly effective solvents for pretreatment of rice straw biomass by selective removal of lignin. Biotechnol. Bioeng. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24522 (2012)
Liu, Z., Li, L., Liu, C., Xu, A.: Pretreatment of corn straw using the alkaline solution of ionic liquids. Bioresour. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.117 (2018)
Silva, S.P.M., Costa Lopes, A.M., Roseiroa, L.B., Lukasik, R.B.: Novel pre-treatment and fractionation method for lignocellulosic biomass using ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 3, 16040–16050 (2013)
Lau, B.B.Y., Yeung, T., Patterson, R.J., Aldous, L.: A cation study on rice husk biomass pretreatment with aqueous hydroxides: cellulose solubility does not correlate with improved enzymatic hydrolysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5, 5320–5329 (2017)
Yang, C.Y., Fang, T.J.: Kinetics of enzymatic hydrolysis of rice straw by the pretreatment with a bio-based basic ionic liquid under ultrasound. Process Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.01.013 (2015)
Jeong, G.T., Ra, C.H., Hong, Y.K., Kim, J.K., Kong, I.S., Kim, S.K., Park, D.H.: Conversion of red-algae Gracilaria verrucosa to sugars, levulinic acid and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 38, 207–217 (2015)
Fukuoka, A., Dhepe, P.L.: Catalytic conversion of cellulose into sugar alcohols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 5161 – 5163 (2006)
Santos, D., Silva, U.F., Duarte, F.A., Bizzi, C.A., Flores, E.M.M., Mello, P.A.: Ultrasound-assisted acid hydrolysis of cellulose to chemical building blocks: application to furfural synthesis. Ultrason. Sonochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.04.034 (2017)
Nandiwale, K.Y., Galande, N.D., Thakur, P., Sawant, S.D., Zambre, V.P., Bokade, V.V.: One-pot synthesis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by cellulose hydrolysis over highly active bimodal micro/mesoporous H-ZSM-5 catalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2, 1928–1932 (2014)
Zhou, L., Liang, R., Ma, Z., Wu, T., Wu, Y.: Conversion of cellulose to HMF in ionic liquid catalyzed by bifunctional ionic liquids. Bioresour. Technol. 129, 450–455 (2013)
Kim, B., Jeong, J., Lee, D., Kim, S., Yoon, H.J., Lee, Y.S., Cho, J.K.: Direct transformation of cellulose into 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural using a combination of metal chlorides in imidazolium ionic liquid. Green Chem. 13, 1503 (2011)
Tang, X., Zuo, M., Li, Z., Liu, H., Xiong, C., Zeng, X., Sun, Y., Hu, L., Liu, S., Lei, T., Lin, L.: Green processing of lignocellulosic biomass and its derivatives in deep eutectic solvents. ChemSusChem. 10, 2696–2706 (2017)
Lee, Y.C., Dutta, S., Wu, K.C.W.: Integrated, cascading enzyme-/chemocatalytic cellulose conversion using catalysts based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ChemSusChem. 7, 3241–3246 (2014)
Lee, Y.C., Chen, T.C., Chiu, Y.T., Wu, K.C.W.: An effective cellulose-to-glucose-to-fructose conversion sequence by using enzyme immobilized Fe3O4-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles as recyclable biocatalysts. ChemCatChem. 5, 2153–2157 (2013)
Alama, M.I., Dea, S., Singh, B., Saha, B., Abu-Omarb, M.M.: Titanium hydrogenphosphate: an efficient dual acidic catalyst for 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) production. Appl. Catal. A 486, 42–48 (2014)
Kuo, I.J., Suzuki, N., Yamauchi, Y., Wu, K.C.W.: Cellulose-to-HMF conversion using crystalline mesoporous titania and zirconia nanocatalysts in ionic liquid systems. RSC Adv. 3, 2028–2034 (2013)
Hsu, W.H., Lee, Y.Y., Peng, W.H., Wu, K.C.W.: Cellulosic conversion in ionic liquids (ILs): effects of H2O/cellulose molar ratios, temperatures, times, and different ILs on the production of monosaccharides and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). Catal. Today 174, 65–69 (2011)
Sert, M., Aslanoglu, A., Ballice, L.: Conversion of sunflower stalk based cellulose to the valuable products using choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents. Renew. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.10.083 (2017)
Li, X.C., Peng, K., Xia, Q., Liu, X., Wang, Y.: Efficient conversion of cellulose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over niobia/carbon composites. Chem. Eng. J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.105 (2017)
Yan, L., Zhao, Y., Gu, Q., Li, W.: Isolation of highly purity cellulose from wheat straw using a modified aqueous biphasic system. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 6, 282–291 (2012)
Assanosi, A.A., Farah, M.M., Wood, J., Duri, B.A.: A facile acidic choline chloride–p-TSA DES-catalyzed dehydration of fructose to 5-hydroxymethlfurfural. RSC Adv. 4, 39359–39364 (2014)
Workman, J., Weyer, L.: Practical guide to interpretive near infrared spectroscopy, CRC Press, Boca Raton. (2008)
Osborne, B.G.: Near infrared spectroscopy in food analysis, encyclopedia of analytical chemistry. Willey, New York (2006)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful Punjab engineering college (Deemed to be University), Chandigarh for necessary facility and SAIF-CIL Punjab University, Chandigarh for spectroscopic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12649_2019_603_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary material 1 Experimental procedures for extraction of cellulose, hemi-cellulose, lignin, synthesis of HMF from cellulose, comparison table for 5-HMF.Characterization details of all isolated lignocellulosic components and 5-HMF, etc. (DOCX 135 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, S., Gupta, N. & Singh, V. Choline Based Basic Ionic Liquid (BIL)/Acidic DES Mediated Cellulose Rich Fractionation of Agricultural Waste Biomass and Valorization to 5-HMF. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 3345–3354 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00603-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00603-2