Abstract
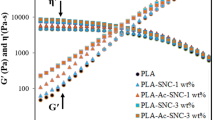
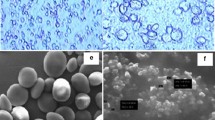
The development of low-cost bio-nanocomposites based on square-shaped starch nanocrystals (SNCs) is a promising approach for maintaining environmental sustainability. This study reports on a method for the preparation of bio-nanocomposites from polylactic acid (PLA) and SNC derived from acid hydrolysis of waxy maize starch. PLA–SNC bio-nanocomposites were prepared by incorporating SNC at 1, 3 and 5 wt% by dispersing them in PLA matrix using dichloromethane as a solvent. Morphological, thermal, crystalline and rheological properties of neat PLA, neat SNC and PLA–SNC bio-nanocomposites have been investigated to observe the effect of SNC loading. SNC loading at 3 wt% was found to be the optimum loading to improve the storage modulus, complex dynamic viscosity, and crystallinity, while 5 wt% loading caused agglomerations which led to a decrease in the above properties. Thermogravimetric analysis result suggested that both the SNC and PLA–SNC bio-nanocomposites were thermally stable from 25 to 240 °C. Electron microscopy study showed the effective dispersion of SNC in PLA.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajwa, D.S., Bajwa, S.G., Holt, G., Srinivasan, R., Coffelt, T., Nakayama, F., Gesch, R.: Recycling of ligno-cellulosic and polyethylene wastes from agricultural operations in thermoplastic composites. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 5(4), 709–714 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-013-9263-6
Fortunati, E., Peltzer, M., Armentano, I., Torre, L., Jiménez, A., Kenny, J.M.: Effects of modified cellulose nanocrystals on the barrier and migration properties of PLA nano-biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 90(2), 948–956 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.06.025
Raquez, J.-M., Habibi, Y., Murariu, M., Dubois, P.: Polylactide (PLA)-based nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 38(10–11), 1504–1542 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.05.014
Bouthegourd, E., Rajisha, K., Kalarical, N., Saiter, J.M., Thomas, S.: Natural rubber latex/potato starch nanocrystal nanocomposites: correlation morphology/electrical properties. Mater. Lett. 65(23–24), 3615–3617 (2011)
Condes, M.C., Anon, M.C., Mauri, A.N., Dufresne, A.: Amaranth protein films reinforced with maize starch nanocrystals. Food Hydrocoll. 47, 146–157 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.01.026
Li, X., Qiu, C., Ji, N., Sun, C., Xiong, L., Sun, Q.: Mechanical, barrier and morphological properties of starch nanocrystals-reinforced pea starch films. Carbohydr. Polym. 121, 155–162 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.12.040
Garcia, N.L., Ribba, L., Dufresne, A., Aranguren, M.I., Goyanes, S.: Physico-mechanical properties of biodegradable starch nanocomposites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 294(3), 169–177 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.200800271
Yu, J., Ai, F., Dufresne, A., Gao, S., Huang, J., Chang, P.R.: Structure and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid) filled with (starch nanocrystal)-graft-poly(ε -caprolactone). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 293(9), 763–770 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.200800134
Fortunati, E., Armentano, I., Zhou, Q., Iannoni, A., Saino, E., Visai, L., Berglund, L.A., Kenny, J.M.: Multifunctional bionanocomposite films of poly(lactic acid), cellulose nanocrystals and silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 87(2), 1596–1605 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.09.066
Madhavan Nampoothiri, K., Nair, N.R., John, R.P.: An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour. Technol. 101(22), 8493–8501 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.092
Le Corre, D., Bras, J., Dufresne, A.: Starch nanoparticles: a review. Biomacromolecules 11(5), 1139–1153 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/bm901428y
Yin, Z., Zeng, J., Wang, C., Pan, Z.: Preparation and properties of cross-linked starch nanocrystals/polylactic acid nanocomposites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/454708
Luzi, F., Fortunati, E., Di Michele, A., Pannucci, E., Botticella, E., Santi, L., Kenny, J.M., Torre, L., Bernini, R.: Nanostructured starch combined with hydroxytyrosol in poly(vinyl alcohol) based ternary films as active packaging system. Carbohydr. Polym. 193, 239–248 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.079
Espino-Pérez, E., Gilbert, R.G., Domenek, S., Brochier-Salon, M.C., Belgacem, M.N., Bras, J.: Nanocomposites with functionalised polysaccharide nanocrystals through aqueous free radical polymerisation promoted by ozonolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 135, 256–266 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.005
Garcia, N.L., Lamanna, M., D’Accorso, N., Dufresne, A., Aranguren, M., Goyanes, S.: Biodegradable materials from grafting of modified PLA onto starch nanocrystals. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 97(10), 2021–2026 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.03.032
Gao, H., Hu, S., Su, F., Zhang, J., Tang, G.: Mechanical, thermal, and biodegradability properties of PLA/modified starch blends. Polym. Compos. 32(12), 2093–2100 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.21241
Garcia, N.L., Fama, L., D’Accorso, N.B., Goyanes, S.: Biodegradable starch nanocomposites. In: Thakur, K.V., Thakur, K.M. (eds.) Eco-friendly Polymer Nanocomposites: Processing and Properties, vol. 75, pp. 17–77. Springer, New Delhi (2015)
Rajisha, K., Maria, H., Pothan, L., Ahmad, Z., Thomas, S.: Preparation and characterization of potato starch nanocrystal reinforced natural rubber nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 67, 147–153 (2014)
Visakh, P.M., Thomas, S.: Preparation of bionanomaterials and their polymer nanocomposites from waste and biomass. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 1(1), 121–134 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-010-9009-7
Tikapunya, T., Zou, W., Yu, W., Powell, P.O., Fox, G.P., Furtado, A., Henry, R.J., Gilbert, R.G.: Molecular structures and properties of starches of Australian wild rice. Carbohydr. Polym. 172, 213–222 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.046
LeCorre, D., Bras, J., Dufresne, A.: Influence of botanic origin and amylose content on the morphology of starch nanocrystals. J. Nanopart. Res. 13(12), 7193–7208 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-011-0634-2
Liu, D., Wu, Q., Chen, H., Chang, P.R.: Transitional properties of starch colloid with particle size reduction from micro- to nanometer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 339(1), 117–124 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.07.035
Shi, A., Li, D., Wang, L., Li, B., Adhikari, B.: Preparation of starch-based nanoparticles through high-pressure homogenization and miniemulsion cross-linking: influence of various process parameters on particle size and stability. Carbohydr. Polym. 83(4), 1604–1610 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.011
Le Corre, D., Vahanian, E., Dufresne, A., Bras, J.: Enzymatic pretreatment for preparing starch nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules. 13(1), 132 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/bm201333k
Sun, Q., Gong, M., Li, Y., Xiong, L.: Effect of retrogradation time on preparation and characterization of proso millet starch nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 111, 133–138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.03.094
Singh, V., Ali, S.Z.: Acid degradation of starch. The effect of acid and starch type. Carbohydr. Polym. 41(2), 191–195 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(99)00086-7
Jayakody, J.A.L.P.: The effect of acid hydrolysis on granular morphology and physicochemical properties of native cereal starch granules. Memorial University of Newfoundland (2001)
Angellier, H., Choisnard, L., Molina-Boisseau, S., Ozil, P., Dufresne, A.: Optimization of the preparation of aqueous suspensions of waxy maize starch nanocrystals using a response surface methodology. Biomacromolecules 5(4), 1545–1551 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/bm049914u
Le Corre, D., Bras, J., Choisnard, L., Dufresne, A.: Optimization of the batch preparation of starch nanocrystals to reach daily time-scale. Starch - Stärke 64(6), 489–496 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201100145
Mohammad Amini, A., Razavi, S.M.A.: A fast and efficient approach to prepare starch nanocrystals from normal corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 57, 132–138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.01.022
Sungsanit, K., Kao, N., Bhattacharya, S., Pivsaart, S.: Physical and rheological properties of plasticized linear and branched PLA. Korea–Aust. Rheol. J. 22(3), 187–195 (2010)
Murariu, M., Dechief, A.-L., Ramy-Ratiarison, R., Paint, Y., Raquez, J.-M., Dubois, P.: Recent advances in production of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) nanocomposites: a versatile method to tune crystallization properties of PLA. Nanocomposites 1(2), 71–82 (2015)
Turner, J., Riga, A., O’Connor, A., Zhang, J., Collis, J.: Characterization of drawn and undrawn poly-l-lactide films by differential scanning calorimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 75(1), 257–268 (2004)
Mathew, A.P., Oksman, K., Sain, M.: The effect of morphology and chemical characteristics of cellulose reinforcements on the crystallinity of polylactic acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 101(1), 300–310 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.23346
Bel Haaj, S., Thielemans, W., Magnin, A., Boufi, S.: Starch nanocrystals and starch nanoparticles from waxy maize as nanoreinforcement: a comparative study. Carbohydr. Polym. 143, 310 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.01.061
Li, W., Corke, H., Beta, T.: Kinetics of hydrolysis and changes in amylose content during preparation of microcrystalline starch from high-amylose maize starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 69(2), 398–405 (2007)
Jayakody, L., Hoover, R.: The effect of lintnerization on cereal starch granules. Food Res. Int. 35(7), 665–680 (2002)
LeCorre, D., Bras, J., Dufresne, A.: Influence of native starch’s properties on starch nanocrystals thermal properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 87(1), 658–666 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.08.042
Zhang, Z., Zhao, S., Xiong, S.: Physicochemical properties of Indica rice starch modified by mechanical activation and octenyl succinic anhydride. Starch - Stärke (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201600008
Putaux, J.-L., Molina-Boisseau, S., Momaur, T., Dufresne, A.: Platelet nanocrystals resulting from the disruption of waxy maize starch granules by acid hydrolysis. Biomacromolecules 4(5), 1198 (2003)
Condés, M.C., Añón, M.C., Dufresne, A., Mauri, A.N.: Composite and nanocomposite films based on Amaranth biopolymers. Food Hydrocoll. 74(Supplement C), 159–167 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.07.013
Liu, X., Wang, Y., Yu, L., Tong, Z., Chen, L., Liu, H., Li, X.: In: Tester, R.F. (ed.), Thermal Degradation and Stability of Starch Under Different Processing Conditions, vol. 65. pp. 48–60. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, Weinheim (2013)
Jiang, D.D., Yao, Q., McKinney, M.A., Wilkie, C.A.: TGA/FTIR studies on the thermal degradation of some polymeric sulfonic and phosphonic acids and their sodium salts. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 63(3), 423–434 (1999)
Lin, N., Yu, J., Chang, P., Li, J., Huang, J.: Poly(butylene succinate)-based biocomposites filled with polysaccharide nanocrystals: structure and properties. Polym. Compos. 32(3), 472–482 (2011)
Mukherjee, T., Kao, N., Gupta, R., Quazi, N., Bhattacharya, S.: Evaluating the state of dispersion on cellulosic biopolymer by rheology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43200
Nasseri, R., Mohammadi, N.: Starch-based nanocomposites: a comparative performance study of cellulose whiskers and starch nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.029
Galkin, O., Vekilov, P.G.: Mechanisms of homogeneous nucleation of polymers of sickle cell anemia hemoglobin in deoxy state. J. Mol. Biol. 336(1), 43–59 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2003.12.019
Narimissa, E., Gupta, R.K., Choi, H.J., Kao, N., Jollands, M.: Morphological, mechanical, and thermal characterization of biopolymer composites based on polylactide and nanographite platelets. Polym. Compos. 33(9), 1505–1515 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.22280
Lin, N., Huang, J., Chang, P.R., Feng, J., Yu, J.: Surface acetylation of cellulose nanocrystal and its reinforcing function in poly(lactic acid). Carbohydr. Polym. 83(4), 1834–1842 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.047
Mukherjee, T., Czaka, M., Kao, N., Gupta, R.K., Choi, H.J., Bhattacharya, S.: Dispersion study of nanofibrillated cellulose based poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 102, 537–542 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.11.047
Mukherjee, T., Sani, M., Kao, N., Gupta, R.K., Quazi, N., Bhattacharya, S.: Improved dispersion of cellulose microcrystals in polylactic acid (PLA) based composites applying surface acetylation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 101, 655–662 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2013.07.032
Lin, N., Chen, G., Huang, J., Dufresne, A., Chang, P.R.: Effects of polymer-grafted natural nanocrystals on the structure and mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid): a case of cellulose whisker-graft-polycaprolactone. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 113(5), 3417–3425 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.30308
Chen, X., Kalish, J., Hsu, S.L.: Structure evolution of α′-phase poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Sci. B 49(20), 1446–1454 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.22327
Furuhashi, Y., Yoshie, N.: Stereocomplexation of solvent-cast poly(lactic acid) by addition of non-solvents. Polym. Int. 61(2), 301–306 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.3190
Chen, Y., Cao, X., Chang, P.R., Huneault, M.A.: Comparative study on the films of poly(vinyl alcohol)/pea starch nanocrystals and poly(vinyl alcohol)/native pea starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 73(1), 8–17 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.10.015
Gonzalez, K., Retegi, A., Gonzalez, A., Eceiza, A., Gabilondo, N.: Starch and cellulose nanocrystals together into thermoplastic starch bionanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 117, 83–90 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.09.055
Arrieta, M.P., Fortunati, E., Dominici, F., Rayón, E., López, J., Kenny, J.M.: Multifunctional PLA–PHB/cellulose nanocrystal films: processing, structural and thermal properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 107, 16–24 (2014)
Das, K., Ray, D., Banerjee, I., Bandyopadhyay, N., Sengupta, S., Mohanty, A.K., Misra, M.: Crystalline morphology of PLA/clay nanocomposite films and its correlation with other properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 118(1), 143–151 (2010)
Agustin, M.B., Ahmmad, B., Alonzo, S.M.M., Patriana, F.M.: Bioplastic based on starch and cellulose nanocrystals from rice straw. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 33(24), 2205–2213 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/0731684414558325
Fortunati, E., Luzi, F., Puglia, D., Petrucci, R., Kenny, J.M., Torre, L.: Processing of PLA nanocomposites with cellulose nanocrystals extracted from Posidonia oceanica waste: innovative reuse of coastal plant. Ind. Crops Prod. 67, 439–447 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.01.075
Frone, A.N., Berlioz, S., Chailan, J.-F., Panaitescu, D.M.: Morphology and thermal properties of PLA–cellulose nanofibers composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 91(1), 377–384 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.08.054
Krishnamachari, P., Zhang, J., Lou, J., Yan, J., Uitenham, L.: Biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/clay nanocomposites by melt intercalation: a study of morphological, thermal, and mechanical properties. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 14(4), 336–350 (2009)
Arias, A., Heuzey, M.-C., Huneault, M.A., Ausias, G., Bendahou, A.: Enhanced dispersion of cellulose nanocrystals in melt-processed polylactide-based nanocomposites. Cellulose 22(1), 483–498 (2015)
Sungsanit, K., Kao, N., Bhattacharya, S.: Properties of linear poly(lactic acid)/polyethylene glycol blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 52(1), 108–116 (2012)
Sullivan, E., Moon, R., Kalaitzidou, K.: Processing and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals/polylactic acid nanocomposite films. Materials 8(12), 8106–8116 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8125447
Hu, F., Lin, N., Chang, P.R., Huang, J.: Reinforcement and nucleation of acetylated cellulose nanocrystals in foamed polyester composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 129, 208–215 (2015)
Reinsch, V.E., Kelley, S.S.: Crystallization of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) in wood fiber-reinforced composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 64(9), 1785–1796 (1997). 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19970531)64:9<1785::AID-APP15>3.0.CO;2-X
Fortunati, E., Armentano, I., Zhou, Q., Puglia, D., Terenzi, A., Berglund, L.A., Kenny, J.M.: Microstructure and nonisothermal cold crystallization of PLA composites based on silver nanoparticles and nanocrystalline cellulose. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 97(10), 2027–2036 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.03.027
Pei, A., Zhou, Q., Berglund, L.A.: Functionalized cellulose nanocrystals as biobased nucleation agents in poly(l-lactide) (PLLA)—crystallization and mechanical property effects. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70(5), 815–821 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.01.018
Li, H., Cao, Z., Wu, D., Tao, G., Zhong, W., Zhu, H., Qiu, P., Liu, C.: Crystallisation, mechanical properties and rheological behaviour of PLA composites reinforced by surface modified microcrystalline cellulose. Plast. Rubber Compos. 45(4), 181–187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1179/1743289815Y.0000000040
Gupta, A., Simmons, W., Schueneman, G.T., Hylton, D., Mintz, E.A.: Rheological and thermo-mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid)/lignin-coated cellulose nanocrystal composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5(2), 1711–1720 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02458
Hatzikiriakos, S.G., Rathod, N., Muliawan, E.B.: The effect of nanoclays on the processibility of polyolefins. Polym. Eng. Sci. 45(8), 1098–1107 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.20388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takkalkar, P., Ganapathi, M., Dekiwadia, C. et al. Preparation of Square-Shaped Starch Nanocrystals/Polylactic Acid Based Bio-nanocomposites: Morphological, Structural, Thermal and Rheological Properties. Waste Biomass Valor 10, 3197–3211 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0372-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0372-0