Abstract
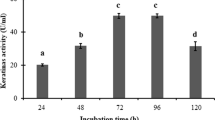
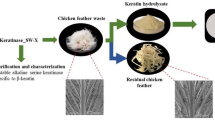
Bacillus tequilensis hsTKB2, produced extracellular alkaline (9–10.5), thermostable (50–80 °C), halophilic (0–30 %), organic solvent tolerant keratinolytic protease. The maximum enzyme production was observed in high alkaline condition (pH 10) at 45 °C in sea water as supporting medium and chicken feathers as substrate with cell-immobilization of chitin flakes. The molecular mass of purified enzyme was estimated to be about 59.89 kDa by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and MALDI-TOF analysis. The apparent Km for the enzyme activity on keratin was 1.9 mg mL−1. Optimum temperature and pH for keratinolytic protease activity were 70 °C and 10.5 respectively. The effect of organic solvents on the enzyme activity showed that this enzyme was more stable in the presence of non-polar organic solvents than polar solvents. Circular dichroism spectroscopy revealed that at pH 10.5 and temperature 70 °C, the enzyme upholds a typical secondary structure (α-helix 25.23 %, β-sheet 61.02 %, turn 11.97 % and coil 1.78 %). Mn2+ and toluene were influenced the enzyme activity by effecting structural changes. This enzyme folded into its active conformation inside the cell and secreted outside. Furthermore the tolerability with surfactants and commercial solid and liquid detergents appeared to be a favorable approach towards laundry and dishwashing detergents.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Averhoff, B., Müller, V.: Exploring research frontiers in microbiology: recent advances in halophilic and thermophilic extremophiles. Res. Microbiol. 161, 506–514 (2010)
Banik, R.M., Prakash, M.: Laundery detergent compatibility of the alkaline protease from Bacillus cereus. Microbiol. Res. 159(2), 135–140 (2004)
Maurer, K.H.: Detergent proteases. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 15, 330–334 (2004)
Deng, A., Wu, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, G.Q., Wen, T.Y.: Purification and characterization of a surfactant-stable high alkaline protease from Bacillus sp. B001. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 7100–7106 (2010)
Shivanand, P., Jayaraman, G.: Production of extracellular protease from halotolerant bacterium, Bacillus aquimaris strain VITP4 isolated from Kumta coast. Process Biochem. 44, 1088–1094 (2009)
Paul, T., Das, A., Mandal, A., Halder, S.K., Mohapatra, P.K.D., Pati, B.R., Mondal, K.C.: Biochemical and structural characterization of a detergent stable alkaline serine keratinase from Paenibacillus woosongensis TKB2: a potential additive for laundry detergent. Waste Biomass. Valor. 5, 563–574 (2014)
Paul, T., Halder, S.K., Das, A., Bera, S., Maity, C., Mandal, A., Das, P.S., Mohapatra, P.K.D., Pati, B.R., Mondal, K.C.: Exploitation of chicken feather waste as a plant growth promoting agent using keratinase producing novel isolate Paenibacillus woosongensis TKB2. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2, 50–57 (2013)
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Riaz, M., Perveen, R., Javed, M.R., Nadeem, H.: Kinetic and thermodynamic properties of novel glucoamylase from Humicola sp. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 41, 558–564 (2007)
Das, A., Ghosh, U., Das Mohapatra, P.K., Pati, B.R., Mondal, K.C.: Study on thermodynamics and adsorption kinetics of purified endoglucanase (Cmcase) from Penicilliumnotatum NCIM No-923 produced under mixed solid-state fermentation of waste cabbage and bagasse. Braz. J. Microbiol. 43, 1103–1111 (2012)
Saqib, A.A.N., Hassan, M., Khan, N.F., Baig, S.: Thermostability of crude endoglucanase from Aspergillus fumigatus grown under solid state fermentation (SSF) and submerged fermentation (SmF). Proc. Biochem. 45, 641–646 (2010)
Dixon, M., Webb, C.: Enzyme kinetics. In: Dixon, M., Webb, E.C. (eds.) Enzymes, 3rd edn, pp. 47–206. Academic Press, New York (1979)
Iyer, P.V., Ananthanarayan, L.: Enzyme stability and stabilization aqueous and non-aqueous environment. Proc. Biochem. 43, 1019–1032 (2008)
Griffin, H., Dintzis, F.R., Krull, L., Baker, F.L.: A microfibril generating factor from the enzyme complex of Trichodermareesei. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 26, 269–300 (1984)
Bhattacharyya, A., Babu, C.R.: Purification and biochemical characterization of a serine protease inhibitor from Derris trifoliate Lour. Seeds: insight into structural and antimalarial features. Phytochemistry 70, 703–712 (2009)
Singh, S.K., Singh, S.K., Tripathi, V.R., Garg, S.K.: Purification, characterization and secondary structure elucidation of a detergent stable, halotolerant, thermoalkaline protease from Bacillus cereus SIU1. Proc. Biochem. 47, 1479–1487 (2010)
Beg, Q.K., Sahai, V., Gupta, R.: Statistical media optimization and alkaline protease production from Bacillus mojavensis in a bioreactor. Proc. Biochem. 39, 203–209 (2003)
Sana, B., Ghosh, D., Saha, M., Mukherjee, J.: Purification and characterization of a salt, solvent, detergent and bleach tolerant protease from a new gamma Proteobacterium isolated from the marine environment of the Sundarbans. Proc. Biochem. 41, 208–215 (2006)
Joo, H.S., Chang, C.S.: Production of protease from a new alkalophilic Bacillus sp. I-312 grown on soybean meal: optimization and some properties. Proc. Biochem. 40, 1263–1270 (2005)
Hadder, A., Agrebi, R., Bougatef, A., Hmidet, N., SellamiKamoun, A., Nasri, M.: Two detergent stable alkaline serine-proteases from Bacillus mojavensis A21: purification, characterization and potential application as a laundry detergent additive. Bioresour. Technol. 100(13), 3366–3373 (2009)
Karen, R., Capes, M.D., Dassarma, S.: Function and biotechnology of extremophilic enzymes in low water activity. Aquat. Biosyst. 8, 1–15 (2012)
Doukyu, N., Ogino, H.: Organic solvent-tolerant enzymes. Biochem. Eng. J. 48, 270–282 (2010)
Thumar, J.T., Singh, S.P.: Two-step purification of a highly thermostable alkaline protease from salt-tolerant alkaliphilic Streptomyces clavuligerus strain Mit-1. J. Chromatogr. B 854, 198–203 (2007)
Rahman, R.N.Z.R.A., Geok, L.P., Basri, M., Salleh, A.B.: An organic solvent-stable alkaline protease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain K: enzyme purification and characterization. Enzymes Microb. Technol. 39, 1484–1491 (2006)
Badoei-Dalfard, A., Karami, Z.: Screening and isolation of an organic solvent tolerant-protease from Bacillus sp. JER02: activity optimization by response surface methodology. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 89, 15–23 (2013)
Ozturk, S., Ozeren-Morgan, M., Dilgimen, A.S., Denizci, A.A., Arikan, B., Kazan, D.: Alkaline serine protease from halotolerant Bacillus licheniformis BA17. Ann. Microbiol. 59, 83–90 (2009)
Rachadech, W., Navacharoen, A., Ruangsit, W., Pongtharangkul, T., Vangnai, A.: An organic solvent-, detergent-, and thermostable alkaline protease from the mesophilic, organic solvent-tolerant Bacillus licheniformis 3C5. Microbiology 79(5), 620–629 (2010)
Gessesse, A.: The use of nug meal as a low-cost substrate for the production of alkaline protease by the alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. AR-009 and some properties of the enzyme. Bioresour. Technol. 62, 59–61 (1997)
Singh, J., Batra, N., Sobti, R.C.: Serine alkaline protease from a newly isolated Bacillus sp. SSR1. Proc. Biochem. 36, 781–785 (2001)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of UGC-RFSMS Fellowship scheme [F.11-114/2008 (BSR)] for present research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, T., Das, A., Mandal, A. et al. Smart Cleaning Properties of a Multi Tolerance Keratinolytic Protease from an Extremophilic Bacillus tequilensis hsTKB2: Prediction of Enzyme Modification Site. Waste Biomass Valor 5, 931–945 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-014-9310-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-014-9310-y