Abstract
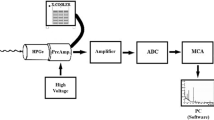
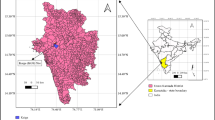
Indoor radon studies have been carried out in the environs of some areas of Sirsa district, Haryana, India using LR-115 type II plastic track detectors. LR-115 Type II films in the bare mode were exposed for one year on three month basis to cover all seasons for the measurement of indoor radon levels. The work has been undertaken for health risk assessment. The average radon concentration in dwellings in most of the villages falls in the action level (200–600 Bq m−3) recommended by International Commission on Radiological Protection. The radon values in some of the dwellings exceed the action level and may be unsafe from the health hazard point of view. The variation due to the ventilation conditions and contribution of building materials to the indoor radon in dwellings are also discussed. The positive values of winter-summer ratio of radon concentration also confirm that level of radon concentration is high in winters as compared to the summers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNSCEAR: United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (New York: United Nations) (1994)
D L Henshaw, J P Eatough and R B Richardson Lancet 355 1008 (1990)
ICRP Ann. ICRP (ICRP Pub., 65) (1993)
U C Mishra and T V Ramachandran Proceedings Third International Conference on Rare Gas Geo-Chemistry Amritsar p310 (1997)
R C Ramola, M S Kandari, R B S Rawat, T V Ramachandran and V M Choubey J. Environmental Radioact. 39 1 (1998)
S Singh, R Malhotra, J Kumar and L Singh Radiation Measurements 34 505 (2001)
K P Eappen, T V Ramachandran, A N Shaikh and Y S Mayya Radiation Protection and Environment 24 410 (2001)
M Raghavayya Bulletin of Radiation Protection 17 1 (1994)
UNSCEAR: United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (New York: United Nations) (2000)
N Sharma and H S Virk Proc. Xlth Natl. Symp. SSNTD Oct 12–14 Amritsar p259 (1998)
S Singh, B Singh and J Kumar Proc. Xlth Natl. Symp. SSNTD Oct. 12–14 Amritsar p69 (1998)
R Kaul, K Umamaheshwar, S Chandrashekaran, R D Deshmukh and B M Swarmukar J. Geological Society of India 41 243 (1993)
R D Evans, J H Harley, W Jacobi, A S MacLean, W A Mills and C G Stewart Nature 290 98 (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehra, R., Singh, S. & Kumar, S. Passive integrating radon studies for environmental monitoring in Sirsa district, Haryana, India using solid state nuclear track detectors. Indian J Phys 83, 1191–1196 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-009-0100-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-009-0100-5