Abstract
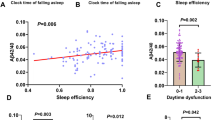
As brain insults, sleep disorders could enhance microglial activation and aggravate neuroinflammation. Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (sTREM2) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) serves as a readout for TREM2-associated microglial responses. We aimed to study the association of sleep characteristics with CSF sTREM2 in cognitively normal (CN) older adults. Linear and non-linear regression analyses were conducted in 830 participants with measurements of sleep characteristics and CSF sTREM2, after adjusting for age, sex, education, the Chinese-Modified Mini-Mental State Examination (CM-MMSE) scores, and APOE4 status. These analyses were also performed in amyloid-negative (A −) and amyloid-positive (A +) individuals. Linear relationships between sleep characteristics and CSF sTREM2 were found. In all the participants, sleep efficiency score in Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) (p = 0.037) showed a positive linear association with CSF sTREM2. In A + individuals, the grade of PSQI total score (p = 0.011) as well as subjective sleep quality score (p = 0.048) and sleep efficiency score (p < 0.001) in PSQI were positively associated with CSF sTREM2. Besides, several U-shaped relationships were revealed of sleep-time measures, such as insufficient or excessive nocturnal sleep duration, with CSF sTREM2 in A + individuals (the optimal model: bedtime 22:21 p.m., time to fall asleep 22:52 p.m., nocturnal sleep duration 7.36 h). In A − individuals, the above relationships were not found. Poor self-reported sleep characteristics and sleep indicators were associated with higher CSF sTREM2, suggesting that sleep might play an important role in the regulation of TREM2-associated microglial activity.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- sTREM2:
-
Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- CN:
-
Cognitively normal
- MCI:
-
Mild cognitive impairment
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- NIA–AA:
-
National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association
- CM-MMSE:
-
Chinese-Modified Mini-Mental State Examination
- MoCA:
-
Montreal Cognitive Assessment
- A − :
-
Amyloid-negative
- A + :
-
Amyloid-positive
- PSQI:
-
Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- TREM2:
-
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2
- ADAM:
-
Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein
- CABLE:
-
Chinese Alzheimer’s Biomarker and Lifestyle
- RFLP:
-
Restriction fragment length polymorphism
- SD:
-
Standardized deviations
References
Abel T, Havekes R, Saletin JM, Walker MP (2013) Sleep, plasticity and memory from molecules to whole-brain networks. Curr Biol 23(17):R774-788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.07.025
Bellesi M, de Vivo L, Chini M, Gilli F, Tononi G, Cirelli C (2017) Sleep loss promotes astrocytic phagocytosis and microglial activation in mouse cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 37(21):5263–5273. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3981-16.2017
Brown BM, Rainey-Smith SR, Villemagne VL, Weinborn M, Bucks RS, Sohrabi HR, Laws SM, Taddei K, Macaulay SL, Ames D et al (2016) The relationship between sleep quality and brain amyloid burden. Sleep 39(5):1063–1068. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.5756
Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ (1989) The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res 28(2):193–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4
Chen KL, Xu Y, Chu AQ, Ding D, Liang XN, Nasreddine ZS, Dong Q, Hong Z, Zhao QH, Guo QH (2016) Validation of the Chinese version of Montreal cognitive assessment basic for screening mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc 64(12):e285–e290. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14530
Condello C, Yuan P, Schain A, Grutzendler J (2015) Microglia constitute a barrier that prevents neurotoxic protofibrillar Aβ42 hotspots around plaques. Nat Commun 6:6176. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7176
Cui GH, Yao YH, Xu RF, Tang HD, Jiang GX, Wang Y, Wang G, Chen SD, Cheng Q (2011) Cognitive impairment using education-based cutoff points for CMMSE scores in elderly Chinese people of agricultural and rural Shanghai China. Acta Neurol Scand 124(6):361–367. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2010.01484.x
Fawale MB, Ismaila IA, Mustapha AF, Komolafe MA, Ibigbami O (2017) Correlates of sleep quality and sleep duration in a sample of urban-dwelling elderly Nigerian women. Sleep Health 3(4):257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2017.05.008
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, Jacobs AH, Wyss-Coray T, Vitorica J, Ransohoff RM et al (2015) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 14(4):388–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(15)70016-5
Hong S, Beja-Glasser VF, Nfonoyim BM, Frouin A, Li S, Ramakrishnan S, Merry KM, Shi Q, Rosenthal A, Barres BA et al (2016) Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models. Science 352(6286):712–716. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad8373
Hou XH, Bi YL, Tan MS, Xu W, Li JQ, Shen XN, Dou KX, Tan CC, Tan L, Yu JT (2019) Genome-wide association study identifies Alzheimer’s risk variant in MS4A6A influencing cerebrospinal fluid sTREM2 levels. Neurobiol Aging 84:241.e213-241.e220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.05.008
Hu H, Tan L, Bi YL, Xu W, Tan L, Shen XN, Hou XH, Ma YH, Dong Q, Yu JT (2021) Association between methylation of BIN1 promoter in peripheral blood and preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Psychiatry 11(1):89. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01218-9
Hulette CM, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Murray MG, Saunders AM, Mash DC, McIntyre LM (1998) Neuropathological and neuropsychological changes in “normal” aging: evidence for preclinical Alzheimer disease in cognitively normal individuals. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57(12):1168–1174. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005072-199812000-00009
Imbach LL, Valko PO, Li T, Maric A, Symeonidou ER, Stover JF, Bassetti CL, Mica L, Werth E, Baumann CR (2015) Increased sleep need and daytime sleepiness 6 months after traumatic brain injury: a prospective controlled clinical trial. Brain 138(Pt 3):726–735. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awu391
Kiernan EA, Smith SM, Mitchell GS, Watters JJ (2016) Mechanisms of microglial activation in models of inflammation and hypoxia: implications for chronic intermittent hypoxia. J Physiol 594(6):1563–1577. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp271502
Kleinberger G, Yamanishi Y, Suárez-Calvet M, Czirr E, Lohmann E, Cuyvers E, Struyfs H, Pettkus N, Wenninger-Weinzierl A, Mazaheri F et al (2014) TREM2 mutations implicated in neurodegeneration impair cell surface transport and phagocytosis. Sci Transl Med 6(243):243–286. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3009093
Kober DL, Brett TJ (2017) TREM2-ligand interactions in health and disease. J Mol Biol 429(11):1607–1629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.04.004
Konishi H, Kiyama H (2018) Microglial TREM2/DAP12 Signaling: a double-edged sword in neural diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 12:206. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00206
Lee J, Kim DE, Griffin P, Sheehan PW, Kim DH, Musiek ES, Yoon SY (2020) Inhibition of REV-ERBs stimulates microglial amyloid-beta clearance and reduces amyloid plaque deposition in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell 19(2):e13078. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13078
Lu K, Chen J, Wu S, Chen J, Hu D (2015) Interaction of sleep duration and sleep quality on hypertension prevalence in adult Chinese males. J Epidemiol 25(6):415–422. https://doi.org/10.2188/jea.JE20140139
Ma LZ, Tan L, Bi YL, Shen XN, Xu W, Ma YH, Li HQ, Dong Q, Yu JT (2020) Dynamic changes of CSF sTREM2 in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: the CABLE study. Mol Neurodegener 15(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-020-00374-8
Madore C, Yin Z, Leibowitz J, Butovsky O (2020) Microglia, lifestyle stress, and neurodegeneration. Immunity 52(2):222–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2019.12.003
Möller-Levet CS, Archer SN, Bucca G, Laing EE, Slak A, Kabiljo R, Lo JC, Santhi N, von Schantz M, Smith CP et al (2013) Effects of insufficient sleep on circadian rhythmicity and expression amplitude of the human blood transcriptome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(12):E1132-1141. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1217154110
Nguyen ND, Tucker MA, Stickgold R, Wamsley EJ (2013) Overnight sleep enhances hippocampus-dependent aspects of spatial memory. Sleep 36(7):1051–1057. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.2808
Parhizkar S, Arzberger T, Brendel M, Kleinberger G, Deussing M, Focke C, Nuscher B, Xiong M, Ghasemigharagoz A, Katzmarski N et al (2019) Loss of TREM2 function increases amyloid seeding but reduces plaque-associated ApoE. Nat Neurosci 22(2):191–204. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0296-9
Piccio L, Buonsanti C, Cella M, Tassi I, Schmidt RE, Fenoglio C, Rinker J 2nd, Naismith RT, Panina-Bordignon P, Passini N et al (2008) Identification of soluble TREM-2 in the cerebrospinal fluid and its association with multiple sclerosis and CNS inflammation. Brain 131(Pt 11):3081–3091. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awn217
Reiman EM, Chen K, Liu X, Bandy D, Yu M, Lee W, Ayutyanont N, Keppler J, Reeder SA, Langbaum JB et al (2009) Fibrillar amyloid-beta burden in cognitively normal people at 3 levels of genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(16):6820–6825. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0900345106
Rowe CC, Ellis KA, Rimajova M, Bourgeat P, Pike KE, Jones G, Fripp J, Tochon-Danguy H, Morandeau L, O’Keefe G et al (2010) Amyloid imaging results from the Australian Imaging, Biomarkers and Lifestyle (AIBL) study of aging. Neurobiol Aging 31(8):1275–1283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.04.007
Soldan A, Pettigrew C, Cai Q, Wang MC, Moghekar AR, O’Brien RJ, Selnes OA, Albert MS (2016) Hypothetical preclinical Alzheimer disease groups and longitudinal cognitive change. JAMA Neurol 73(6):698–705. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.0194
Song WM, Joshita S, Zhou Y, Ulland TK, Gilfillan S, Colonna M (2018) Humanized TREM2 mice reveal microglia-intrinsic and-extrinsic effects of R47H polymorphism. J Exp Med 215(3):745–760. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20171529
Sprecher KE, Bendlin BB, Racine AM, Okonkwo OC, Christian BT, Koscik RL, Sager MA, Asthana S, Johnson SC, Benca RM (2015) Amyloid burden is associated with self-reported sleep in nondemented late middle-aged adults. Neurobiol Aging 36(9):2568–2576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.05.004
Stokholm MG, Iranzo A, Østergaard K, Serradell M, Otto M, Svendsen KB, Garrido A, Vilas D, Borghammer P, Santamaria J et al (2017) Assessment of neuroinflammation in patients with idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 16(10):789–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(17)30173-4
Stowell RD, Sipe GO, Dawes RP, Batchelor HN, Lordy KA, Whitelaw BS, Stoessel MB, Bidlack JM, Brown E, Sur M et al (2019) Noradrenergic signaling in the wakeful state inhibits microglial surveillance and synaptic plasticity in the mouse visual cortex. Nat Neurosci 22(11):1782–1792. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0514-0
Wang Y, Cella M, Mallinson K, Ulrich JD, Young KL, Robinette ML, Gilfillan S, Krishnan GM, Sudhakar S, Zinselmeyer BH et al (2015) TREM2 lipid sensing sustains the microglial response in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Cell 160(6):1061–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.049
Wang Y, Ulland TK, Ulrich JD, Song W, Tzaferis JA, Hole JT, Yuan P, Mahan TE, Shi Y, Gilfillan S et al (2016) TREM2-mediated early microglial response limits diffusion and toxicity of amyloid plaques. J Exp Med 213(5):667–675. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20151948
Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, Chen MJ, Liao Y, Thiyagarajan M, O’Donnell J, Christensen DJ, Nicholson C, Iliff JJ et al (2013) Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 342(6156):373–377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241224
Xu W, Tan CC, Zou JJ, Cao XP, Tan L (2020) Sleep problems and risk of all-cause cognitive decline or dementia: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 91(3):236–244. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2019-321896
Zeng Y, Chen H, Ni T, Ruan R, Feng L, Nie C, Cheng L, Li Y, Tao W, Gu J et al (2015) GxE interactions between FOXO genotypes and drinking tea are significantly associated with prevention of cognitive decline in advanced age in China. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 70(4):426–433. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glu060
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the colleagues who have made contributions to build the CABLE cohort.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91849126), the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1314700), Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2018SHZDZX01) and Zhangjiang Lab, Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute, and the State Key Laboratory of Neurobiology and Frontiers Center for Brain Science of Ministry of Education, Fudan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HYH, LZM, HH, LT, and JTY did the manuscript preparation and drafting. HYH, LZM, HH, YLB, XNS, YNO, YHM, and JTY did the clinical assessments and data acquisition. LT and JTY did the clinical diagnosis. HYH, LZM, and HH did the data analysis and interpretation. LT and JTY are responsible for the study conception and design. All authors have contributed to the manuscript, revising and editing critically for important intellectual content, given final approval of the version, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work presented here.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The design of CABLE was approved by the institutional review boards of Qingdao Municipal Hospital. According to the Declaration of Helsinki, written informed consent was obtained from all participants or their guardians.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, HY., Ma, LZ., Hu, H. et al. Associations of Sleep Characteristics with Cerebrospinal Fluid sTREM2 in Cognitively Normal Older Adults: the CABLE Study. Neurotox Res 39, 1372–1380 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00383-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00383-5