Abstract
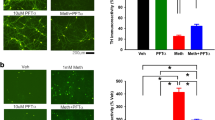
Methamphetamine (METH), a psychostimulant with highly neurotoxic effects, has been known to induce neuronal apoptosis in part through an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathway. Melatonin is an endogenous antioxidant compound that exerts protective effects against several neurodegenerative conditions, including METH-induced neurotoxicity, via various mechanisms. However, the role of melatonin in ER stress is still relatively unclear. In the present study, we investigated ER stress and neuronal apoptosis following METH treatment and the role of melatonin in METH-mediated ER stress-induced cell death in the SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line. We found that METH caused the overexpression of ER stress-related genes, including C/EBP homologous protein and spliced X-box binding protein 1, in dose- and time-dependent manners. Moreover, METH time-dependently activated caspase-12 and -3, leading to cellular apoptosis. Furthermore, we demonstrated that pretreatment with melatonin attenuated the overexpression of ER stress-related genes and the cleavages of caspase-12 and -3 caused by METH exposure. Flow cytometry revealed that METH-mediated neuronal apoptosis was also prevented by melatonin. These findings suggest the protective effects of melatonin against ER stress and apoptosis caused by METH and other harmful agents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beauvais G, Atwell K, Jayanthi S, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL (2011) Involvement of dopamine receptors in binge methamphetamine-induced activation of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial stress pathways. PLoS One 6:e28946
Cadet JL, Ordonez SV, Ordonez JV (1997) Methamphetamine induces apoptosis in immortalized neural cells: protection by the proto-oncogene, bcl-2. Synapse 25:176–184
Cadet JL, Jayanthi S, Deng X (2005) Methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis involves the activation of multiple death pathways. Rev Neurotox Res 8:199–206
Calfon M, Zeng H, Urano F, Till JH, Hubbard SR, Harding HP, Clark SG, Ron D (2002) IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 415:92–96
Carloni S, Albertini MC, Galluzzi L, Buonocore G, Proietti F, Balduini W (2014) Melatonin reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress and preserves sirtuin 1 expression in neuronal cells of newborn rats after hypoxia-ischemia. J Pineal Res 57:192–199
Cox JS, Shamu CE, Walter P (1993) Transcriptional induction of genes encoding endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins requires a transmembrane protein kinase. Cell 73:1197–1206
Cubells JF, Rayport S, Rajendran G, Sulzer D (1994) Methamphetamine neurotoxicity involves vacuolation of endocytic organelles and dopamine-dependent intracellular oxidative stress. J Neurosci 14:2260–2271
Deng X, Cadet JL (2000) Methamphetamine-induced apoptosis is attenuated in the striata of copper-zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 83:121–124
Deng X, Wang Y, Chou J, Cadet JL (2001) Methamphetamine causes widespread apoptosis in the mouse brain: evidence from using an improved TUNEL histochemical method. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 93:64–69
Fernandez A, Ordonez R, Reiter RJ, Gonzalez-Gallego J, Mauriz JL (2015) Melatonin and endoplasmic reticulum stress: relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J Pineal Res 59:292–307
Flamment M, Hajduch E, Ferre P, Foufelle F (2012) New insights into ER stress-induced insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23:381–390
Fujita E, Kouroku Y, Jimbo A, Isoai A, Maruyama K, Momoi T (2002) Caspase-12 processing and fragment translocation into nuclei of tunicamycin-treated cells. Cell Death Differ 9:1108–1114
Hetz C (2012) The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:89–102
Hetz C, Martinon F, Rodriguez D, Glimcher LH (2011) The unfolded protein response: integrating stress signals through the stress sensor IRE1alpha. Physiol Rev 91:1219–1243
Jackson-Lewis V, Blesa J, Przedborski S (2012) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(Suppl 1):S183–S185
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Noailles PA, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL (2004) Methamphetamine induces neuronal apoptosis via cross-talks between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria-dependent death cascades. FASEB J 18:238–251
Jayanthi S, McCoy MT, Beauvais G, Ladenheim B, Gilmore K, Wood W 3rd, Becker K, Cadet JL (2009) Methamphetamine induces dopamine D1 receptor-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress-related molecular events in the rat striatum. PLoS One 4:e6092
Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC (2008) Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:1013–1030
Kitamura O, Tokunaga I, Gotohda T, Kubo S (2007) Immunohistochemical investigation of dopaminergic terminal markers and caspase-3 activation in the striatum of human methamphetamine users. Int J Leg Med 121:163–168
Klongpanichapak S, Phansuwan-Pujito P, Ebadi M, Govitrapong P (2007) Melatonin protects SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells from amphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. J Pineal Res 43:65–73
Lin AM, Fang SF, Chao PL, Yang CH (2007) Melatonin attenuates arsenite-induced apoptosis in rat brain: involvement of mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum pathways and aggregation of alpha-synuclein. J Pineal Res 43:163–171
Lin AM, Feng SF, Chao PL, Yang CH (2009) Melatonin inhibits arsenite-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. J Pineal Res 46:64–70
Ling ZQ, Tian Q, Wang L, Fu ZQ, Wang XC, Wang Q, Wang JZ (2009) Constant illumination induces Alzheimer-like damages with endoplasmic reticulum involvement and the protection of melatonin. J Alzheimers Dis 16:287–300
Martinez JA, Zhang Z, Svetlov SI, Hayes RL, Wang KK, Larner SF (2010) Calpain and caspase processing of caspase-12 contribute to the ER stress-induced cell death pathway in differentiated PC12 cells. Apoptosis 15:1480–1493
Miyazaki I, Asanuma M, Diaz-Corrales FJ, Fukuda M, Kitaichi K, Miyoshi K, Ogawa N (2006) Methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity is regulated by quinone-formation-related molecules. FASEB J 20:571–573
Mustafa Rizvi SH, Parveen A, Verma AK, Ahmad I, Arshad M, Mahdi AA (2014) Aluminium induced endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated cell death in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line is independent of p53. PLoS One 9:e98409
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature 403:98–103
Nashine S, Liu Y, Kim BJ, Clark AF, Pang IH (2015) Role of C/EBP homologous protein in retinal ganglion cell death after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56:221–231
Nguyen XK, Lee J, Shin EJ, Dang DK, Jeong JH, Nguyen TT, Nam Y, Cho HJ, Lee JC, Park DH, Jang CG, Hong JS, Nabeshima T, Kim HC (2015) Liposomal melatonin rescues methamphetamine-elicited mitochondrial burdens, pro-apoptosis, and dopaminergic degeneration through the inhibition PKCdelta gene. J Pineal Res 58:86–106
Rao RV, Castro-Obregon S, Frankowski H, Schuler M, Stoka V, del Rio G, Bredesen DE, Ellerby HM (2002) Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program. An Apaf-1-independent intrinsic pathway. J Biol Chem 277:21836–21842
Rusyniak DE (2013) Neurologic manifestations of chronic methamphetamine abuse. Psychiatr Clin N Am 36:261–275
Sano R, Reed JC (2013) ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:3460–3470
Silva RM, Ries V, Oo TF, Yarygina O, Jackson-Lewis V, Ryu EJ, Lu PD, Marciniak SJ, Ron D, Przedborski S, Kholodilov N, Greene LA, Burke RE (2005) CHOP/GADD153 is a mediator of apoptotic death in substantia nigra dopamine neurons in an in vivo neurotoxin model of parkinsonism. J Neurochem 95:974–986
Suwanjang W, Phansuwan-Pujito P, Govitrapong P, Chetsawang B (2010) The protective effect of melatonin on methamphetamine-induced calpain-dependent death pathway in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cultured cells. J Pineal Res 48:94–101
Szegezdi E, Fitzgerald U, Samali A (2003) Caspase-12 and ER-stress-mediated apoptosis: the story so far. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1010:186–194
Tajiri S, Oyadomari S, Yano S, Morioka M, Gotoh T, Hamada JI, Ushio Y, Mori M (2004) Ischemia-induced neuronal cell death is mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway involving CHOP. Cell Death Differ 11:403–415
Wang X (2009) The antiapoptotic activity of melatonin in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther 15:345–357
Wisessmith W, Phansuwan-Pujito P, Govitrapong P, Chetsawang B (2009) Melatonin reduces induction of Bax, caspase and cell death in methamphetamine-treated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cultured cells. J Pineal Res 46:433–440
Wu J, Kaufman RJ (2006) From acute ER stress to physiological roles of the unfolded protein response. Cell Death Differ 13:374–384
Yamamoto BK, Raudensky J (2008) The role of oxidative stress, metabolic compromise, and inflammation in neuronal injury produced by amphetamine-related drugs of abuse. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 3:203–217
Yoneda T, Imaizumi K, Oono K, Yui D, Gomi F, Katayama T, Tohyama M (2001) Activation of caspase-12, an endoplastic reticulum (ER) resident caspase, through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2-dependent mechanism in response to the ER stress. J Biol Chem 276:13935–13940
Yoo YM, Jeung EB (2010) Melatonin suppresses cyclosporine A-induced autophagy in rat pituitary GH3 cells. J Pineal Res 48:204–211
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by funds from the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. Program, the Thailand Research Fund (TRF) (DPG 5780001 and IRG 5780009), and Mahidol University Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wongprayoon, P., Govitrapong, P. Melatonin Protects SH-SY5Y Neuronal Cells Against Methamphetamine-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptotic Cell Death. Neurotox Res 31, 1–10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9647-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9647-z