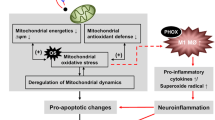
Abstract
The abuse of the illicit drug methamphetamine (METH) is a major concern because it can cause terminal degeneration and neuronal cell death in the brain. METH-induced cell death occurs via processes that resemble apoptosis. In the present review, we discuss the role of various apoptotic events in the causation of METH-induced neuronal apoptosisin vitro andin vivo. Studies using comprehensive approaches to gene expression profiling have allowed for the identification of several genes that are up-regulated or down-regulated after an apoptosis-inducing dose of the drug. Further experiments have also documented the fact that the drug can cause demise of striatal enkephalinergic neurons by cross-talks between mitochondria-, endo-plasmic reticulum- and receptor-mediated apoptotic events. These neuropathological observations have also been reported in models of drug-induced neuroplastic alterations used to mimic drug addiction (Nestler, 2001).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SF and Y Itzhak(1998) Effects of 7-nitroindazole, an NOS inhibitor on methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotoxicity in mice.Ann. NYAcad. Sci. 844, 122–130.
Allen RT, MW Cluckand DK Agrawal (1998) Mechanisms controlling cellular suicide: role of Bcl-2 and caspases.Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 54, 427–445.
Asanuma M, T Hayashi, SV Ordonez, N Ogawa and JL Cadet(2000) Direct interactions of methamphetamine with the nucleus.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 80, 237–243.
Axt KJand ME Molliver (1991) Immunocytochemical evidence for meth-amphetamine-induced serotonergic axon loss in the rat brain.Synapse 9, 302–313.
Cadet JL and C Brannock (1998) Free radicals and the pathobiology ofbrain dopamine systems.Neurochem. Int. 32, 117–131.
Cadet JL, P Sheng, S Ali, R Rothman, E Carlson and C Epstein (1994) Attenuation of methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in copper/zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic mice.J. Neurochem. 62, 380–383.
Cadet JL, SV Ordonez and JV Ordonez (1997) Methamphetamine induces apoptosis in immortalized neural cells: protection by the proto-oncogene, bcl-2.Synapse 25, 176–184.
Cadet JL, S Jayanthi, MT McCoy, M Vawterand B Ladenheim (2001) Temporal profiling of methamphetamine-induced changes in gene expression in the mouse brain: evidence from cDNA array.Synapse 41, 40–48.
Cadet JL, MT McCoy and B Ladenheim (2002) Distinct gene expression signatures in the striata of wild-type and heterozygous c-fos knockout mice following methamphetamine administration: evidence from cDNA array analyses.Synapse 44, 211–226.
Callahan BT, BJ Cord, J Yuan, UD McCann and GA Ricaurte (2001) Inhibitors of Na(+)/H(+) and Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange potentiate methamphetamine-induced dopamine neurotoxicity: possible role of ionic dysregulation in methamphetamine neurotoxicity.J. Neurochem. 77, 1348–1362.
Cappon GD, C Pu and CV Vorhees (2000) Time-course of methamphet-amine-induced neurotoxicity in rat caudate-putamen after single-dose treatment.Brain Res. 863, 106–111.
Chan P, DA Di Monte, JJ Luo, LE DeLanney, I Irwin and JW Langston (1994) Rapid ATP loss caused by methamphetamine in the mouse striatum: relationship between energy impairment and dopaminergic neurotoxicity.J. Neurochem. 62, 2484–2487.
Chapman DE, GR Hanson, RP Kesnerand KA Keefe (2001) Long-term changes in basal ganglia function after a neurotoxic regimen of metham-phetamine.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 296, 520–527.
Chynn KY(1968) Technique for experimental embolization of cerebral arteries and repetitive selective internal carotid arteriography in dogs.Invest. Radiol. 3, 275–279.
Cohen GM(1997) Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis.Biochem. J. 326, 1–16.
Conci F, V D’Angelo, D Tampieri and G Vecchi(1988) Intracerebral hemorrhage and angiographic beading following amphetamine abuse.Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 9, 77–81.
Crabtree GR and EN Olson (2002) NFAT signaling: choreographing the social lives of cells.Cell 109 (Suppl.), S67-S79.
De Vito MJ and GC Wagner (1989) Methamphetamine-induced neuronal damage: a possible role for free radicals.Neuropharmacology 28, 1145–1150.
Deng X and JL Cadet (2000) Methamphetamine-induced apoptosis is attenuated in the striata of copper-zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic mice.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 83, 121–124.
Deng X, B Ladenheim, LI Tsao and JL Cadet(1999) Null mutation of c-fos causes exacerbation of methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity.J. Neurosci. 19, 10107–10115.
Deng X, Y Wang, J Chou and JL Cadet (2001) Methamphetamine causes widespread apoptosis in the mouse brain: evidence from using an improved TUNEL histochemical method.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 93, 64–69.
Deng X, NS Cai, MT McCoy, W Chen, MA Trush and JL Cadet (2002a) Methamphetamine induces apoptosis in an immortalized rat striatal cell line by activating the mitochondrial cell death pathway.Neuropharmacology 42, 837–845.
Deng X, S Jayanthi, B Ladenheim, IN Krasnova and JL Cadet (2002b) Mice with partial deficiency of c-Jun show attenuation of methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis.Mol. Pharmacol. 62, 993–1000.
Derijard B, J Raingeaud, T Barrett, IH Wu, J Han, RJ Ulevitch and RJ Davis (1995) Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms.Science 267, 682–685.
Eisch AJ, LC Schmued and JF Marshall (1998) Characterizing cortical neuron injury with Fluoro-Jade labeling after a neurotoxic regimen of methamphetamine.Synapse 30, 329–333.
Ernst T, L Chang, M Leonido-Yee and O Speck (2000) Evidence for long-term neurotoxicity associated with methamphetamine abuse: a 1H MRS study.Neurology 54, 1344–1349.
Ferri KF and G Kroemer(2001) Organelle-specific initiation of cell death pathways.Nat. Cell. Biol. 3, E255-E263.
Frey K, M Kilbourn and T Robinson (1997) Reduced striatal vesicular monoamine transporters after neurotoxic but not after behaviorally-sensitizing doses of methamphetamine.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 334, 273–279.
Fukui K, T Nakajima, H Kariyama, A Kashiba, N Kato, I Tohyama and H Kimura (1989) Selective reduction of serotonin immunoreactivity in some forebrain regions of rats induced by acute methamphetamine treatment; quantitative morphometric analysis by serotonin immunocyto-chemistry.Brain Res. 482, 198–203.
Fukumura M, GD Cappon, C Pu, HW Broening and CV Vorhees (1998) A single dose model of methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in rats: effects on neostriatal monoamines and glial fibrillary acidic protein.Brain Res. 806, 1–7.
Fukunaga Kand E Miyamoto (1998) Role of MAP kinase in neurons,Mol. Neurobiol. 16, 79–95.
Fumagalli F, RR Gainetdinov, KJ Valenzano and MG Caron (1998) Role of dopamine transporter in methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity: evidence from mice lacking the transporter.J. Neurosci. 18, 4861–4869.
Fumagalli F, RR Gainetdinov, YM Wang, KJ Valenzano, GW Millerand MG Caron(1999) Increased methamphetamine neurotoxicity in hetero- zygous vesicular monoamine transporter 2 knock-out mice.J. Neurosci. 19, 2424–2431.
Gamaley IA and IV Klyubin (1999) Roles of reactive oxygen species: signaling and regulation of cellular functions.Int. Rev. Cytol. 188, 203–255.
Giovanni A, LP Liang, TG Hastings and MJ Zigmond (1995) Estimating hydroxyl radical content in rat brain using systemic and intraventricular salicylate: impact of methamphetamine.J. Neurochem. 64, 1819–1825.
Gluck MR, LY Moy, E Jayatilleke, KA Hogan, L Manzino and PK Sonsalla (2001) Parallel increases in lipid and protein oxidative markers in several mouse brain regions after methamphetamine treatment.J. Neurochem. 79, 152–160.
Hirata H, M Asanuma and JL Cadet(1998) Superoxide radicals are mediators of the effects of methamphetamine onZif268 (Egr-1,NGFI-A) in the brain: evidence from using CuZn superoxide dismutase transgenic mice.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 58, 209–216.
Hotchkiss A and JW Gibb (1980a) Blockade of methamphetamine-induced depression of tyrosine hydroxylase by GABA transaminase inhibitors.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 66, 201–205.
Hotchkiss AJ and JW Gibb (1980b) Long-term effects of multiple doses of methamphetamine on tryptophan hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase activity in rat brain.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 214, 257–262.
Imam SZ, J el-Yazal, GD Newport, Y Itzhak, JL Cadet, W Slikker Jr and SF Ali (2001) Methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity: role of peroxynitrite and neuroprotective role of antioxidants andperoxynitrite decomposition catalysts.Ann. NYAcad. Sci. 939, 366–380.
Itzhak Y and SF Ali(1996) The neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, 7- nitroindazole, protects against methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicityin vivo. J. Neurochem. 67, 1770–1773.
Janicke RU, P Ng, ML Sprengart and AG Porter (1998) Caspase-3 is required for alpha-fodrin cleavage but dispensable for cleavage of other death substrates in apoptosis.J. Biol. Chem. 273, 15540–15545.
Jayanthi S, B Ladenheim and JL Cadet (1998) Methamphetamine-induced changes in antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in copper/zinc-superoxide dismutase transgenic mice.Ann. NYAcad. Sci. 844, 92–102.
Jayanthi S, X Deng, M Bordelon, MT McCoy and JL Cadet(2001) Methamphetamine causes differential regulation of pro-death and anti-deathBcl-2 genes in the mouse neocortex.FASEB J. 15, 1745–1752.
Jayanthi S, M TMcCoy, B Ladenheim and JL Cadet(2002)Methamphetamine causes coordinate regulation of SRC, cas, crk, and the junN-terminal kinase-jun pathway.Mol. Pharmacol. 61, 1124–1131.
Jayanthi S, X Deng, PA Noailles, B Ladenheim and JL Cadet (2004) Methamphetamine induces neuronal apoptosis via cross-talks between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria-dependent death cascades.FASEB J. 18, 238–251.
Jayanthi S, X Deng, B Ladenheim, MT McCoy, A Cluster, NS Cai and JL Cadet (2005) Calcineurin/NFAT-induced up-regulation of the Fas ligand/Fas death pathway is involved in methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 868–873.
Karin M (1991) Signal transduction and gene control,Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 3, 467–473.
Karin M(1995) The regulation ofAP-1 activity by mitogen-activated protein kinases.J.Biol. Chem. 270, 16483–16486.
Kluck RM, E Bossy-Wetzel, DR Green and DD Newmeyer (1997) The release of cytochromec from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis.Science 275, 1132–1136.
Kogan FJ, WK Nichols and JW Gibb (1976) Influence of methamphetamine on nigral and striatal tyrosine hydroxylase activity and on striatal dopa-mine levels.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 36, 363–371.
Korsmeyer SJ, JR Shutter, DJ Veis, DE Merry and ZN Oltvai (1993) Bcl-2/Bax: a rheostat that regulates an anti-oxidant pathway and cell death.Semin. Cancer Biol. 4, 327–332.
Kothakota S, T Azuma, C Reinhard, A Klippel, J Tang, K Chu, TJ McGarry, MW Kirschner, K Koths, DJ Kwiatkowski and LT Williams (1997) Caspase-3-generated fragment of gelsolin: effector of morphological change in apoptosis.Science 278, 294–298.
Kramer JC, VS Fischman and DC Littlefield(1967) Amphetamine abuse. Pattern and effects of high doses taken intravenously.JAMA 201, 305–309.
Lan KC, YF Lin, FC Yu, CS Lin and P Chu(1998) Clinical manifestations and prognostic features of acute methamphetamine intoxication.J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 97, 528–533.
LaVoie MJand TG Hastings(1999) Dopamine quinone formation and protein modification associated with the striatal neurotoxicity of meth-amphetamine: evidence against a role for extracellular dopamine.J. Neurosci. 19, 1484–1491.
Leist Mand P Nicotera(1998) Apoptosis, excitotoxicity, and neuropathology.Exp. Cell. Res. 239, 183–201.
Li-Weber M, O Laur and PH Krammer (1999) Novel Egr/NF-AT composite sites mediate activation of the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) ligand promoter in response to T cell stimulation.Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 3017–3027.
Macian F, C Garcia-Rodriguez and A Rao (2000) Gene expression elicited by NFAT in the presence or absence of cooperative recruitment ofFos and Jun.Embo J. 19, 4783–4795.
Marek GJ, G Vosmer and LS Seiden (1990) Dopamine uptake inhibitors block long-term neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine upon dopaminergic neurons.Brain Res. 513, 274–279.
Mashima T, M Naito and T Tsuruo (1999) Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal actin plays a positive role in the process of morphological apoptosis.Oncogene 18, 2423–2430.
McCullough KD, JL Martindale, LO Klotz, TY Aw and NJ Holbrook (2001) Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down- regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the cellular redox state.Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 1249–1259.
Minden A, A Lin, T Smeal, B Derijard, M Cobb, R Davis and M Karin (1994) c-JunN-terminal phosphorylation correlates with activation of the JNK subgroup but not the ERK subgroup of mitogen-activated protein kinases.Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 6683–6688.
Moriguchi T, F Toyoshima, N Masuyama, H Hanafusa, Y Gotoh and E Nishida (1997) A novel SAPK/JNK kinase, MKK7, stimulated by TNFalpha and cellular stresses.Embo J. 16, 7045–7053.
Murachi T, K Tanaka, M Hatanaka and T Murakami (1980) Intracellular Ca2+-dependent protease (calpain) and its high-molecular-weight endogenous inhibitor (calpastatin).Adv. Enzyme Regul. 19, 407–424.
Nagata S(1999) Fas ligand-induced apoptosis.Annu. Rev. Genet. 33, 29–55.
Nagata S and P Golstein (1995) The Fas death factor.Science 267, 1449–1456.
Nakagawa T and J Yuan (2000) Cross-talk between two cysteine protease families. Activation of caspase-12 by calpain in apoptosis.J. Cell. Biol. 150, 887–894.
Nakagawa T, H Zhu, N Morishima, E Li, J Xu, BA Yankner and J Yuan (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta.Nature 403, 98–103.
Nakayama M, T Koyama and I Yamashita (1993) Long-lasting decrease in dopamine uptake sites following repeated administration of methamphet- amine in the rat striatum.Brain Res. 601, 209–212.
Nestler EJ(2001) Molecular basis of long-term plasticity underlying addiction.Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 119–128.
O’Callaghan JP and DB Miller (1994) Neurotoxicity profiles of substituted amphetamines in the C57BL/6J mouse.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 270, 741–751.
Paschen W(2001) Dependence of vital cell function on endoplasmic reticulum calcium levels: implications for the mechanisms underlying neuronal cell injury in different pathological states.Cell Calcium 29, 1–11.
Rao A, C Luo and PG Hogan (1997) Transcription factors of the NFAT family: regulation and function.Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15, 707–747.
Ravagnan L, T Roumier and G Kroemer (2002) Mitochondria, the killer organelles and their weapons.J. Cell. Physiol. 192, 131–137.
Reed JC, H Zha, C Aime-Sempe, S Takayama and HG Wang (1996) Structure-function analysis of Bcl-2 family proteins. Regulators of pro- grammed cell death.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 406, 99–112.
Ricaurte GA, RW Guillery, LS Seiden, CR Schuster and RY Moore (1982) Dopamine nerve terminal degeneration produced by high doses of methylamphetamine in the rat brain.Brain Res. 235, 93–103.
Ricaurte GA, R Fuller, KW Perry, LS Seiden and CR Schuster(1983) Fluoxetine increases long-lasting neostriatal dopamine depletion after administration of d-methamphetamine and d-amphetamine.Neuropharmacology 22, 1165–1169.
Salanova V and R Taubner(1984) Intracerebral haemorrhage and vasculitis secondary to amphetamine use.Postgrad. Med. J. 60, 429–430.
Schmued LC and JF Bowyer(1997) Methamphetamine exposure can produce neuronal degeneration in mouse hippocampal remnants.Brain Res. 759, 135–140.
Seiden LSand KE Sabol (1996) Methamphetamine and methylene-dioxymethamphetamine neurotoxicity: possible mechanisms of cell destruction.NIDA Res. Monogr. 163, 251–276.
Seiden LSand G Vosmer (1984) Formation of 6-hydroxydopamine in caudate nucleus of the rat brain after a single large dose of methylamphetamine.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 21, 29–31.
Sheng P, C Cerruti, S Aliand JL Cadet (1996) Nitric oxide is a mediator of methamphetamine (METH)-induced neurotoxicity.In vitro evidence from primary cultures of mesencephalic cells.Ann. NYAcad. Sci. 801, 174–186.
Shimizu S, Y Eguchi, W Kamiike, Y Akao, H Kosaka, J Hasegawa, H Matsuda and Y Tsujimoto (1996) Involvement of ICE family proteases in apoptosis induced by reoxygenation of hypoxic hepatocytes.Am. J. Physiol. 271, G949-G958.
Simon SL, C Domier, J Carnell, P Brethen, R Rawson and W Ling (2000) Cognitive impairment in individuals currently using methamphetamine.Am. J. Addict. 9, 222–231.
Sonsalla PKand RE Heikkila (1988) Neurotoxic effects of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2, 3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and methamphetamine in several strains of mice.Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 12, 345–354.
Sonsalla PK, JW Gibb and GR Hanson (1986) Roles of D1 and D2 dopamine receptor subtypes in mediating the methamphetamine-induced changes in monoamine systems.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 238, 932–937.
Stefanis L(2005) Caspase-dependent and -independent neuronal death: two distinct pathways to neuronal injury.Neuroscientist 11, 50–62.
Steranka LR and E Sanders-Bush (1980) Long-term effects of continuous exposure to amphetamine on brain dopamine concentration and synaptosomal uptake in mice.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 65, 439–443.
Stumm G, J Schlegel, T Schafer, C Wurz, HD Mennel, JC Krieg and H Vedder (1999) Amphetamines induce apoptosis and regulation of bcl-x splice variants in neocortical neurons.FASEB J. 13, 1065–1072.
Susin SA, N Zamzami, M Castedo, T Hirsch, P Marchetti, A Macho, E Daugas, M Geuskens and G Kroemer(1996) Bcl-2 inhibits the mitochondrial release of an apoptogenic protease.J. Exp. Med. 184, 1331–1341.
Thiriet N, X Deng, M Solinas, B Ladenheim, W Curtis, SR Goldberg, RD Palmiter and JL Cadet (2005) Neuropeptide Y protects against methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis in the mouse striatum.J. Neurosci. 25.
Thomas DM, DM Francescutti-Verbeem, X Liu and DM Kuhn (2004) Identification of differentially regulated transcripts in mouse striatum following methamphetamine treatment--an oligonucleotide microarray approach.J. Neurochem. 88, 380–393.
Toth R, E Szegezdi, U Reichert, JM Bernardon, S Michel, P Ancian, K Kis-Toth, Z Macsari, L Fesus and Z Szondy (2001) Activation-induced apoptosis and cell surface expression of Fas (CD95) ligand are reciprocally regulated by retinoic acid receptor alpha and gamma and involve nur77 in T cells.Eur. J. Immunol. 31, 1382–1391.
Utz PJ and P Anderson (2000) Life and death decisions: regulation of apoptosis by proteolysis of signaling molecules.Cell Death Differ. 7, 589–602.
Villemagne V, J Yuan, DF Wong, RF Dannals, G Hatzidimitriou, WB Mathews, HT Ravert, J Musachio, UD McCann and GA Ricaurte (1998) Brain dopamine neurotoxicity in baboons treated with doses of methamphetamine comparable to those recreationally abused by humans: evidence from [11C]WIN-35,428 positron emission tomography studies and directin vitro determinations.J. Neurosci. 18, 419–427.
Volkow ND, L Chang, GJ Wang, JS Fowler, D Franceschi, M Sedler, SJ Gatley, E Miller, R Hitzemann, YS Ding and J Logan (2001a) Loss of dopamine transporters in methamphetamine abusers recovers with protracted abstinence.J. Neurosci. 21, 9414–9418.
Volkow ND, L Chang, G Wang, JS Fowler, M Leonido-Yee, D Franceschi, MJ Sedler, SJ Gatley, R Hitzemann, YS Ding, J Logan, C Wong and EN Miller(2001b) Association of dopamine transporter reduction with psychomotor impairment in methamphetamine abusers.Am. J. Psychiatry 158, 377–382.
Wagner GC, GA Ricaurte, LS Seiden, CR Schuster, RJ Miller and J Westley (1980) Long-lasting depletions of striatal dopamine and loss of dopamine uptake sites following repeated administration of methamphetamine.Brain Res. 181, 151–160.
Weissman BA, R Brandeis, E Gilat, G Cohen, D Alkalay, I Rabinovitz, H Sonego. and L Raveh(2004) Monitoring drug-induced neurodegeneration by imaging of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors.Ann. NYAcad. Sci. 1025, 584–589.
Wilson JM, KS Kalasinsky, AI Levey, C Bergeron, G Reiber, RM Anthony, GA Schmunk, K Shannak, JW Haycock and SJ Kish (1996) Striatal dopamine nerve terminal markers in human, chronic methamphetamine users.Nat. Med. 2, 699–703.
Woolverton WL, GA Ricaurte, LS Forno and LS Seiden (1989) Long-term effects of chronic methamphetamine administration in rhesus monkeys.Brain Res. 486, 73–78.
Yamamoto BKand W Zhu (1998) The effects of methamphetamine on the production of free radicals and oxidative stress.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 287, 107–114.
Yang J, X Liu, K Bhalla, CN Kim, AM Ibrado, J Cai, TI Peng, DP Jones and X Wang (1997) Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked [see comments].Science 275, 1129–1132.
Yoshizumi M, J Abe, J Haendeler, Q Huang and BC Berk (2000) Src and Cas mediate JNK activation but not ERK1/2 and p38 kinases by reactive oxygen species.J. Biol. Chem. 275, 11706–11712.
Yui K, K Goto, S Ikemoto, T Ishiguro, B Angrist, GE Duncan, BB Sheitman, JA Lieberman, SH Bracha and SF Ali (1999) Neurobiological basis of relapse prediction in stimulant-induced psychosis and schizophrenia: the role of sensitization.Mol. Psychiatry 4, 512–523.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cadet, J.L., Jayanthi, S. & Deng, X. Methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis involves the activation of multiple death pathways. Review. neurotox res 8, 199–206 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033973
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033973