Abstract
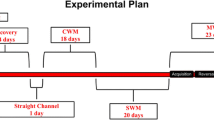
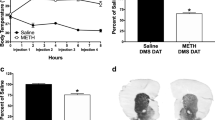
Methamphetamine (METH) triggers a disruption of the monoaminergic system and METH abuse leads to negative emotional states including depressive symptoms during drug withdrawal. However, it is currently unknown if the acute toxic dosage of METH also causes a long-lasting depressive phenotype and persistent monoaminergic deficits. Thus, we now assessed the depressive-like behaviour in mice at early and long-term periods following a single high METH dose (30 mg/kg, i.p.). METH did not alter the motor function and procedural memory of mice as assessed by swimming speed and escape latency to find the platform in a cued version of the water maze task. However, METH significantly increased the immobility time in the tail suspension test at 3 and 49 days post-administration. This depressive-like profile induced by METH was accompanied by a marked depletion of frontostriatal dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotransmission, indicated by a reduction in the levels of dopamine, DOPAC and HVA, tyrosine hydroxylase and serotonin, observed at both 3 and 49 days post-administration. In parallel, another neurochemical feature of depression—astroglial dysfunction—was unaffected in the cortex and the striatal levels of the astrocytic protein marker, glial fibrillary acidic protein, were only transiently increased at 3 days. These findings demonstrate for the first time that a single high dose of METH induces long-lasting depressive-like behaviour in mice associated with a persistent disruption of frontostriatal dopaminergic and serotonergic homoeostasis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinho P, Cunha RA, Oliveira C (2010) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 16:2766–2778
Allaman I, Bélanger M, Magistretti PJ (2011) Astrocyte–neuron metabolic relationships: for better and for worse. Trends Neurosci 34:76–87
Banasr M, Duman RS (2008) Glial loss in the prefrontal cortex is sufficient to induce depressive-like behaviors. Biol Psychiatry 64:863–870
Berton O, Hahn CG, Thase ME (2012) Are we getting closer to valid translational models for major depression? Science 338:75–79
Bora E, Harrison BJ, Davey CG, Yücel M, Pantelis C (2012) Meta-analysis of volumetric abnormalities in cortico-striatal-pallidal-thalamic circuits in major depressive disorder. Psychol Med 42:671–681
Brière FN, Fallu J-S, Janosz M, Pagani LS (2012) Prospective associations between meth/amphetamine (speed) and MDMA (ecstasy) use and depressive symptoms in secondary school students. J Epidemiol Community Health 66:990–994
Cappon GD, Pu C, Vorhees CV (2000) Time-course of methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in rat caudate-putamen after single-dose treatment. Brain Res 863:106–111
Carvalho M, Carmo H, Costa VM, Capela JP, Pontes H, Remião F, Carvalho F, Bastos MDL (2012) Toxicity of amphetamines: an update. Arch Toxicol 86:1167–1231
Cryan JF, Hoyer D, Markou A (2003) Withdrawal from chronic amphetamine induces depressive-like behavioral effects in rodents. Biol Psychiatry 54:49–58
Cryan JF, Mombereau C, Vassout A (2005) The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:571–625
Darke S, Kaye S, McKetin R, Duflou J (2008) Major physical and psychological harms of methamphetamine use. Drug Alcohol Rev 27:253–262
Davidson C, Gow AJ, Lee TH, Ellinwood EH (2001) Methamphetamine neurotoxicity: necrotic and apoptotic mechanisms and relevance to human abuse and treatment. Brain Res Rev 36:1–22
Drevets WC, Price JC, Kupfer DJ, Kinahan PE, Lopresti B, Holt D, Mathis C (1999) PET measures of amphetamine-induced dopamine release in ventral versus dorsal striatum. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:694–709
Dzirasa K, Covington HE 3rd (2012) Increasing the validity of experimental models for depression. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1265:36–45
El Yacoubi M, Vaugeois JM (2007) Genetic rodent models of depression. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:3–7
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (2012) Annual report 2012: the state of the drugs problem in Europe. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg
Fanselow MS, Dong HW (2010) Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 65:7–19
Friedman SD, Castañeda E, Hodge GK (1998) Long-term monoamine depletion, differential recovery, and subtle behavioral impairment following methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:35–44
Glasner-Edwards S, Marinelli-Casey P, Hillhouse M, Ang A, Mooney LJ, Rawson R (2009) Depression among methamphetamine users. J Nerv Ment Dis 197:225–231
Gonçalves J, Baptista S, Martins T, Milhazes N, Borges F, Ribeiro CF, Malva JO, Silva AP (2010) Methamphetamine-induced neuroinflammation and neuronal dysfunction in the mice hippocampus: preventive effect of indomethacin. Eur J Neurosci 31:315–326
Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E, Daumann J (2009) Neurotoxicity of drugs of abuse–the case of methylenedioxyamphetamines (MDMA, ecstasy), and amphetamines. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 11:305–317
Grace CE, Schaefer TL, Herring NR, Graham DL, Matthew R, Gudelsky GA, Williams MT, Vorhees CV (2010) Effect of a neurotoxic dose regimen of (+)-methamphetamine on behavior, plasma corticosterone, and brain monoamines in adult C57BL/6 mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32:346–355
Herring NR, Gudelsky GA, Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2010) (+)-Methamphetamine-induced monoamine reductions and impaired egocentric learning in adrenalectomized rats is independent of hyperthermia. Synapse 64:773–785
Holmes PV (2003) Rodent models of depression: reexamining validity without anthropomorphic inference. Crit Rev Neurobiol 15:143–174
Homer BD, Solomon TM, Moeller RW, Mascia A, DeRaleau L, Halkitis PN (2008) Methamphetamine abuse and impairment of social functioning: a review of the underlying neurophysiological causes and behavioral implications. Psychol Bull 134:301–310
Hotchkiss AJ, Morgan ME, Gibb JW (1979) The long-term effects of multiple doses of methamphetamine on neostriatal tryptophan hydroxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase, choline acetyltransferase and glutamate decarboxylase activities. Life Sci 25:1373–1378
Iijima M, Koike H, Chaki S (2013) Effect of an mGlu2/3 receptor antagonist on depressive behavior induced by withdrawal from chronic treatment with methamphetamine. Behav Brain Res 246:24–28
Imam SZ, Ali SF (2001) Aging increases the susceptibility to methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in rats: correlation with peroxynitrite production and hyperthermia. J Neurochem 78:952–959
Jang C-G, Whitfield T, Schulteis G, Koob GF, Wee S (2013) A dysphoric-like state during early withdrawal from extended access to methamphetamine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 225:753–763
Johanson CE, Frey KA, Lundahl LH, Keenan P, Lockhart N, Roll J, Galloway GP, Koeppe RA, Kilbourn MR, Robbins T, Schuster CR (2006) Cognitive function and nigrostriatal markers in abstinent methamphetamine abusers. Psychopharmacology 185:327–338
Kimelberg HK, Nedergaard M (2010) Functions of astrocytes and their potential as therapeutic targets. Neurotherapeutics 7:338–353
Kish SJ, Fitzmaurice PS, Boileau I, Schmunk GA, Ang L-C, Furukawa Y, Chang L-J, Wickham DJ, Sherwin A, Tong J (2009) Brain serotonin transporter in human methamphetamine users. Psychopharmacology 202:649–661
Kitamura O, Tokunaga I, Gotohda T, Kubo S (2007) Immunohistochemical investigation of dopaminergic terminal markers and caspase-3 activation in the striatum of human methamphetamine users. Int J Leg Med 121:163–168
Kitamura O, Takeichi T, Wang EL, Tokunaga I, Ishigami A, Kubo S (2010) Microglial and astrocytic changes in the striatum of methamphetamine abusers. Leg Med (Tokyo) 12:57–62
Krasnova IN, Cadet JL (2009) Methamphetamine toxicity and messengers of death. Brain Res Rev 60:379–407
Krishnan V, Nestler EJ (2010) Linking molecules to mood: new insight into the biology of depression. Am J Psychiatry 167:1305–1320
Lee S, Jeong J, Kwak Y, Park SK (2010) Depression research: where are we now? Mol Brain 3:8
Lemke M, Fuchs G, Gemende I, Herting B, Oehlwein C, Reichmann H, Rieke J, Volkmann J (2004) Depression and Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 251:24–27
London ED, Simon SL, Berman SM, Mandelkern MA, Lichtman AM, Bramen J, Shinn AK, Miotto K, Learn J, Dong Y, Matochik JA, Kurian V, Newton T, Woods R, Rawson R, Ling W (2004) Mood disturbances and regional cerebral metabolic abnormalities in recently abstinent methamphetamine abusers. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:73–84
Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP (2003) Elevated environmental temperature and methamphetamine neurotoxicity. Environ Res 92:48–53
Moszczynska A, Fitzmaurice P, Ang L, Kalasinsky KS, Schmunk GA, Peretti FJ, Aiken SS, Wickham DJ, Kish SJ (2004) Why is Parkinsonism not a feature of human methamphetamine users? Brain 127:363–370
Nestler EJ, Carlezon WA (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine reward circuit in depression. Biol Psychiatry 59:1151–1159
Nutt DJ, Baldwin DS, Clayton AH, Elgie R, Lecrubier Y, Montejo AL, Papakostas GI, Souery D, Trivedi MH, Tylee A (2006) Consensus statement and research needs: the role of dopamine and norepinephrine in depression and antidepressant treatment. J Clin Psychiatry 67(Suppl 6):46–49
O’Callaghan J, Miller D (1994) Neurotoxicity profiles of substituted amphetamines in the C57BL/6J mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:741–751
O’Callaghan JP, Sriram K, Miller DB (2008) Defining “neuroinflammation”. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1139:318–330
Panenka WJ, Procyshyn RM, Lecomte T, Macewan GW, Flynn SW, Honer WG, Barr AM (2012) Methamphetamine use: a comprehensive review of molecular, preclinical and clinical findings. Drug Alcohol Depend 129:1–13
Páv M, Kovárů H, Fiserová A, Havrdová E, Lisá V (2008) Neurobiological aspects of depressive disorder and antidepressant treatment: role of glia. Physiol Res 57:151–164
Pekny M, Nilsson M (2005) Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Glia 50:427–434
Pereira FC, Lourenço ES, Borges F, Morgadinho T, Ribeiro CF, Macedo TR, Ali SF (2006) Single or multiple injections of methamphetamine increased dopamine turnover but did not decrease tyrosine hydroxylase levels or cleave caspase-3 in caudate-putamen. Synapse 60:185–193
Pereira FC, Cunha-Oliveira T, Viana SD, Travassos AS, Nunes S, Silva C, Prediger RD, Rego AC, Ali SF, Ribeiro CAF (2012) Disruption of striatal glutamatergic/GABAergic homeostasis following acute methamphetamine in mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34:522–529
Prediger RDS, Batista LC, Medeiros R, Pandolfo P, Florio JC, Takahashi RN (2006) The risk is in the air: intranasal administration of MPTP to rats reproducing clinical features of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 202:391–403
Rajkowska G, Stockmeier CA (2013) Astrocyte pathology in major depressive disorder: insights from human postmortem brain tissue. Curr Drug Targets 14:1225–1236
Rawson RA, Huber A, Brethen P, Obert J, Gulati V, Shoptaw S, Ling W (2002) Status of methamphetamine users 2–5 years after outpatient treatment. J Addict Dis 21:107–119
Renoir T, Païzanis E, El Yacoubi M, Saurini F, Hanoun N, Melfort M, Lesch KP, Hamon M, Lanfumey L (2008) Differential long-term effects of MDMA on the serotoninergic system and hippocampal cell proliferation in 5-HTT knock-out vs. wild-type mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:1149–1162
Rowe DC, Stever C, Gard JM, Cleveland HH, Sanders ML, Abramowitz A, Kozol ST, Mohr JH, Sherman SL, Waldman ID (1998) The relation of the dopamine transporter gene (DAT1) to symptoms of internalizing disorders in children. Behav Gen 28:215–225
Sailasuta N, Abulseoud O, Harris KC, Ross BD (2010) Glial dysfunction in abstinent methamphetamine abusers. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:950–960
Sanacora G, Banasr M (2013) From pathophysiology to novel antidepressant drugs: glial contributions to the pathology and treatment of mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 73:1172–1179
Savitz JB, Drevets WC (2012) Neuroreceptor imaging in depression. Neurobiol Dis 52:49–65
Scott JC, Woods SP, Matt GE, Meyer RA, Heaton RK, Atkinson JH, Grant I (2007) Neurocognitive effects of methamphetamine: a critical review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychol Rev 17:275–297
Segman RH, Shalev AY (2003) Genetics of posttraumatic stress disorder. CNS Spectr 8:693–698
Sekine Y, Ouchi Y, Takei N, Yoshikawa E, Nakamura K, Futatsubashi M, Okada H, Minabe Y, Suzuki K, Iwata Y, Tsuchiya KJ, Tsukada H, Iyo M, Mori N (2006) Brain serotonin transporter density and aggression in abstinent methamphetamine abusers. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:90–100
Semple SJ, Grant I, Patterson TL (2005) Negative self-perceptions and sexual risk behavior among heterosexual methamphetamine users. Subst Use Misuse 40:1797–1810
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) A new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 85:367–370
Tulloch I, Afanador L, Mexhitaj I, Ghazaryan N, Garzagongora AG, Angulo JA (2011) A single high dose of methamphetamine induces apoptotic and necrotic striatal cell loss lasting up to 3 months in mice. Neuroscience 193:162–169
Wilson JM, Kalasinsky KS, Levey AI, Bergeron C, Reiber G, Anthony RM, Schmunk GA, Shannak K, Haycock JW, Kish SJ (1996) Striatal dopamine nerve terminal markers in human, chronic methamphetamine users. Nat Med 2:699–703
Xu W, Zhu JPQ, Angulo JA (2005) Induction of striatal pre- and postsynaptic damage by methamphetamine requires the dopamine receptors. Synapse 58:110–121
Zhu JP, Xu W, Angulo JA (2005) Disparity in the temporal appearance of methamphetamine-induced apoptosis and depletion of dopamine terminal markers in the striatum of mice. Brain Res 1049:171–181
Zorick T, Nestor L, Miotto K, Sugar C, Hellemann G, Scanlon G, Rawson R, London ED (2010) Withdrawal symptoms in abstinent methamphetamine-dependent subjects. Addiction 105:1809–1818
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by PEst-C/SAU/UI3282/2011 and by FCP011 (Faculty of Medicine, University of Coimbra, Portugal). SDV is a recipient of a PhD grant from Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT, Portugal, SFRH/BD/78166/2011). The experiments comply with the current laws of Portugal.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, C.D., Neves, A.F., Dias, A.I. et al. A Single Neurotoxic Dose of Methamphetamine Induces a Long-Lasting Depressive-Like Behaviour in Mice. Neurotox Res 25, 295–304 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9423-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9423-2