Abstract
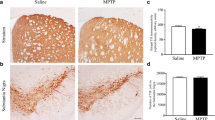
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder affecting approximately 1 % of the population older than 60 years. The administration of the proneurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in mice is the most widely used approach to elucidate the mechanisms of cell death involved in PD. However, the magnitude of the PD-like neurodegeneration induced by MPTP depends on many variables, including the regimen of its administration. It has been demonstrated that intranasal (i.n.) administration of MPTP constitutes a new route of toxin delivery to the brain that mimics environmental exposure to neurotoxins. Previous data showed that mice submitted to chronic and acute i.n. MPTP treatment displayed a robust (~80 %) and moderate (~55 %) loss of striatal dopamine, respectively. However, little is known about the neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory processes following a subacute i.n. MPTP administration in mice. Here, the C57BL/6 mice were infused intranasally with MPTP (1 mg/nostril/day) during 4 consecutive days. At 7 and 28 days after the last administration, the subacute i.n. MPTP regime decreased the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-labeling in the striatum (40–50 %) and substantia nigra (25–30 %) and increased the astrogliosis in such brain areas at both time points. Taken together, our data showed that the subacute administration of MPTP into the nasal cavity of C57BL/6 mice induces long-lasting neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation in the nigrostriatal pathway, thus representing a valuable animal model for the investigation of neuroprotective strategies in PD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar AS Jr., Tristao FSM, Amar M, Chevarin C, Lanfumey L, Mongeau R, Corti O, Prediger RD, Raisman-Vozari R (2013) Parkin-knockout mice did not display increased vulnerability to intranasal administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Neurotox Res. doi:10.1007/s12640-013-9389-0
Anandhan A, Janakiraman U, Manivasagam T (2012) Theaflavin ameliorates behavioral deficits, biochemical indices and monoamine transporters expression against subacute 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 218:257–267
Aoki E, Yano R, Yokoyama H, Kato H, Araki T (2009) Role of nuclear transcription factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) for MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahyropyridine)-induced apoptosis in nigral neurons of mice. Exp Mol Pathol 86:57–64
Aubin N, Curet O, Deffois A, Carter C (1998) Aspirin and salicylate protect against MPTP-induced dopamine depletion in mice. J Neurochem 71:1635–1642
Ballard PA, Tetrud JW, Langston JW (1985) Permanent human parkinsonism due to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP): seven cases. Neurology 35:949–956
Bezard E, Yue Z, Kirik D, Spillantini MG (2012) Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: limits and relevance to neuroprotection studies. Mov Disord. doi:10.1002/mds.25108
Block ML, Hong JS (2005) Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog Neurobiol 76:77–98
Bove J, Perier C (2012) Neurotoxin-based models of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 211:51–76
Bove J, Prou D, Perier C, Przedborski S (2005) Toxin-induced models of Parkinson’s disease. NeuroRx 2:484–494
Castro AA, Ghisoni K, Latini A, Quevedo J, Tasca CI, Prediger RD (2012) Lithium and valproate prevent olfactory discrimination and short-term memory impairments in the intranasal 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res 229:208–215
Chiba K, Kubota E, Miyakawa T, Kato Y, Ishizaki T (1988) Characterization of hepatic microsomal metabolism as an in vivo detoxication pathway of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:1108–1115
Chiueh CC, Markey SP, Burns RS, Johannessen JN, Pert A, Kopin IJ (1984) Neurochemical and behavioral effects of systemic and intranigral administration of N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 100:189–194
Choi DK, Pennathur S, Perier C, Tieu K, Teismann P, Wu DC, Jackson-Lewis V, Vila M, Vonsattel JP, Heinecke JW, Przedborski S (2005) Ablation of the inflammatory enzyme myeloperoxidase mitigates features of Parkinson’s disease in mice. J Neurosci 25:6594–6600
Chung YC, Ko HW, Bok E, Park ES, Huh SH, Nam JH, Jin BK (2010) The role of neuroinflammation on the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. BMB Rep 43:225–232
Ciesielska A, Joniec I, Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I, Cudna A, Przybylkowski A, Czlonkowska A, Czlonkowski A (2009) The impact of age and gender on the striatal astrocytes activation in murine model of Parkinson’s disease. Inflamm Res 58:747–753
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909
Dluzen DE, Kefalas G (1996) The effects of intranasal infusion of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) upon catecholamine concentrations within olfactory bulbs and corpus striatum of male mice. Brain Res 741:215–219
Doty RL (2008) The olfactory vector hypothesis of neurodegenerative disease: is it viable? Ann Neurol 63:7–15
Fletcher L, Kohli S, Sprague SM, Scranton RA, Lipton SA, Parra A, Jimenez DF, Digicaylioglu M (2009) Intranasal delivery of erythropoietin plus insulin-like growth factor-I for acute neuroprotection in stroke: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg 111:164–170
Forno LS (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:259–272
Fuller RW, Hemrick-Luecke SK (1990) Tissue concentrations of MPTP and MPP+ after administration of lethal and sublethal doses of MPTP to mice. Toxicol Lett 54:253–262
Gibrat C, Saint-Pierre M, Bousquet M, Levesque D, Rouillard C, Cicchetti F (2009) Differences between subacute and chronic MPTP mice models: investigation of dopaminergic neuronal degeneration and alpha-synuclein inclusions. J Neurochem 109:1469–1482
Gordon GR, Choi HB, Rungta RL, Ellis-Davies GC, MacVicar BA (2008) Brain metabolism dictates the polarity of astrocyte control over arterioles. Nature 456:745–749
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8:382–397
Hirsch E, Graybiel AM, Agid YA (1988) Melanized dopaminergic neurons are differentially susceptible to degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 334:345–348
Jackson-Lewis V, Jakowec M, Burke RE, Przedborski S (1995) Time course and morphology of dopaminergic neuronal death caused by the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Neurodegeneration 4:257–269
Kalaria RN, Mitchell MJ, Harik SI (1987) Correlation of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine neurotoxicity with blood-brain barrier monoamine oxidase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3521–3525
Kim RH, Smith PD, Aleyasin H, Hayley S, Mount MP, Pownall S, Wakeham A, You-Ten AJ, Kalia SK, Horne P, Westaway D, Lozano AM, Anisman H, Park DS, Mak TW (2005) Hypersensitivity of DJ-1-deficient mice to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyrindine (MPTP) and oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5215–5220
Lazzarini M, Martin S, Mitkovski M, Vozari RR, Stühmer W, Bel ED (2013) Doxycycline restrains glia and confers neuroprotection in a 6-OHDA Parkinson model. Glia. doi:10.1002/glia.22496
Lewy FH (1912) Paralysis agitans. In: Lewandowsky M (ed) Pathologische Anatomie. Handbuch der Neurologie. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 920–933
Liberatore GT, Jackson-Lewis V, Vukosavic S, Mandir AS, Vila M, McAuliffe WG, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Przedborski S (1999) Inducible nitric oxide synthase stimulates dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson disease. Nat Med 5:1403–1409
Mayeux R (2003) Epidemiology of neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:81–104
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Akiyama H, McGeer EG (1988) Rate of cell death in Parkinsonism indicates active neuropathological process. Ann Neurol 24:574–576
Meredith GE, Totterdell S, Potashkin JA, Surmeier DJ (2008) Modeling PD pathogenesis in mice: advantages of a chronic MPTP protocol. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14(Suppl 2):S112–S115
Mogi M, Harada M, Riederer P, Narabayashi H, Fujita K, Nagatsu T (1994) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) increases both in the brain and in the cerebrospinal fluid from parkinsonian patients. Neurosci Lett 165:208–210
Moreira EL, Rial D, Aguiar AS Jr, Figueiredo CP, Siqueira JM, DalBo S, Horst H, de Oliveira J, Mancini G, dos Santos TS, Villarinho JG, Pinheiro FV, Marino-Neto J, Ferreira J, De Bem AF, Latini A, Pizzolatti MG, Ribeiro-do-Valle RM, Prediger RD (2010) Proanthocyanidin-rich fraction from Croton celtidifolius Baill confers neuroprotection in the intranasal 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 117:1337–1351
Mulligan SJ, MacVicar BA (2004) Calcium transients in astrocyte endfeet cause cerebrovascular constrictions. Nature 431:195–199
Nagatsu T, Mogi M, Ichinose H, Togari A (2000) Changes in cytokines and neurotrophins in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 60:277–290
Petroske E, Meredith GE, Callen S, Totterdell S, Lau YS (2001) Mouse model of Parkinsonism: a comparison between subacute MPTP and chronic MPTP/probenecid treatment. Neuroscience 106:589–601
Prediger RD, Batista LC, Medeiros R, Pandolfo P, Florio JC, Takahashi RN (2006) The risk is in the air: intranasal administration of MPTP to rats reproducing clinical features of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 202:391–403
Prediger RD, Aguiar AS Jr, Rojas-Mayorquin AE, Figueiredo CP, Matheus FC, Ginestet L, Chevarin C, Bel ED, Mongeau R, Hamon M, Lanfumey L, Raisman-Vozari R (2010) Single intranasal administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in C57BL/6 mice models early preclinical phase of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 17:114–129
Prediger RD, Rojas-Mayorquin AE, Aguiar AS Jr, Chevarin C, Mongeau R, Hamon M, Lanfumey L, Del Bel E, Muramatsu H, Courty J, Raisman-Vozari R (2011) Mice with genetic deletion of the heparin-binding growth factor midkine exhibit early preclinical features of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 118:1215–1225
Prediger RD, Aguiar AS Jr, Matheus FC, Walz R, Antoury L, Raisman-Vozari R, Doty RL (2012) Intranasal administration of neurotoxicants in animals: support for the olfactory vector hypothesis of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 21:90–116
Przedborski S, Vila M (2003) The 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model: a tool to explore the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 991:189–198
Przedborski S, Jackson-Lewis V, Naini AB, Jakowec M, Petzinger G, Miller R, Akram M (2001) The parkinsonian toxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP): a technical review of its utility and safety. J Neurochem 76:1265–1274
Rojo AI, Montero C, Salazar M, Close RM, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Sanchez-Gonzalez MA, de Sagarra MR, Jackson-Lewis V, Cavada C, Cuadrado A (2006) Persistent penetration of MPTP through the nasal route induces Parkinson’s disease in mice. Eur J Neurosci 24:1874–1884
Savitt JM, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2006) Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: molecules to medicine. J Clin Invest 116:1744–1754
Sedelis M, Hofele K, Auburger GW, Morgan S, Huston JP, Schwarting RK (2000) MPTP susceptibility in the mouse: behavioral, neurochemical, and histological analysis of gender and strain differences. Behav Genet 30:171–182
Smeyne RJ, Jackson-Lewis V (2005) The MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 134:57–66
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL, Goedert M (1998) Filamentous alpha-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci Lett 251:205–208
Sriram K, Matheson JM, Benkovic SA, Miller DB, Luster MI, O’Callaghan JP (2002) Mice deficient in TNF receptors are protected against dopaminergic neurotoxicity: implications for Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J 16:1474–1476
Takahashi N, Miner LL, Sora I, Ujike H, Revay RS, Kostic V, Jackson-Lewis V, Przedborski S, Uhl GR (1997) VMAT2 knockout mice: heterozygotes display reduced amphetamine-conditioned reward, enhanced amphetamine locomotion, and enhanced MPTP toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9938–9943
Talegaonkar S, Mishra PR (2004) Intranasal delivery: an approach to bypass the blood brain barrier. Indian J Pharmacol 36:140–147
Tansey MG, Goldberg MS (2010) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiol Dis 37:510–518
Tatton NA, Kish SJ (1997) In situ detection of apoptotic nuclei in the substantia nigra compacta of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated mice using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase labelling and acridine orange staining. Neuroscience 77:1037–1048
Tower DB, Young OM (1973) The activities of butyrylcholinesterase and carbonic anhydrase, the rate of anaerobic glycolysis, and the question of a constant density of glial cells in cerebral cortices of various mammalian species from mouse to whale. J Neurochem 20:269–278
Vanzani MC, Iacono RF, Caccuri RL, Troncoso AR, Berria MI (2006) Regional differences in astrocyte activation in HIV-associated dementia. Medicina (B Aires) 66:108–112
Wang WF, Wu SL, Liou YM, Wang AL, Pawlak CR, Ho YJ (2009) MPTP lesion causes neuroinflammation and deficits in object recognition in Wistar rats. Behav Neurosci 123:1261–1270
Wang AL, Liou YM, Pawlak CR, Ho YJ (2010) Involvement of NMDA receptors in both MPTP-induced neuroinflammation and deficits in episodic-like memory in Wistar rats. Behav Brain Res 208:38–46
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank the financial support and grants provided by the Brazilian agencies Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Programa Ciência sem Fronteiras (CsF), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), CAPES-COFECUB (France/Brazil; 681/2010), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP; thematic project 2012/17626-7), FAPESP/INSERM (2008/55092-9), and Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa Científica e Tecnológica do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC). E.A.D.B. and R.D.P. are supported by research fellowships from CNPq, Brazil.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial or personal conflicts of interest related to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tristão, F.S.M., Amar, M., Latrous, I. et al. Evaluation of Nigrostriatal Neurodegeneration and Neuroinflammation Following Repeated Intranasal 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) Administration in Mice, an Experimental Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotox Res 25, 24–32 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9401-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9401-8