Abstract
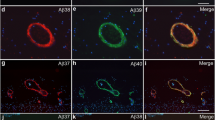
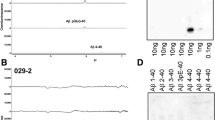
β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilins mutations cause early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease (FAD). Some FAD-based mouse models produce amyloid plaques, others do not. β-Amyloid (Aβ) deposition can manifest as compact and diffuse plaques; it is unclear why the same Aβ molecules aggregate in different patterns. Is there a basic cellular process governing Aβ plaque pathogenesis? We showed in some FAD mouse models that compact plaque formation is associated with a progressive axonal pathology inherent with increased expression of β-secretase (BACE1), the enzyme initiating the amyloidogenic processing of APP. A monoclonal Aβ antibody, 3D6, visualized distinct axon terminal labeling before plaque onset. The present study was set to understand BACE1 and axonal changes relative to diffuse plaque development and to further characterize the novel axonal Aβ antibody immunoreactivity (IR), using triple transgenic AD (3xTg-AD) mice as experimental model. Diffuse-like plaques existed in the forebrain in aged transgenics and were regionally associated with increased BACE1 labeled swollen/sprouting axon terminals. Increased BACE1/3D6 IR at axon terminals occurred in young animals before plaque onset. These axonal elements were also co-labeled by other antibodies targeting the N-terminal and mid-region of Aβ domain and the C-terminal of APP, but not co-labeled by antibodies against the Aβ C-terminal and APP N-terminal. The results suggest that amyloidogenic axonal pathology precedes diffuse plaque formation in the 3xTg-AD mice, and that the early-onset axonal Aβ antibody IR in transgenic models of AD might relate to a cross-reactivity of putative APP β-carboxyl terminal fragments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aho L, Pikkarainen M, Hiltunen M, Leinonen V, Alafuzoff I (2011) Immunohistochemical visualization of amyloid-beta protein precursor and amyloid-beta in extra- and intracellular compartments in the human brain. J Alzheimers Dis 20:1015–1028
Bigl M, Apelt J, Luschekina EA, Lange-Dohna C, Rossner S, Schliebs R (2000) Expression of beta-secretase mRNA in transgenic Tg2576 mouse brain with Alzheimer plaque pathology. Neurosci Lett 292:107–110
Borchelt DR, Ratovitski T, van Lare J, Lee MK, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL, Sisodia SS (1997) Accelerated amyloid deposition in the brains of transgenic mice coexpressing mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron 19:939–945
Burgold S, Bittner T, Dorostkar MM, Kieser D, Fuhrmann M, Mitteregger G, Kretzschmar H, Schmidt B, Herms J (2011) In vivo multiphoton imaging reveals gradual growth of newborn amyloid plaques over weeks. Acta Neuropathol 121:327–335
Cai H, Wang Y, McCarthy D, Wen H, Borchelt DR, Price DL, Wong PC (2001) BACE1 is the major beta-secretase for generation of Aβ peptides by neurons. Nat Neurosci 4:233–234
Cai Y, Xiong K, Zhang XM, Cai H, Luo XG, Feng JC, Clough RW, Struble RG, Patrylo PR, Chu Y, Kordower JH, Yan XX (2010) β-Secretase-1 elevation in aged monkey and Alzheimer’s disease human cerebral cortex occurs around the vasculature in partnership with multisystem axon terminal pathogenesis and β-amyloid accumulation. Eur J Neurosci 32:1223–1238
Castellani RJ, Rolston RK, Smith MA (2010) Alzheimer Disease. Dis Mon 56:484–546
Duyckaerts C, Delatour B, Potier MC (2009) Classification and basic pathology of Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol 118:5–36
Elder GA, Tezapsidis N, Carter J, Shioi J, Bouras C, Li HC, Johnston JM, Efthimiopoulos S, Friedrich VL Jr, Robakis NK (1996) Identification and neuron specific expression of the S182/presenilin-1 protein in human and rodent brain. J Neurosci Res 45:308–320
Fiala JC (2007) Mechanisms of amyloid plaque pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol 114:551–571
Gouras GK, Tampellini D, Takahashi RH, Capetillo-Zarate E (2010) Intraneuronal beta-amyloid accumulation and synapse pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 119:523–541
Herrup K (2010) Reimagining Alzheimer’s disease—an age-based hypothesis. J Neurosci 30:16755–16762
Hirata-Fukae C, Li HF, Hoe HS, Gray AJ, Minami SS, Hamada K, Niikura T, Hua F, Tsukagoshi-Nagai H, Horikoshi-Sakuraba Y, Mughal M, Rebeck GW, LaFerla FM, Mattson MP, Iwata N, Saido TC, Klein WL, Duff KE, Aisen PS, Matsuoka Y (2008) Females exhibit more extensive amyloid, but not tau, pathology in an Alzheimer transgenic model. Brain Res 1216:92–103
Hsiao K, Chapman P, Nilsen S, Eckman C, Harigaya Y, Younkin S, Yang F, Cole G (1996) Correlative memory deficits, Abeta elevation, and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice. Science 274:99–102
Irizarry MC, Locascio JJ, Hyman BT (2001) beta-site APP cleaving enzyme mRNA expression in APP transgenic mice: anatomical overlap with transgene expression and static levels with aging. Am J Pathol 158:173–177
Kim KS, Wegiel J, Sapienza V, Chen J, Hong H, Wisniewski HM (1997) Immunoreactivity of presenilin-1 in human, rat and mouse brain. Brain Res 757:159–163
Laird FM, Cai H, Savonenko AV, Farah MH, He K, Melnikova T, Wen H, Chiang HC, Xu G, Koliatsos VE, Borchelt DR, Price DL, Lee HK, Wong PC (2005) BACE1, a major determinant of selective vulnerability of the brain to amyloid-beta amyloidogenesis, is essential for cognitive, emotional, and synaptic functions. J Neurosci 25:11693–11709
Lazarov O, Lee M, Peterson DA, Sisodia SS (2002) Evidence that synaptically released beta-amyloid accumulates as extracellular deposits in the hippocampus of transgenic mice. J Neurosci 22:9785–9793
Lee MK, Slunt HH, Martin LJ, Thinakaran G, Kim G, Gandy SE, Seeger M, Koo E, Price DL, Sisodia SS (1996) Expression of presenilin 1 and 2 (PS1 and PS2) in human and murine tissues. J Neurosci 16:7513–7525
Lublin AL, Gandy S (2010) Amyloid-beta oligomers: possible roles as key neurotoxins in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mt Sinai J Med 77:43–49
Mastrangelo MA, Bowers WJ (2008) Detailed immunohistochemical characterization of temporal and spatial progression of Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies in male triple-transgenic mice. BMC Neurosci 9:article 81
Oddo S, Caccamo A, Shepherd JD, Murphy MP, Golde TE, Kayed R, Metherate R, Mattson MP, Akbari Y, LaFerla FM (2003) Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles: intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 39:409–421
Pimplikar SW, Nixon RA, Robakis NK, Shen J, Tsai LH (2010) Amyloid-independent mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. J Neurosci 30:14946–14954
Robertson RT, Baratta J, Yu J, LaFerla FM (2009) Amyloid-beta expression in retrosplenial cortex of triple transgenic mice: relationship to cholinergic axonal afferents from medial septum. Neuroscience 164:1334–1346
Sheng JG, Price DL, Koliatsos VE (2002) Disruption of corticocortical connections ameliorates amyloid burden in terminal fields in a transgenic model of Abeta amyloidosis. J Neurosci 22:9794–9799
Struble RG, Ala T, Patrylo PR, Brewer GJ, Yan XX (2010) Is brain amyloid production a cause or a result of dementia of the Alzheimer’s type? J Alzheimers Dis 22:393–399
Thal DR, Capetillo-Zarate E, Del Tredici K, Braak, H (2006) The development of amyloid beta protein deposits in the aged brain. Sci Aging Knowledge Environ 6 re1
van Groen T, Liu L, Ikonen S, Kadish I (2003) Diffuse amyloid deposition, but not plaque number, is reduced in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 double-transgenic mice by pathway lesions. Neuroscience 119:1185–1197
Wegiel J, Kuchna I, Nowicki K, Frackowiak J, Mazur-Kolecka B, Imaki H, Wegiel J, Mehta PD, Silverman WP, Reisberg B, Deleon M, Wisniewski T, Pirttilla T, Frey H, Lehtimäki T, Kivimäki T, Visser FE, Kamphorst W, Potempska A, Bolton D, Currie JR, Miller DL (2007) Intraneuronal Abeta immunoreactivity is not a predictor of brain amyloidosis-beta or neurofibrillary degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 113:389–402
Xiong K, Luo DW, Patrylo PR, Luo XG, Struble RG, Clough RW, Yan XX (2008) Doublecortin-expressing cells are present in layer II across the adult guinea pig cerebral cortex: partial colocalization with mature interneuron markers. Exp Neurol 211:271–282
Yan XX, Li T, Rominger CM, Prakash SR, Wong PC, Olson RE, Zaczek R, Li YW (2004) Binding sites of gamma-secretase inhibitors in rodent brain: distribution, postnatal development, and effect of deafferentation. J Neurosci 24:2942–2952
Zhang XM, Cai Y, Xiong K, Cai H, Luo XG, Feng JC, Clough RW, Struble RG, Patrylo PR, Yan XX (2009) BACE1 elevation in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease is associated with synaptic/axonal pathology and amyloidogenesis: implications for neuritic plaque development. Eur J Neurosci 30:2271–2283
Zhang XM, Xiong K, Cai Y, Cai H, Luo XG, Feng JC, Clough RW, Patrylo PR, Struble RG, Yan XX (2010) Functional deprivation promotes amyloid plaque pathogenesis in Tg2576 mouse olfactory bulb and piriform cortex. Eur J Neurosci 31:710–721
Zhao J, Fu Y, Yasvoina M, Shao P, Hitt B, O’Connor T, Logan S, Maus E, Citron M, Berry R, Binder L, Vassar R (2007) Beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 levels become elevated in neurons around amyloid plaques: implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. J Neurosci 27:3639–3649
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by Illinois Department of Public Health (X.X.Y.), National Institute of Health (1R21NS056371 to P.R.P.), Southern Illinois University Center for Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders (X.X.Y., P.R.P., R.G.S.), intramural program of the National Institute on Aging (H.C.), and Central South University (X.X.Y.). We thank Elan Pharmaceuticals and Drs. H. Akiyama, H. Mori, E. Koo, and P. Davis for providing antibodies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y., Zhang, XM., Macklin, L.N. et al. BACE1 Elevation is Involved in Amyloid Plaque Development in the Triple Transgenic Model of Alzheimer’s Disease: Differential Aβ Antibody Labeling of Early-Onset Axon Terminal Pathology. Neurotox Res 21, 160–174 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-011-9256-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-011-9256-9