Abstract
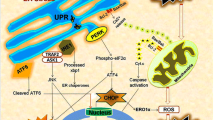
The endoplasmic reticulum(ER) stress plays a vital role in mediating ischemic neuronal cell death. However, very little is known about the role of ER stress in mediating pathophysiological reactions to acute brain injuries. An attempt was therefore made to assess the role of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) induced ER stress and its modulation on outcome of ischemic insult. Focal cerebral ischemia was induced in rats by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 2 h followed by varying time points of reperfusion. The brain loci specific and time-dependent alterations were seen in the expression pattern of molecular markers, i.e., heat-shock protein 70 (HSP70) for cytoplasmic dysfunction, glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), Caspase-12, C/EBP homologous protein/growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible gene 153 (CHOP/GADD153), activating transcription factor 4 (ATF-4), and Processed X-box protein 1 (xbp1) mRNA for ER dysfunction. Further, histological examinations indicated pronounced brain damage, massive neuronal loss, and DNA fragmentation predominantly in the striatum and cortex. The enhanced expression of GRP78, Caspase-12, CHOP/GADD153, ATF4 and processing of xbp1 mRNA in the affected brain regions clearly indicate the critical involvement of ER-mediated cell death/survival mechanisms and also collectively demonstrated the activation of unfolded protein response (UPR). Moreover, Salubrinal, a selective inhibitor of eIF2α dephosphorylation was used to counteract ER stress, which significantly increased the phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit α (eIF2α), leading to reduced brain damage after I/R injury. Therefore, inhibition of ER stress following I/R injury may be used as key therapeutic target for neuroprotection.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Althausen S, Mengesdorf T, Mies G, Olah L, Nairn AC, Proud CG, Paschen W (2001) Changes in the phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2alpha, elongation factor eEF-2 and p70 S6 kinase after transient focal cerebral ischaemia in mice. J Neurochem 78:779–787
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H (1986) Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17:472–476
Belayev L, Busto R, Zhao W, Fernandez G, Ginsberg MD (1999) Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the mouse by intraluminal suture coated with poly-l-lysine: neurological and histological validation. Brain Res 833:181–190
Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2:326–332
Boyce M, Yuan J (2006) Cellular response to endoplasmic reticulum stress: a matter of life or death. Cell Death Differ 13:363–373
Boyce M, Bryant KF, Jousse C, Long K, Harding HP, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Ma D, Coen DM, Ron D, Yuan J (2005) A selective inhibitor of eIF2α dephosphorylation protects cells from ER stress. Science 307:935–939
Calfon M, Zeng H, Urano F, Till JH, Hubbart SR, Harding HP, Clark SG, Ron D (2002) IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing XBP-1 mRNA. Nature 415:92–96
DeGracia DJ, Montie HL (2004) Cerebral ischemia and the unfolded protein response. J Neurochem 91:1–8
DeGracia DJ, Kumar R, Owen CR, Krause GS, White BC (2002) Molecular pathways of protein synthesis inhibition during brain reperfusion: implications for neuronal survival or death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:127–141
Dirnagl U, Simon RP, Hallenbeck JM (2003) Ischemic tolerance and endogenous neuroprotection. Trends Neurosci 26:248–254
Feigin VL (2005) Stroke epidemiology in the developing world. Lancet 365(9478):2160–2161
Ferrer I (2006) Apoptosis: future targets for neuroprotective strategies. Cerebrovasc Dis 2:9–20
Harding HP, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Wek R, Schapira M, Ron D (2000a) Regulated translation initiation controls stress induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell 6:1099–1108
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Bertolotti A, Zeng H, Ron D (2000b) Perk is essential for translational regulation and cell survival during the unfolded protein response. Mole Cell 5:897–904
Harding HP, Zeng H, Zhang Y, Jungries R, Chung P, Plesken H, Sabatini DD, Ron D (2001) Diabetes Mellitus and exocrine pancreatic dysfunction in Perk−/−mice reveals a role for translational control in secretory cell survival. Mol Cell 7:1153–1163
Hayashi T, Saito A, Okuno S, Ferrand-Drake M, Chan PH (2003) Induction of GRP78 by ischemic preconditioning reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress and prevents delayed neuronal cell death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:949–961
Hayashi T, Saito A, Okuno S, Ferrand-Drake M, Dodd RL, Chan PH (2005) Damage to the endoplasmic reticulum and activation of apoptotic machinery by oxidative stress in ischemic neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:41–53
Hossmann KA (1994) Viability thresholds and the penumbra of focal ischemia. Ann Neurol 36:557–565
Hu BR, Martone ME, Jones YZ, Liu CL (2000) Protein aggregation after transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 20:3191–3199
Jousse C, Oyadomari S, Novoa I, Lu PD, Zhang Y, Harding HP, Ron D (2003) Inhibition of a constitutive translation initiation factor 2a phosphatase, CReP, promotes survival of stressed cells. J Cell Biol 163:767–775
Kinouchi H, Sharp FR, Koistinaho J, Hicks K, Kamii H, Chan PH (1993) Induction of heat shock hsp70 mRNA and HSP70 kDa protein in neurons in the “penumbra” following focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Brain Res 619:334–338
Kumar R, Azam S, Sullivan JM, Owen C, Cavener DR, Zhang P, Ron D, Harding HP, Chen JJ, Han A, White BC, Krause GS, DeGracia DJ (2001) Brain ischemia and reperfusion activates the eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinase, PERK. J Neurochem 77:1418–1421
Lange PS, Chavez JC, Pinto JT, Coppola G, Sun CW, Townes TM, Geschwind DH, Ratan RR (2008) ATF4 is an oxidative stress-inducible, prodeath transcription factor in neurons in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med 205:1227–1242
Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Glimcher LH (2003) XBP-1 regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol 23:7448–7459
Lehotský J, Urban P, Pavlíková M, Tatarková Z, Kaminska B, Kaplán P (2009) Molecular mechanisms leading to neuroprotection/ischemic tolerance: effect of preconditioning on the stress reaction of endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:917–925
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Lowry OH, Rosebrouge NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin Phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lu PD, Harding HP, Ron D (2004a) Translation reinitiation at alternative open reading frames regulates gene expression in an integrated stress response. Mol Cell Biol 167:27–33
Lu PD, Jousse C, Marciniak SJ, Zhang Y, Novoa I, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Ron D, Harding HP (2004b) Cytoprotection by pre-emptive conditional phosphorylation of translation initiation factor 2. EMBO J 23:169–179
Luo S, Baumeister P, Yang S, Abcouwer SF, Lee AS (2003) Induction of Grp78/BiP by translational block: activation of the Grp78 promoter by ATF4 through and upstream ATF/CRE site independent of the endoplasmic reticulum stress elements. J Biol Chem 278:37375–37385
Ma Y, Hendershot LM (2001) The unfolding tale of the unfolded protein response. Cell 107:827–830
Mehta SL, Manhas N, Raghubir R (2007) Molecular targets in cerebral ischemia for developing novel therapeutics. Brain Res Rev 54:34–66
Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Takenouchi H, Shibata T, Yasuhiko Y (2002) An endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific caspase cascade in apoptosis. Cytochrome c-independent activation of caspase-9 by caspase-12. J Biol Chem 277:34287–34294
Mouw G, Zechel JL, Gamboa J, Lust WD, Selman WR, Ratcheson RA (2003) Activation of caspase-12, an endoplasmic reticulum resident caspase, after permanent focal ischemia in rat. Neuroreport 14:183–186
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature 403:98–103
Nakka VP, Gusain A, Mehta SL, Raghubir R (2008) Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in cerebral ischemia: multiple neuroprotective opportunities. Mol neurobiol 37:7–38
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11:381–389
Paschen W, Doutheil J (1999) Disturbances of the functioning of endoplasmic reticulum: a key mechanism underlying neuronal cell injury? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:1–18
Paschen W, Mengesdorf T (2005) Cellular abnormalities linked to endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in cerebrovascular disease—therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther 108:362–375
Paschen W, Gissel C, Linden T, Althausen S, Doutheil J (1998) Activation of gadd153 expression through transient cerebral ischemia: evidence that ischemia causes endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 60:115–122
Prostko CR, Brostrom MA, Brostrom CO (1993) Reversible phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha in response to endoplasmic reticular signaling. Mol Cell Biochem 128:255–265
Rajdev S, Hara K, Kokubo Y, Mestril R, Dillmann W, Weinstein PR, Sharp FR (2000) Mice overexpressing rat heat shock protein 70 are protected against cerebral infarction. Ann Neurol 47:782–791
Rao RV, Hermel E, Castro-Obregon S, del Rio G, Ellerby LM, Ellerby HM, Bredesen DE (2001) Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program: mechanism of caspase activation. J Biol Chem 276:33869–33874
Ron D (2002) Translational control in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J Clin Invest 110:1383–1388
Scheuner D, Song B, McEwen E, Liu C, Laybutt R, Gillespie P, Saunders T, Bonner-Weir S, Kaufman RJ (2001) Translational control is required for the unfolded protein response and in vivo glucose homeostasis. Mol Cell 7:1165–1176
Sharp FR, Kinouchi H, Koistinaho J, Chan PH, Sagar SM (1993) HSP70 heat shock gene regulation during ischemia. Stroke 24:I72–I75
Shibata M, Hattori H, Sasaki T, Gotoh J, Hamada J, Fukuuchi Y (2003) Activation of caspase-12 by endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Neuroscience 118:491–499
Sokka AL, Putkonen N, Mudo G, Pryazhnikov E, Reijonen S, Khiroug L, Belluardo N, Lindholm D, Korhonen L (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition protects against excitotoxic neuronal injury in the rat brain. J Neurosci 27:901–908
Strong K, Mathers C, Bonita R (2007) Preventing stroke: saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol 6:182–187
Tajiri S, Oyadomari S, Yano S, Morioka M, Gotoh T, Hamada JI, Ushio Y, Mori M (2004) Ischemia-induced neuronal cell death is mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway involving CHOP. Cell Death Differ 11:403–415
Unal-Cevik I, Kılınc M, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y, Gurer G, Dalkara T (2004) Loss of NeuN immunoreactivity after cerebral ischemia does not indicate neuronal cell loss: a cautionary note. Brain Res 1015:169–174
Urban P, Pavlíková M, Sivonová M, Kaplán P, Tatarková Z, Kaminska B, Lehotský J (2009) Molecular analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress response after global forebrain ischemia/reperfusion in rats: effect of neuroprotectant simvastatin. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:181–192
Van de Craen M, Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Van den Brande I, Van Loo G, Molemans F, Schotte P, Van Criekinge W, Beyaert R, Fiers W (1997) Characterization of seven murine caspase family members. FEBS Lett 403:61–69
Weinstein PR, Hong S, Sharp FR (2004) Molecular identification of the ischemic penumbra. Stroke 35:2666–2670
Yenari MA, Giffard RG, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (1999) The neuroprotective potential of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70). Mol Med Today 5:525–531
Zhang RL, Chopp M, Chen H, Garcia JH (1994) Temporal profile of ischemic tissue damage, neutrophil response, and vascular plugging following permanent and transient (2H) middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Neurol Sci 125:3–10
Zhang P, McGrath B, Li S, Frank A, Zambito F, Reinert J, Gannon M, Ma K, McNaughton K, Cavener DR (2002) The PERK eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinase is required for the development of the skeletal system, postnatal growth, and the function and viability of the pancreas. Mol Cell Biol 22:3864–3874
Acknowledgment
Mr. Venkata Prasuja Nakka and Ms. Anchal Gusain received Senior Research Fellowship from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
+CDRI Communication No. 7749.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure
Coronal brain sections of TTC staining showing the ipsilateral brain damage after 2 h ischemia followed by different time intervals of reperfusion (TIFF 536 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakka, V.P., Gusain, A. & Raghubir, R. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Plays Critical Role in Brain Damage After Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion in Rats. Neurotox Res 17, 189–202 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9110-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9110-5