Abstract
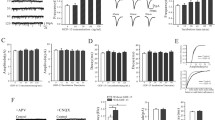
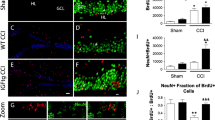
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) protects neurons from apoptosis and in vivo offers neuroprotective support to hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons following ischemia or seizure. IGF-1 signals through IGF-1 receptors activating phosphytidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt or pMAPK pathways. IGF-1 can be induced with injury and microglia and astrocytes may serve as a source of this neurotrophic factor to promote neuronal survival. An acute systemic injection of trimethyltin (TMT; 2 mg/kg, ip) to mice induces apoptosis of dentate granule neurons within 24 h and a differential response of microglia with ramified microglia present in the CA-1 region. Using this model, we studied the role of IGF-1 in the survival of CA-1 pyramidal neurons under conditions of altered synaptic input due to changes in the dentate gyrus. Within 24 h of injection, IGF-1 mRNA levels were elevated in the hippocampus and IGF-1 protein detected in both astrocytes and microglia. IGF-1 was redistributed within the CA-1 neurons corresponding with an increase in cytoplasmic pAkt, elevated PKBα/Akt protein levels, and a decrease in the antagonist, Rho. pMAPK was not detected in CA-1 neurons and ERK2 showed a transient decrease followed by a significant increase, suggesting a lack of recruitment of the pMAPK signaling pathway for neuronal survival. In mice deficient for IGF-1, a similar level of apoptosis was observed in dentate granule neurons as compared to wildtype; however, TMT induced a significant level CA-1 neuronal death, further supporting a role for IGF-1 in the survival of CA-1 neurons.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikin R, Rosenberg L, Maysinger D (2000) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling to Akt mediates survival in isolated canine islets of langerhans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 277:455–461
Alessi DR, Andjelkovic M, Caudwell B, Cron P, Morrice N, Cohen P, Hemmings BA (1996) Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. EMBO J 15(23):6541–6551
Amaral DG, Witter MP (1989) The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience 31:571–591
Ambrosini E, Aloisi F (2004) Chemokines and glial cells: a complex network in the central nervous system. Neurochem Res 29:1017–1038
Balendran A, Casamayor A, Deak M, Paterson A, Gaffney P, Currie R, Downes CP, Alessi DR (1999) PDK1 acquires PDK2 activity in the presence of a synthetic peptide derived from the carboxyl terminus of PRK2. Curr Biol 9(8):393–404
Bence-Hanulec KK, Marshall J, Blair LA (2000) Potentiation of neuronal L calcium channels by IGF-1 requires phosphorylation of the alpha1 subunit on a specific tyrosine residue. Neuron 27:121–131
Blair LA, Marshall J (1997) IGF-1 modulates N and L calcium channels in a PI 3-kinase-dependent manner. Neuron 19:421–429
Blair LA, Bence-Hanulec KK, Mehta S, Franke T, Kaplan D, Marshall J (1999) Akt-dependent potentiation of L channels by insulin-like growth factor-1 is required for neuronal survival. J Neurosci 19:1940–1951
Bondy C, Bach M, Lee W (1992) Mapping of brain insulin and insulin like growth factor receptor gene expression by in situ hybridization. NeuroProtocols 1:240–249
Borgatti P, Martelli AM, Bellacosa A, Casto R, Massari L, Capitani S, Neri LM (2000) Translocation of Akt/PKB to the nucleus of osteoblast-like MC3T3–E1 cells exposed to proliferative growth factors. FEBS Lett 477:27–32
Bruccoleri A, Harry GJ (2000) Chemical-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration and elevations in TNFalpha, TNFbeta IL-1alpha, IP-10, and MCP-1 mRNA in osteopetrotic (op/op) mice. J Neurosci Res 62(1):146–155
Bruccoleri A, Brown H, Harry GJ (1998) Cellular localization and temporal elevation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 alpha, and transforming growth factor-beta 1 mRNA in hippocampal injury response induced by trimethyltin. J Neurochem 71:1577–1587
Butt AJ, Firth SM, Baxter RC (1999) The IGF axis and programmed cell death. Immunol Cell Biol 77(3):256–262
Carson MJ, Bilousova TV, Puntambekar SS, Melchior B, Doose JM, Ethell IM (2007) A rose by any other name? The potential consequences of microglial heterogeneity during CNS health and disease. Neurotherapeutics 4:571–579
Castellino RC, Durden DL (2007) Mechanisms of disease: the PI3K-Akt-PTEN signaling node—an intercept point for the control of angiogenesis in brain tumors. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 3:682–693
Chang LW, Tiemeyer TM, Wenger GR, McMillan DE (1982) Neuropathology of mouse hippocampus in acute trimethyltin intoxication. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 4:149–156
Cheng B, Mattson MP (1992) IGF-1 and IGF-II protect cultured hippocampal and septal neurons against calcium-mediated hypoglycemic damage. J Neurosci 12:1558–1566
Choi SC, Kim SJ, Choi JH, Park CY, Shim WJ, Lim DS (2008a) Fibroblast growth factor-2 and -4 promote the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by the activation of the PI3K-Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Stem Cells Dev 17(4):725–736
Choi Y-S, Cho H-Y, Hoyt KR, Naegele JR, Obrietan K (2008b) IGF-1 receptor-mediated ERK/MAPK signaling couples status epilepticus to progenitor cell proliferation in the subgranular layer of the dentate gyrus. Glia 56:791–800
Crowder RJ, Freeman RS (2000) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta activity is critical for neuronal death caused by inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase or Akt but not for death caused by nerve growth factor withdrawal. J Biol Chem 275(44):34266–34271
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME (1999) Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev 13(22):2905–2927
Davalos D, Gruntzendler J, Yang G, Kim JV, Zuo Y, Jung S, Littman DR, Dustin ML, Gan WB (2005) ATP mediates rapid microglial response to local brain injury in vivo. Nat Neurosci 8:52–758
del Peso L, González-García M, Page C, Herrera R, Nuñez G (1997) Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science 278(5338):687–689
Delcommenne M, Tan C, Gray V, Rue L, Woodgett J, Dedhar S (1998) Phosphoinositide-3- OH kinase-dependent regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 and protein kinase B/AKT by the integrin-linked kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(19):11211–11216
Delree P, Ribbons C, Martin D, Rogister B, Lefebvre PP, Rigo JM, Leprince P, Schoenen J, Moonen G (1993) Plasticity of developing and adult dorsal root ganglion neurons as revealed in vitro. Brain Res Bull 30:231–237
Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, Birnbaum MJ, Yao R, Cooper GM, Segal RA, Kaplan DR, Greenberg ME (1997) Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt. Science 275(5300):661–665
Fiedorowicz A, Figiel I, Kaminska B, Zaremba M, Wilk S, Oderfeld-Nowak B (2001) Dentate granule neuron apoptosis and glia activation in murine hippocampus induced by trimethyltin exposure. Brain Res 912:116–127
Guan J, Williams C, Gunning M, Mallard C, Gluckman P (1993) The effects of IGF-1 treatment after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in adult rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13:609–616
Guan J, Williams CE, Skinner SJM, Mallard EM, Gluckman PD (1996) The effects of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF-2, and des-IGF-1 on neuronal loss after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in adult rats: evidence for a role for IGF binding proteins. Endocrinology 13789:3–898
Harry GJ, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C (2002) The neuroinflammatory components of the trimethyltin (TMT) model of hippocampal neurodegeneration. In: Wood PL (ed) Neuroinflammation: mechanisms and management, 2nd edn. Humana Press Inc, Totowa, pp 301–329
Harry GJ, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C (2003) Dentate gyrus: alterations that occur with hippocampal injury. Neurotoxicology 24:343–356
Harry GJ, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C, Bruccoleri A, Schmechel D (2000) Age-dependent cytokine responses: trimethyltin hippocampal injury in wild-type, APOE knockout, and APOE4 mice. Brain Behav Immun 14:288–304
Harry GJ, Funk JA, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C, McPherson CA, Aoyama M (2008a) The type 1 interleukin 1 receptor is not required for the death of murine hippocampal dentate granule cells and microglia activation. Brain Res 1194:8–20
Harry GJ, Wine RN, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C, Funk JA, McPherson C, Aoyama M (2008b) TNFp55 receptor and TNFp75 receptor are involved in chemical-induced dentate granule cell death. J Neurochem 106:281–298
Hwang IK, Yoo K-Y, Park S-K, Ana S-J, Lee J-Y, Choi SY, Kang JH, Kwon Y-G, Kanga T-C, Won MH (2004) Expression and changes of endogenous insulin-like growth factor-1 in neurons and glia in the gerbil hippocampus and dentate gyrus after ischemic insult. Neurochemistry Int 45:149–156
Imai F, Suzuki H, Oda J, Ninomiya T, Ono K, Sano H, Sawada M (2007) Neuroprotective effect of exogenous microglia in global brain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(3):488–500
Jackson TC, Rani A, Kuman A, Foster TC (2009) Regional hippocampal differences in AKT survival signaling across the lifespan: implications for CA1 vulnerability with aging. Cell Death Diff 16:439–448
Jin S, DiPaola RS, Mathew R, White E (2007) Metabolic catastrophe as a means to cancer cell death. J Cell Sci 12037:9–383
Johansen FF, Zimmer J, Diemer NH (1987) Early loss of somatostatin neurons in dentate hilus after cerebral ischemia in the rat precedes CA-1 pyramidal cell loss. Acta Neuropathol 73:110–114
Johnston BM, Mallard EC, Williams CE, Gluckman PD (1996) Insulin-like growth factor-1 is a potent neuronal rescue agent after hypoxic-ischemic injury in fetal lambs. J Clin Invest 97(2):300–308
Kadar T, Dachir S, Shukitt-Hale B, Levy A (1998) Sub-regional hippocampal vulnerability in various animal models leading to cognitive dysfunction. J Neural Transm 105:987–1004
Kanthasamy AG, Yun RJ, Nguyen B, Truong DD (1999) Effect of riluzole on the neurological and neuropathological changes in an animal model of cardiac arrest-induced movement disorder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288(3):1340–1348
Kenchappa P, Yadav A, Singh G, Nandana S, Banerjee K (2004) Rescue of TNFalpha-inhibited neuronal cells by IGF-1 involves Akt and c-Jun N terminal kinases. J Neurosci Res 76:466–474
Kielian T (2004) Microglia and chemokines in infectious diseases of the nervous system: views and reviews. Front Biosci 9:732–750
Kitamura Y, Takata K, Inden M, Tsuchiya D, Yanagisawa D, Nakata J, Taniguchi T (2004) Intracerebroventricular injection of microglia protects against focal brain ischemia. J Pharmacol Sci 94:203–206
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia, a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Lalancette-Hébert M, Gowing G, Simard A, Weng YC, Kriz J (2007) Selective ablation of proliferating microglial cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain. J Neurosci 27(10):2596–2605
Lambertsen KL, Clausen BH, Babcock AA, Gregersen R, Fenger C, Nielsen HH, Haugaard LS, Wirenfeldt M, Nielsen M, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Bluethmann H, Faergeman NJ, Meldgaard M, Deierborg T, Finsen B (2009) Microglia protect neurons against ischemia by synthesis of tumor necrosis factor. J Neurosci 29(5):1319–1330
Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C, Harry GJ (2005) Molecular profiles of mRNA levels in laser capture microdisected murine hippocampal regions differentially responsive to TMT-induced cell death. J Neurochem 93:206–220
Lefebvre PP, Martin D, Staecker H, Weber T, Moonen G, Van De Water TR (1992) TGF-β1 expression is initiated in adult auditory neurons by sectioning of the auditory nerve. Neuroreport 3:295–298
Leinninger GM, Backus C, Uhler MD, Lentz SI, Feldman EL (2004) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt effectors mediate insulin-like growth factor-I neuroprotection in dorsal root ganglia neurons. FASEB J 18(13):1544–1546
Li L, Qu Y, Mao M, Xiong Y, Mu D (2008) The involvement of phosphoinositid 3-kinase/Akt pathway in the activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in the developing rat brain after hypoxia-ischemia. Brain Res 1197:152–158
Lindholm D, Carroll P, Tzimagiogis G, Thoenen H (1996) Autocrine-paracrine regulation of hippocampal neuron survival by IGF-1 and the neurotrophins BDNF, NT-3 and NT-4. Eur J Neurosci 8(7):1452–1460
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1993) Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 75(1):59–72
Matthews CC, Feldman EL (1996) Insulin-like growth factor I rescues SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells from hyperosmotic induced programmed cell death. JCell Physiol 166(2):323–331
McPherson C, Kubik J, Wine R, Lefebevre d’Hellencourt C, Harry GJ (2003) Alterations in cyclin A, B, and D1 in mouse dentate gyrus following TMT-induced hippocampal damage. Neurotoxicity Res 5:339–354
Nakagomi S, Suzuki Y, Namikawa K, Kiryu-Seo S, Kiyama H (2003) Expression of the activating transcription factor 3 prevents c-Jun N-terminal kinase-induced neuronal death by promoting heat shock protein 27 expression and Akt activation. J Neurosci 23:5187–5196
Nakao N, Odin P, Lindvall O, Brundin P (1996) Differential trophic effects of basic fibroblast growth factor, insulin-like growth factor-1, and neurotrophin-3 on striatal neurons in culture. Exp Neurol 138:144–157
Neumann J, Gunzer M, Gutzeit HO, Ullrich O, Reymann KG, Dinkel K (2006) Microglia provide neuroprotection after ischemia. FASEB J 20:714–716
Nicholas RS, Stevens S, Wing MG, Compston DA (2002) Microglia derived IGF-2 prevents TNFalpha induced death of mature oligodendrocytes in vitro. J Neuroimmunol 124:36–44
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG (2002) The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal 14(5):381–395
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F (2005) Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 308:1314–1318
Nitta A, Xheng W-H, Quirion R (2004) Insulin-like growth factor 1 prevents neuronal cell death induced by corticosterone through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. J Neurosci Res 76:98–103
O’Donnell SL, Frederick TJ, Krady JK, Vannucci SJ, Wood TL (2002) IGF-I and microglia/macrophage proliferation in the ischemic mouse brain. Glia 39(1):85–97
Otto VI, Stahel PF, Rancan M, Kariya K, Shohami E, Yatsiv I, Eugster HP, Kossmann T, Trentz O, Morganti-Kossmann MC (2001) Regulation of chemokines and chemokine receptors after experimental closed head injury. Neuroreport 12:2059–2064
Plas DR, Thompson CB (2005) Akt-dependent transformation: there is more to growth than just surviving. Oncogene 24(50):743574
Quirk SM, Harman RM, Cowan RG (2000) Regulation of Fas antigen (Fas, CD95)-mediated apoptosis of bovine granulosa cells by serum and growth factors. Biol Reprod 63:1278–1284
Raivich G (2005) Like cops on the beat, the active role of resting microglia. Trends Neurosci 28:571–573
Reuhl KR, Cramner JM (1984) Developmental neuropathology of organotin compounds. Neurotoxicology 5:187–204
Rezaie P, Trillo-Pazos G, Greenwood J, Everall IP, Male DK (2002) Motility and ramification of human fetal microglia in culture: an investigation using time-lapse video microscopy and image analysis. Exp Cell Res 274:68–82
Richards RG, Klotz DM, Bush MR, Walmer DK, DiAugustine RP (2001) E2-induced degradation of uterine insulin receptor substrate-2: requirement for an IGF-I- stimulated, proteosome-dependent pathway. Endocrinology 142(9):3842–3849
Riemenschneider MJ, Betensky RA, Pasedag SM, Louis DN (2006) AKT activation in human glioblastomas enhances proliferation via TSC2 and S6 kinase signaling. Cancer Res 66:5618–5623
Rogister B, Delree P, Lepnince P, Martin D, Sadzot C, Malgrange B, Munaut C, Rigo JM, Lefebvre PP, Octave JN, Schoenen J, Moonen G (1993) Transforming growth factor-b1 as a neuronoglial signal during peripheral nervous system response to injury. J Neurosci Res 34:32–34
Russell JW, Windebank AJ, Schenone A, Feldman EL (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-I prevents apoptosis in neurons after nerve growth factor withdrawal. J Neurobiol 36(4):455–467
Russo VC, Kobayashi K, Najdovska S, Baker NL, Werther GA (2004) Neuronal protection from glucose deprivation via modulation of glucose transport and inhibition of apoptosis: a role for the insulin-like growth factor system. Brain Res 1009:40–53
Song K, Cornelius SC, Reiss M, Danielpour D (2003) Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits transcriptional responses of transforming growth factor-beta by phosphatidylinositol 3- kinase/Akt-dependent suppression of the activation of Smad3 but not Smad2. J Biol Chem 278:38342–38351
Spires TL, Orne JD, SantaCruz K, Pitstick R, Carlson GA, Ashe KH, Hyman BT (2006) Region- specific dissociation of neuronal loss and neurofibrillary pathology in a mouse model of tauopathy. Am J Pathol 186:1598–1607
Streit WJ (2002) Microglia as neuroprotective, immunocompetent cells of the CNS. Glia 40:133–139
Tikka TM, Koistinaho JE (2001) Minocycline provides neuroprotection against N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotoxicity by inhibiting microglia. J Immunol 166(12):7527–7533
Venters HD, Dantzer R, Kelley KW (2000) A new concept in neurodegeneration: TNFalpha is a silencer of survival signals. Trends Neurosci 23:175–180
West MJ, Kawas CH, Stewart WF, Rudow GL, Troncoso JC (2004) Hippocampal neurons in pre-clinical Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 25:1205–1212
Xu G, Zhang W, Bertram P, Zheng XF, McLeod H (2004) Pharmacogenomic profiling of the PI3K/PTEN-AKT-mTOR pathway in common human tumors. Int J Oncol 24(4):893–900
Yamada M, Tanabe K, Wada K, Shimoke K, Ishikawa Y, Ikeuchi T, Koizumi S, Hatanaka H (2001) Differences in survival-promoting effects and intracellular signaling properties of BDNF and IGF-1 in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. J Neurochem 78(5):940–951
Yamaguchi H, Wang HG (2001) The protein kinase PKB/Akt regulates cell survival and apoptosis by inhibiting Bax conformational change. Oncogene 20(53):7779–7786
Yamaguchi A, Tamatani M, Matsuzaki H, Namikawa K, Kiyama H, Vitek MP, Mitsuda N, Tohyama M (2001) Akt activation protects hippocampal neurons from apoptosis by inhibiting transcriptional activity of p53. J Biol Chem 276:5256–5264
Yrjänheikki J, Keinänen R, Pellikka M, Hökfelt T, Koistinaho J (1998) Tetracyclines inhibit microglial activation and are neuroprotective in global brain ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(26):15769–15774
Zhang SX, Gozal D, Sachleben LR Jr, Rane M, Klein JB, Gozal E (2003) Hypoxia induces an autocrine-paracrine survival pathway via platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)- B/PDGF-beta receptor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling in RN46A neuronal cells. FASEB J 17(12):1709–1711
Zhang L, Li L, Prabhakaran K, Borowitz JL, Isom GE (2006) Trimethyltin-induced apoptosis is associated with upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and Bax in a hippocampal cell line. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 216(1):34–43
Zheng WH, Kar S, Quirion R (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-1-induced phosphorylation of transcription factor FKHRL1 is mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt kinase and role of this pathway in insulin-like growth factor-1-induced survival of cultured hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol 62(2):225–233
Zhu CZ, Auer RN (1994) Intraventricular administration of insulin and IGF-1 in transient forebrain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 14:237–242
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wine, R.N., McPherson, C.A. & Harry, G.J. IGF-1 and pAKT Signaling Promote Hippocampal CA1 Neuronal Survival Following Injury to Dentate Granule Cells. Neurotox Res 16, 280–292 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9060-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9060-y