Abstract
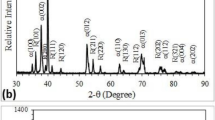
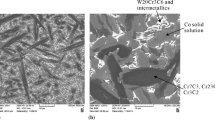
Powder metallurgical Cu–Ti alloys with different titanium additions produced by hot pressing were characterized by optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, and hardness, wear and bending tests. The addition of titanium to copper caused the formation of different intermetallic layers around titanium particles. The titanium content of the intermetallics decreased from the center of the particle to the copper matrix. The hardness, wear resistance, and bending strength of the materials increased with increasing Ti content, whereas strain in the bending test decreased. Worn surface analyses showed that different wear mechanisms were active during the wear test of specimens with different chemical compositions. Changes in the properties of the materials with titanium addition were explained by the high hardness of different Cu–Ti intermetallic phases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Ranjbar Motlagh, M.H. Maghsoudi, and S. Serajzadeh, Softening behaviour of alumina reinforced copper processed by equal channel angular pressing, Mater. Sci. Technol., 30(2014), No. 2, p. 220.
K. Song, X. Guo, S. Liang, P. Zhao, and Y. Zhang, Relationship between interfacial stress and thermal expansion coefficient of copper-matrix composites with different reinforced phases, Mater. Sci. Technol., 30(2014), No. 2, p. 171.
S.Z. Han, M. Goto, J.H. Ahn, S.H. Lim, S. Kim, and J. Lee, Grain growth in ultrafine grain sized copper during cyclic deformation, J. Alloys Compd., 615(2014), Suppl. 1, p. S587.
S.B. Chandrasekhar, N.P. Wasekar, M. Ramakrishna, P.S. Babu, T.N. Rao, and B.P. Kashyap, Dynamic strain ageing in fine grained Cu–1wt%Al2O3 composite processed by two step ball milling and spark plasma sintering, J. Alloys Compd., 656(2016), p. 423.
J.H. Nie, C.C. Jia, X. Jia, Y.F. Zhang, and X.B. Liang, Fabrication and thermal conductivity of copper matrix composites reinforced by tungsten-coated carbon nanotubes, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 19(2012), No. 5, p. 446.
S. Semboshi, S. Orimo, H. Suda, W. Gao, and A. Sugawara, Aging of copper−titanium dilute alloys in hydrogen atmosphere: influence of prior-deformation on strength and electrical conductivity, Mater. Trans., 52(2011), No. 12, p. 2137.
Y. Tang, G. Zhu, Y. Kang, L. Yue, and X. Jiao, Effect of microstructure on the fatigue crack growth behavior of Cu–Be–Co–Ni alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 663(2016), p. 784.
P. Behjati, H.V. Dastjerdi, and R. Mahdavi, Influence of ageing process on sound velocity in C17200 copper−beryllium alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 505(2010), No. 2, p. 739.
L. Yagmur, Effect of microstructure on internal friction and Young’s modulus of aged Cu–Be alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 523(2009), No. 1-2, p. 65.
A. Kamegawa, T. Kuriiwa, and M. Okada, Effects of dehydrogenation heat-treatment on electrical−mechanical properties for hydrogenated Cu–3mass%Ti alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 566(2013), p. 1.
S. Li, Z. Li, X. Zhu, S.H. Li, L.N. Shen, and Q.Y. Dong, Microstructure and property of Cu–2.7Ti–0.15Mg–0.1Ce–0.1Zr alloy treated with a combined aging process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 640(2016), p. 345.
S. Nagarjuna, Thermal conductivity of Cu–4.5Ti alloy, Bull. Mater. Sci., 27(2004), No. 1, p. 69.
F. Hernadez-Santiago, N. Cayetano-Castro, V.M. Lopez-Hirata, H.J. Dorantes-Rosales, and J.J. Cruz-Rivera, Precipitation kinetics in a Cu–4mass% Ti alloy, Mater. Trans., 45(2004), No. 7, p. 2312.
D.E. Laughlin and J.W. Cahn, Spinodal decomposition in age hardening copper–titanium alloys, Acta Metall., 23(1975), No. 3, p. 329.
A. Datta and W.A. Soffa, The structure and properties of age hardened Cu–Ti alloys, Acta Metall., 24(1976), No. 11, p. 987.
S. Semboshi, S. Sato, M. Ishikuro, K. Wagatsuma, A. Iwase, and T. Takasugi, Investigation of precipitation behavior in age-hardenable Cu–Ti alloys by an extraction-based approach, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 45(2014), No. 8, p. 3401.
A. Chanda and M. De, X-ray characterization of the microstructure of α-CuTi alloys by Rietveld’s method, J Alloys Compd., 313(2000), No. 1-2, p. 104.
S. Nagarjuna, M. Srinivas, K. Balasubramanian, and D.S. Sarma, Effect of alloying content on high cycle fatigue behaviour of Cu–Ti alloys, Int. J. Fatigue, 19(1997), No. 1, p. 51.
R. Nishio, T.J. Konno, and S. Semboshi, Transmission electron microscopy observations on Cu–Ti alloy systems, Mater. Sci. Forum, 502(2005), p. 163.
S. Semboshi, S. Yamauchi, and H. Numakura, Formation of titanium hydride in dilute Cu–Ti alloy by aging in hydrogen atmosphere and its effects on electrical and mechanical properties, Mater Trans., 54(2013), No. 4, p. 520.
S. Nagarjuna and D.S. Sarma, Effect of cobalt additions on the age hardening of Cu–4.5Ti alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 37(2002), No. 10, p. 1929.
W.A. Soffa and D.E. Laughlin, High-strength age hardening copper–titanium alloys: redivivus, Prog. Mater. Sci., 49(2004), No. 3-4, p. 347.
S. Nagarjuna and M. Srinivas, High temperature tensile behaviour of a Cu–1.5wt% Ti alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 335(2002), No. 1-2, p. 89.
S. Nagarjuna, K. Balasubramanian, and D.S. Sarma, Effect of Ti additions on the electrical resistivity of copper, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 225(1997), No. 1-2, p. 118.
M. Sobhani, A. Mirhabibi, H. Arabi, and R.M.D. Brydson, Effects of in situ formation of TiB2 particles on age hardening behavior of Cu–1wt% Ti–1wt% TiB2, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 577(2013), p. 16.
S. Nagarjuna, K. Balasubramanian, and D. S Sarma, Effect of prior cold work on mechanical properties, electrical conductivity and microstructure of aged Cu–Ti alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 34(1999), No. 12, p. 2929.
S.S. Naboychenko, I.B. Murashova, and O.D. Neikov, Production of copper and copper alloy powders, [in] O.D. Neikov, S.S. Naboychenko, I.V. Murashova, V.G. Gopienko, I.V. Frishberg, and D.V. Lotsko, Handbook of Non-ferrous Metal Powders: Technologies and Applications, Elsevier Science, Oxford, 2009, p. 331.
H.L. Hao, W. Mo, Y.H. Lv, S.L. Ye, R.N. Gu, and P. Wu, The effect of trace amount of Ti and W on the powder metallurgy process of Cu, J. Alloys Compd., 660(2016), p. 204.
K. Dash, B.C. Ray, and D. Chaira, Synthesis and characterization of copper–alumina metal matrix composite by conventional and spark plasma sintering, J. Alloys Compd., 516(2012), p. 78.
E. Akbarzadeh and S.E. Shakib, Comparison of effective parameters for copper powder production via electrorefining and electrowinning cells and improvement using DOE methods, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 18(2011), No. 6, p. 731.
M. Shabani, M.H. Paydar, and M.M. Moshkar, Fabrication and densification enhancement of SiC-particulate-reinforced copper matrix composites prepared via the sinter−forging process, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 21(2014), No. 9, p. 934.
F. Wang, Y. Li, K. Wakoh, Y. Koizumi, and A. Chiba, Cu–Ti–C alloy with high strength and high electrical conductivity prepared by two-step ball-milling processes, Mater. Des., 61(2014), p. 70.
J. Ružić, J. Stašić, V. Rajković, and D. Božić, Strengthening effect in precipitation and dispersion hardened powder metallurgy copper alloys, Mater. Des., 49(2013), p. 746.
Z. Ni, H. Zhao, P. Mi, and F. Ye, Effect of sintering time on the bending strength and CTE of SiC/Al–35Si composite, Vacuum, 124(2016), p. 28.
F. Akhlaghi and A. Zare-Bidaki, Influence of graphite content on the dry sliding and oil impregnated sliding wear behavior of Al 2024-graphite composites produced by in situ powder metallurgy method, Wear, 266(2009), No. 1-2, p. 37.
R. Yamanoglu, E. Karakulak, M. Zeren, and F.G. Koç, Effect of nickel on microstructure and wear behaviour of pure aluminium against steel and alumina counterfaces, Int. J. Cast Met. Res., 26(2013), No. 5, p. 289.
K. Sang, Y. Weng, Z. Huang, X. Hui, and H. Li, Preparation and interpenetrating alumina–copper composites, Ceram. Int., 42(2016), No. 5, p. 6129.
G.H.A. Bagheri, The effect of reinforcement percentages on properties of copper matrix composites reinforced with TiC particles, J. Alloys Compd., 676(2016), p. 120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karakulak, E. Characterization of Cu–Ti powder metallurgical materials. Int J Miner Metall Mater 24, 83–90 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1381-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1381-x