Abstract
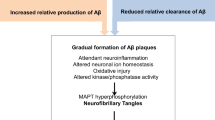
The first disease modifying drugs targeting beta amyloid that were tested in phase II and III clinical trials have been disappointing. We believe that failures descended from a leaky drug development pipeline where insufficient attention has been devoted to valid animal models and valid imaging markers of disease progression. In the future, valid animal models will need to take into greater consideration the natural and molecular history of AD, where both beta amyloid and tau play a key role. Valid imaging markers of disease progression will need to be identified in humans and translated into animal versions. Future testing of putative disease modifying drugs in valid animal models with valid imaging markers of disease progression will allow to maximize the predictability of their effect in phase II and III clinical trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith AD. Imaging the progression of Alzheimer pathology through the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:4135–4137.
Fox NC, Scahill RI, Crum WR, Rossor MN. Correlation between rates of brain atrophy and cognitive decline in AD. Neurology. 1999;52:1687–1689.
Fox NC, Cousens S, Scahill R, Harvey RJ, Rossor MN. Using serial registered brain magnetic resonance imaging to measure disease progression in Alzheimer disease: power calculations and estimates of sample size to detect treatment effects. Arch Neurol. 2000;57:339–344.
Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMEA). Guideline on Medicinal Products for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias. London, 24 July 2008, Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/553/95 Rev. 1
Fox NC, Black RS, Gilman S, Rossor MN, Griffith SG, Jenkins L, Koller M; AN1792(QS-21)-201 Study. Effects of Abeta immunization (AN1792) on MRI measures of cerebral volume in Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2005;64:1563–1572.
Gilman S, Koller M, Black RS, Jenkins L, Griffith SG, Fox NC, Eisner L, Kirby L, Rovira MB, Forette F, Orgogozo JM; AN1792(QS-21)-201 Study Team. Clinical effects of Abeta immunization (AN1792) in patients with AD in an interrupted trial. Neurology. 2005;64:1553–1562.
Jack CR Jr, Petersen RC, Xu Y, O’Brien PC, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ, Boeve BF, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E. Rates of hippocampal atrophy correlate with change in clinical status in aging and AD. Neurology. 2000;55:484–489.
Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82:239–259.
Delacourte A, David JP, Sergeant N, Buee L, Wattez A, Vermersch P, Ghozali F, Fallet-Bianco C, Pasquier F, Lebert F, Petit H, Di Menza C. The biochemical pathway of neurofibrillary degeneration in aging and Alzheimer1s disease. Neurology. 1999;52:1158–1165.
Ridha BH, Barnes J, Bartlett JW, Godbolt A, Pepple T, Rossor MN, Fox NC. Tracking atrophy progression in familial Alzheimer’s disease: a serial MRI study. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:828–834.
Bouwman FH, van der Flier WM, Schoonenboom NS, van Elk EJ, Kok A, Rijmen F, Blankenstein MA, Scheltens P. Longitudinal changes of CSF biomarkers in memory clinic patients. Neurology. 2007;69:1006–1011.
Borg J, Chereul E. Differential MRI patterns of brain atrophy in double or single transgenic mice for APP and/or SOD. J Neurosci Res. 2008 Jul 21 [Epub ahead of print].
Lau JC, Lerch JP, Sled JG, Henkelman RM, Evans AC, Bedell BJ. Longitudinal neuroanatomical changes determined by deformation-based morphometry in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage. 2008 Aug 1;42(1):19–27.
Kawarabayashi T, Younkin LH, Saido TC, Shoji M, Ashe KH, Younkin SG. Age-dependent changes in brain, CSF, and plasma amyloid (beta) protein in the Tg2576 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci. 2001;21:372–381.
Stoub TR, Rogalski EJ, Leurgans S, Bennett DA, Detoledo-Morrell L. Rate of entorhinal and hippocampal atrophy in incipient and mild AD: Relation to memory function. Neurobiol Aging. 2008 Sep 20. [Epub ahead of print]
Casas C, Sergeant N, Itier J M, Blanchard V, Wirths O, van der Kolk N, Vingtdeux V, van de Steeg E, Ret G, Canton T, Drobecq H, Clark A, Bonici B, Delacourte A, Benavides J, Schmitz C, Tremp G, Bayer TA, Benoit P, Pradier L. Massive CA1/2 neuronal loss with intraneuronal and N-terminal truncated Abeta42 accumulation in a novel Alzheimer transgenic model. Am J Pathol. 2004;165:1289–1300.
Delacourte A, Sergeant N, Champain D, Wattez A, Maurage CA, Lebert F, Pasquier F, David JP. Nonoverlapping but synergetic tau and APP pathologies in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 2002;59:398–407.
Takahashi RH, Capetillo-Zarate E, Lin MT, Milner TA, Gouras GK. Co-occurrence of Alzheimer’s disease -amyloid and tau pathologies at synapses. Neurobiol Aging. 2008 Sep 2. [Epub ahead of print]
DeMattos RB, Bales KR, Cummins DJ, Dodart JC, Paul SM, Holtzman DM. Peripheral anti-A beta antibody alters CNS and plasma A beta clearance and decreases brain A beta burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:8850–8855.
May et al., Multi-compartmental pharmaco-dynamic assessment of the functional gamma-secretase inhibitor LY450139 dihydrate in PDAPP transgenic mice and nontransgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 2004;25suppl 25:65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frisoni, G.B., Delacourte, A. Neuroimaging outcomes in clinical trials in Alzheimer’s disease. J Nutr Health Aging 13, 209–212 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-009-0060-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-009-0060-7