Abstract
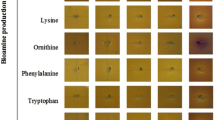
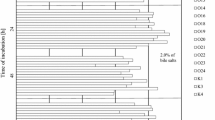
Colonization of Lactobacillus plantarum 423 and Enterococcus mundtii ST4SA in the gastro-intestinal tract was determined by using Wistar rats as model. The strains were administered through intragastric gavage over 14 days. FISH with strain-specific oligonucleotide probes indicated that Lact. plantarum 423 adhered to the surfaces of the ileum and the cecum. Enterococcus mundtii ST4SA, on the other hand, adhered to the surfaces of the cecum and colon. Results obtained by DGGE have shown that strains 423 and ST4SA excluded Enterobacteriaceae, but not lactic acid bacteria, from the cecum and colon. No signs of perforation of epithelial cells by strains 423 and ST4SA were detected. The spleen and liver appeared healthy and blood counts were normal, suggesting that the strains are not pathogenic. Both strains produce antimicrobial peptides active against a number of pathogens and may be considered as probiotics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adawi D, Molin G, Ahrne S, Jeppsson B (1999) Modulation of the colonic bacterial flora affects differently bacterial translocation and liver injury in an acute liver injury model. Microbial Ecol Health Dis 11:47–54
Adlerberth I, Hanson LA, Svanborg C (1995) Adhesins of Escherichia coli associated with extra-intestinal pathogenicity confer binding to colonic epithelial cells. Microb Pathog 18:373–385
Alcid DV, Troke M, Andszewski S, John JF (1994) Probiotics as a source of Enterococcus feacium. Abstracts of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, Abstract no. 123
Botes M (2008) Survival of probiotic lactic acid bacteria in the intestinal tract, their adhesion to epithelial cells and their ability to compete with pathogenic microorganisms. PhD dissertation, University of Stellenbosch, Stellenbosch, South Africa
De Vuyst L, Vandamme EJ (1994) Nisin, a lantibiotic produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis: properties, biosynthesis, fermentation and application. In: de Vuyst L, Vandamme EJ (eds) Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 151–221
Franks AH, Harmsen HJM, Raangs GC, Jansen GJ, Schut F, Welling GW (1998) Variations of bacterial populations in human feces measured by fluorescent in situ hybridisation with group-specific 16S rRNA-targeted oilgonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3336–3345
Franz CMAP, Holzapfel WH, Stiles ME (1999) Enterococci at the crossroads of food safety? Int J Food Microbiol 47:1–24
Franz CMAP, Stiles ME, Schleifer KH, Holzapfel WH (2003) Enterococci in foods—a conundrum for food safety. Int J Food Microbiol 88:105–122
Granato D, Bergonzelli GE, Pridmore RD, Marvin L, Rouvet M, Corthesy-Theulaz IE (2004) Cell surface-associated elongation factor Tu mediates the attachment of Lactobacillus johnsonii NCC533(La1) to human intestinal cells and mucins. Infect Immun 72:2160–2169
Granger M, Van Reenen CA, Dicks LMT (2008) Effect of gastro-intestinal conditions on Enterococcus mundtii ST4SA and production of bacteriocin ST4SA, as recorded by real-time PCR. Int J Food Microbiol 123:277–280
Herias MV, Midtvedt T, Hanson LA (1995) Role of Escherichia coli P fimbriae in intestinal colonisation in gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun 63:4781–4789
Kandler O, Weiss N (1986) Genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, 212 AL. In: Sneath PHA, Mair NS, Sharpe ME, Holt JG (eds) Bergeys manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2. The Williams & Wilkens Co., Baltimore, pp 1209–1234
Kirjavainen PV, Ouwehand AC, Isolauri E, Salminen SJ (1998) The ability of probiotic bacteria to bind to human intestinal mucus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 167:185–189
Knoetze H (2007) Characterization of a broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptide from Enterococcus mundtii active against bacteria associated with middle-ear infections. MSc thesis, University of Stellenbosch, Stellenbosch, South Africa
Kops SK, Lowe DK, Bement WM, West AB (1996) Migration of Salmonella typhi through intestinal epithelial monolayers: an in vitro study. Microbiol Immunol 40:799–811
Lara-Villoslada F, Sierra S, Martin R, Delgad S, Rodríguez JM, Olivares M, Xaus J (2007) Safety assessment of two probiotic strains, Lactobacillus coryniformis CECT5711 and Lactobacillus gasseri CECT5714. J Appl Microbiol 103:175–184
Lick S, Drescher K, Heller KJ (2001) Survival of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus in the terminal ileum of fistulated Gottingen minipigs. Appl Environ Microbiol 9:4137–4143
Mack DR, Ahrne S, Hyde L, Wei S, Hollingsworth MA (2003) Extracellular MUC3 mucin secretion follows adherence of Lactobacillus strains to intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Gut 52:827–833
Mangell P, Nejdfors P, Wang M, Ahrne S, Westrom B, Thorlacius H, Jeppsson B (2002) Lactobacillus plantarum 299V inhibits Escherichia coli-induced intestinal permeability. Dig Dis Sci 47:511–516
Mao Y, Nobaek S, Kasravi B, Adawi D, Stenram U, Molin G, Jeppsson B (1996) The effects of Lactobacillus strains and oat fiber on methotrexate-induced enterocolitis in rats. Gastroenterology 111:334–344
Mare L, Wolfaardt GM, Dicks LMT (2006) Adhesion of Lactobacillus plantarum 423 and Lactobacillus salivarius 241 to the intestinal tract of piglets, as recorded with fluorescent in situ hybridisation (FISH) and production of plantaricin 423 by cells colonised to the ileum. J Appl Microbiol 100:838–845
McConnell EL, Basit AW, Murdan S (2008) Measurements of rat and mouse gastrointestinal pH, fluid and lymphoid tissue, and implications for in vivo experiments. J Pharm Pharmacol 60:63–70
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Ouwehand AC, Kirjavainen PV, Gronlund MM, Isolauri E, Salminen SJ (1999) Adhesion of probiotic microorganisms to intestinal mucus. Int Dairy J 9:623–630
Pavan S, Desreumaux P, Mercenier A (2003) Use of mouse models to evaluate the persistence, safety and immune modulation capacities of lactic acid bacteria. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 10:696–701
Pretzer G, Snel J, Molenaar D, Wiersma A, Bron PA, Lambert WM, De Vos W, Van der Meer R, Smits MA, Kleerebezem M (2005) Biodiversity-based identification and functional characterisation of the mannose specific adhesin of L. plantarum. J Bacteriol 187:6128–6136
Ramiah K, Van Reenen CA, Dicks LMT (2007) Expression of the mucus adhesion genes mub and mapA, adhesion-like factor EF-Tu and bacteriocin gene plaA of Lactobacillus plantarum 423 monitored with real-time PCR. Int J Food Microbiol 116:405–409
Ramiah K (2008) Characterization of the adhesion genes of probiotic lactic acid bacteria. PhD dissertation, University of Stellenbosch, Stellenbosch 7600, South Africa
Saarela M, Mogensen G, Fondén R, Mättö J, Mattila-Sandholm T (2000) Probiotic bacteria: safety, functional and technological properties. J Biotechnol 84:197–215
Sambrook JE, Fritsch F, Maniatis J (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Spitz J, Yuhan R, Koutsouris A, Blatt C, Alverdy J, Hecht G (1995) Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli adherence to intestinal epithelial monolayers diminishes barrier function. Am J Physiol 268:G374–G379
Van Reenen CA, Dicks LMT, Chikindas ML (1998) Isolation, purification and partial characterization of plantaricin 423, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum. J Appl Microbiol 84:1131–1137
Wadstrom T (1998) Adherence traits and mechanisms of microbial adhesion in the gut. Baillier’s Clin Trop Med Commun Dis 3:417–433
Wells CL, Maddaus MA, Simmons RL (1988) Proposed mechanisms for the translocation of intestinal bacteria. Rev Infect Dis 10:958–978
Wells CL, Jechorek RP, Twiggs LB, Brooker DC (1990) Recovery of viable bacteria from pelvic lymph nodes of patients with gynecologic tumors. J Infect Dis 162:1216–1218
Wells CL, Erlandsen SL (1991) Localisation of translocating Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis and Enterococcus faecalis within cecal and colonic tissues of monoassociated mice. Infect Immun 59:4693–4697
Zhou JS, Shu Q, Rutherfurd KJ, Prasad J, Gopal PK, Gill HS (2000) Acute oral toxicity and bacterial translocation studies on potentially probiotic strains of lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem Toxicol 38:153–161
Acknowledgments
We thank Cipla Medpro (Pty) Ltd and the National Research Foundation, South Africa, for funding the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramiah, K., ten Doeschate, K., Smith, R. et al. Safety Assessment of Lactobacillus plantarum 423 and Enterococcus mundtii ST4SA Determined in Trials with Wistar Rats. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 1, 15–23 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-009-9010-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-009-9010-2