Abstract
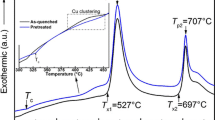
A systematic microstructure-oriented magnetic property investigation for Al/CoCrFeNi nanocrystalline high-entropy alloys composite (nc-HEAC) is presented. In the initial state, the Al/CoCrFeNi nc-HEAC is composed of face-centered cubic (FCC)-Al, FCC-CoCrFeNi and hexagonal close-packed (HCP)-CoNi phases. High energy synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy were used to reveal the relationship between microstructure evolution and magnetic mechanism of Al/CoCrFeNi nc-HEAC during heat treatment. At low-temperature annealing stage, the magnetic properties are mainly contributed by the HCP-CoNi phase. With the increase of temperature, the diffusion-induced phase transition process including the transformation of AlCoCrFeNi HEA from FCC to BCC structure and the growth of B2 phase plays a dominant role in the magnetic properties. It was found that the magnetic properties can be effectively regulated through the control of the thermal diffusion process. The nano dual-phase thermal diffusion-induced phase transition behavior of nanocomposites prepared based on laser-IGC technology provides guidance for the diffusion process and microstructure evolution of two phases in composites.
Graphical abstract

摘要
本文系统研究了Al/CoCrFeNi纳米晶高熵合金复合材料 (nc-HEAC) 微观结构演变对磁性能的影响机制。在初始状态下, Al/CoCrFeNi nc-HEAC由面心立方结构的FCC-Al、FCC-CoCrFeNi和六方密排结构的HCP-CoNi相组成。利用高能同步辐射X射线衍射 (XRD) 和高分辨透射电子显微镜 (HRTEM) 研究了Al/CoCrFeNi nc-HEAC在热处理过程中的微观结构演变与磁性机理的关系。在低温退火阶段, 磁性主要由HCP-CoNi相贡献。随着温度的升高, 扩散诱导相变过程 (包括AlCoCrFeNi HEA从FCC转变为BCC结构和B2相的增多) 对磁性起主导作用。研究发现, 通过控制热扩散过程可以有效地调节磁性能。基于laser-IGC技术制备的纳米复合材料的纳米双相热扩散诱导相变行为为复合材料中两相的扩散过程和微观结构演化提供了指导。





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niu SZ, Kou HC, Wang J, Li JS. Improved tensile properties of Al0.5CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy by tailoring microstructures. Rare Metal. 2021;40(9):2508.
Rao JC, Diao HY, Ocelík V, Vainchtein D, Zhang C, Kuo C, Tang Z, Guo W, Poplawsky D, Zhou Y, Liaw PK, Hosson JTMD. Secondary phases in AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys: an in-situ TEM heating study and thermodynamic appraisal. Acta Mater. 2017;131(3):206.
Yang HX, Li JS, Guo T, Wang WY, Kou HC, Wang J. Evolution of microstructure and hardness in a dual-phase Al0.5CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy with different grain sizes. Rare Metal. 2020;39(2):156.
Wang WR, Wang WL, Yeh JW. Phases, microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. J Alloy Compd. 2014;589(7):143.
Yang T, Xia S, Liu S, Wang C, Liu S, Zhang Y, Xue JM, Yan S, Wang YG. Effects of Al addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxCoCrFeNi High-entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2015;648(9):15.
Zhang Y, Zhang M, Li D, Zuo T, Zhou K, Gao M, Sun B, Shen TD. Compositional design of soft magnetic high entropy alloys by minimizing magnetostriction coefficient in (Fe0.3Co0.5Ni0.2)100–x(Al1/3Si2/3)x system. Metals. 2019;9(3):382.
Hariharan VS, Karati A, Parida T, John R, Babu DA, Murty BS. Effect of Al addition and homogenization treatment on the magnetic properties of CoFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. J Mater Sci. 2020;55(36):17204.
Zhao C, Li J, He Y, Wang J, Wang WY, Kou HC, Wang J. Effect of strong magnetic field on the microstructure and mechanical-magnetic properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. J Alloy Compd. 2020;820:153407.
Guo YX, Liu QB, Shang XJ. In situ TiN-reinforced CoCr2FeNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloy composite coating fabricated by laser cladding. Rare Metal. 2019;39(9):1190.
Lu T, Scudino S, Chen W, Wang P, Li D, Mao M, Kang LM, Liu YX, Fu ZQ. The influence of nanocrystalline CoNiFeAl0.4Ti0.6Cr0.5 high-entropy alloy particles addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCp/7075Al composites. Mater Sci Eng A. 2018;726(4):126.
Karthik GM, Panikar S, Ram GDJ, Kottada RS. Additive manufacturing of an aluminum matrix composite reinforced with nanocrystalline high-entropy alloy particles. Mater Sci Eng A. 2017;679(10):193.
Yang X, Dong P, Yan ZF, Cheng BY, Zhai X, Chen HS, Zhang HX, Wang WX. AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy particle reinforced 5083Al matrix composites with fine grain structure fabricated by submerged friction stir processing. J Alloy Compd. 2020;836:155411.
Liu Y, Chen J, Li Z, Wang X, Fan X, Liu J. Formation of transition layer and its effect on mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy/Al composites. J Alloy Compd. 2019;780(11):558.
Yuan Z, Tian W, Li F, Fu Q, Hu Y, Wang X. Microstructure and properties of high-entropy alloy reinforced aluminum matrix composites by spark plasma sintering. J Alloy Compd. 2019;806(7):901.
Huhn WP, Widom M. Prediction of A2 to B2 phase transition in the high-entropy alloy Mo-Nb-Ta-W. Jom. 2013;65(5):1772.
Liu H, Liu J, Chen P, Yang H. Microstructure and high temperature wear behaviour of in-situ TiC reinforced AlCoCrFeNi-based high-entropy alloy composite coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Optics Laser Technol. 2019;118(5):140.
Wang JJ, Wu SS, Fu S, Liu SN, Yan MY, Lai QQ, Lan S, Hahn H, Feng T. Ultrahigh hardness with exceptional thermal stability of a nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy prepared by inert gas condensation. Scripta Mater. 2020;187(6):335.
Na SM, Yoo JH, Lambert PK, Jones NJ. Room-temperature ferromagnetic transitions and the temperature dependence of magnetic behaviors in FeCoNiCr-based high-entropy alloys. AIP Advances. 2018;8(5):056412.
Lucas MS, Mauger L, Muñoz JA, Xiao Y, Sheets AO, Semiatin SL, Horwath J, Turgut Z. Magnetic and vibrational properties of high-entropy alloys. J Appl Phys. 2011;109(7):07E307.
Huang S, Li W, Li X, Schönecker S, Bergqvist L, Holmström E, Varga LK, Vitos L. Mechanism of magnetic transition in FeCrCoNi-based high entropy alloys. Mater Des. 2016;103(4):71.
Hung PT, Kawasaki M, Han JK, Lábár JL, Gubicza J. Microstructure evolution in a nanocrystalline CoCrFeNi multi-principal element alloy during annealing. Mater Chara. 2021;171:110807.
Wu Z, Bei H, Pharr GM, George EP. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater. 2014;81(8):428.
Lu P, Zhang TW, Zhao D, Ma SG, Li Q, Wang ZH. Mechanical behaviors and texture evolution of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy under shear-tension deformation. J Alloy Compd. 2020;815:152479.
Wang B, He H, Naeem M, Lan S, Harjo S, Kawasaki T, Nie YX, Kui HW, Ungár T, Ma D, Stoica AD, Li Q, Ke YB, Liu CT, Wang XL. Deformation of CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy at large strain. Scripta Mater. 2018;155(6):54.
Liu J, Guo X, Lin Q, He Z, An X, Li L, Liaw PK, Liao XZ, Yu LP, Lin JP, Xie L, Ren JL, Zhang Y. Excellent ductility and serration feature of metastable CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy at extremely low temperatures. Sci China Mater. 2018;62(6):853.
Kao YF, Chen TJ, Chen SK, Yeh JW. Microstructure and mechanical property of as-cast, -homogenized, and -deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0≤x≤2) high-entropy alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2009;488(1):57.
Butler T, Weaver M. Influence of annealing on the microstructures and oxidation behaviors of Al8(CoCrFeNi)92, Al15(CoCrFeNi)85, and Al30(CoCrFeNi)70 high-entropy alloys. Metals. 2016;6(9):222.
Butler TM, Weaver ML. Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNi multi-component high-entropy alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2016;674(2):229.
Jiang S, Wang H, Wu Y, Liu X, Chen H, Yao M, Gault B, Ponge D, Raabe D, Hirata A, Chen MW, Wang YD, Lu ZP. Ultrastrong steel via minimal lattice misfit and high-density nanoprecipitation. Nature. 2017;544(7651):460.
Fan L, Yang T, Zhao Y, Luan J, Zhou G, Wang H, Jiao ZB, Liu CT. Ultrahigh strength and ductility in newly developed materials with coherent nanolamellar architectures. Nat Commun. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20109-z.
Wang J, Wu S, Fu S, Liu S, Ren Z, Yan M, Chen SQ, Lan S, Hahn H, Feng T. Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy with tunable ferromagnetic properties. J Mater Sci Technol. 2021;77(10):126.
Schuh B, Mendez-Martin F, Völker B, George EP, Clemens H, Pippan R, Hohenwarter A. Mechanical properties, microstructure and thermal stability of a nanocrystalline CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy after severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 2015;96(6):258.
Klimova MV, Shaysultanov DG, Zherebtsov SV, Stepanov ND. Effect of second phase particles on mechanical properties and grain growth in a CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2019;748(1):228.
Kelly R, Miotello A, Braren B, Gupta A, Casey K. Primary and secondary mechanisms in laser-pulse sputtering. Nucl Instrum Meth B. 1992;65:187.
Geohegan DB, Puretzky AA. Dynamics of laser ablation plume penetration through low pressure background gases. Appl Phys Lett. 1995;67(2):197.
Wood JNLRF, Chen KR, Geohegan DB, Puretzky AA. Dynamics of plume propagation, splitting, and nanoparticle formation during pulsed-laser ablation. Appl Surf Sci. 1998;127–129:151.
Garrelie F, Champeaux C, Catherinot A. Study by a Monte Carlo simulation of the influence of a background gas on the expansion dynamics of a laser-induced plasma plume. Appl Phys A. 1999;69:45.
Lu W, Sun D, Yu H. Synthesis and magnetic properties of size-controlled CoNi alloy nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd. 2013;546(8):229.
Aubry E, Liu T, Billard A, Dekens A, Perry F, Mangin S, Hauet T. Influence of the Cr and Ni concentration in CoCr and CoNi alloys on the structural and magnetic properties. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;422(9):391.
Mohanta M, Parida SK, Sahoo A, Hussain Z, Gupta M, Reddy VR, Medicherla VRR. Structural and magnetic properties of CoNi surface alloys. Physica B. 2019;572(7):105.
Zhao C, Li J, Liu Y, Wang WY, Kou H, Beaugnon E, Wang J. Tailoring mechanical and magnetic properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy via phase transformation. J Mater Sci Technol. 2021;73(8):83.
Kao YF, Chen SK, Chen TJ, Chu PC, Yeh JW, Lin SJ. Electrical, magnetic, and Hall properties of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2011;509(5):1607.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2021YFB3802800), the Equipment Advance Research field Fund (No. 80922010401), equipment project of China (JZX7Y20210162400201), Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Joint Laboratory for Neutron Scattering Science and Technology, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. 30919011404 and 30919011107), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51871120 and 51571119) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20200019). Tao Feng acknowledges the support from Qing Lan project and the distinguished professor project of Jiangsu province. We acknowledge the support of the Karlsruhe Nano Micro Facility for the microstructure characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JJ., Kou, ZD., Fu, S. et al. Microstructure and magnetic properties evolution of Al/CoCrFeNi nanocrystalline high-entropy alloy composite. Rare Met. 41, 2038–2046 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01931-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01931-w