Abstract
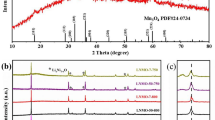
Spherical cathode material LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for lithium-ion batteries was synthesized by hydroxide co-precipitation method. X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electrochemical measurements were carried out to characterize prepared LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material. SEM images show that the LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material is constituted by micro-sized spherical particles (with a diameter of around 8 μm). XRD patterns reveal that the structure of prepared LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material belongs to Fd3m space group. Electrochemical tests at 25 °C show that the LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material prepared after annealing at 600 °C has the best electrochemical performances. The initial discharge capacity of prepared cathode material delivers 113.5 mAh·g−1 at 1C rate in the range of 3.50–4.95 V, and the sample retains 96.2% (1.0C) of the initial capacity after 50 cycles. Under different rates with a cutoff voltage range of 3.50–4.95 V at 25 °C, the discharge capacities of obtained cathode material can be kept at about 145.0 (0.1C), 126.8 (0.5C), 113.5 (1.0C) and 112.4 mAh·g−1 (2.0C), the corresponding initial coulomb efficiencies retain above 95.2% (0.1C), 95.0% (0.5C), 92.5% (1.0C) and 94.8% (2.0C), respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang J, Yao XY, Zhou XF, Liu ZP. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of layered lithium transition metal oxides. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(8):2544.
Yang SY, Wang XY, Yang XK, Bai YS, Liu ZL, Shu HB, Wei QL. Determination of the chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium ions in spherical Li[Ni0.5Mn0.3Co0.2]O2. Electrochim Acta. 2012;66(4):88.
Gu YJ, Li Y, Fu Y, Zang QF, Liu HQ, Ding JX, Wang YM, Wang HF, Ni JF. LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 synthesized through ammonia-mediated carbonate precipitation. Electrochim Acta. 2015;176(125):1029.
Mo MY, Hu KS, Hong XT, Guo JS, Ye CC, Li AJ. Improved cycling and rate performance of Sm-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for 5 V lithium ion batteries. Appl Surf Sci. 2014;290(3):412.
Hu M, Pang XL, Zhou Z. Recent progress in high-voltage lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2013;237(3):229.
Yun FL, Tang L, Li WC, Jin WR, Pang J, Lu SG. Thermal behavior analysis of a pouch type Li[Ni0.7Co0.15Mn0.15]O2-based lithium-ion battery. Rare Met. 2016;35(4):309.
Ren L, Li XE, Wang FF, Han Y. Spindle LiFePO4 particles as cathode of lithium-ion batteries synthesized by solvothermal method with glucose as auxiliary reductant. Rare Met. 2015;34(10):731.
Liu DL, Du LC, Liu YF, Chen YB. Effects of Mn-precursor on performances of LiMn2O4 cathode material for lithium ion battery. Rare Met Mater Eng. 2014;43(11):2584.
Hu M, Tian Y, Su LW, Wei JP, Zhou Z. Preparation and Ni-doping effect of nanosized truncated octahedral LiCoMnO4 as cathode materials for 5 V Li-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(22):12185.
Rodriguez-Caravjal J, Rousse G, Masquelier C, Hervieeu M. Electronic crystallization in a lithium battery material: columnar ordering of electrons and holes in the spinel LiMn2O4. Phys Rev Lett. 1998;81(21–23):4660.
Huang HT, Vincent CA, Bruce PG. Capacity loss of lithium manganese oxide spinel in LiPF6/ethylene carbonate-dimethyl carbonate electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc. 1999;146(2):481.
Zhang MH, Liu YZ, Xia YG, Qi B, Wang J, Liu ZP. Simplified co-precipitation synthesis of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with improved physical and electrochemical performance. J Alloys Compd. 2014;598(12):73.
Fang X, Lu Y, Ding N, Feng XY, Liu C, Chen CH. Electrochemical properties of nano- and micro-sized LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 synthesized via thermal decomposition of a ternary eutectic Li–Ni–Mn acetate. Electrochim Acta. 2010;55(3):832.
Wang HL, Xia H, Lai MO, Lu L. Enhancements of rate capability and cyclic performance of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by trace Ru-dopping. Electrochem Commun. 2009;11(7):1539.
Wu P, Zheng XL, Zhou C, Gu GF, Tong DG. Improved electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5−x Rh x Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for 5 V lithium ion batteries via Rh-doping. Mater Chem Phys. 2013;138(2–3):716.
Yang Z, Jiang Y, Kim JH, Wu Y, Li GL, Huang YH. The LiZnxNi0.5−xMn1.5O4 spinel with improved high voltage stability for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2014;117(4):76.
Hu M, Tian Y, Wei JP, Wang DG, Zhou Z. Porous hollow LiCoMnO4 microspheres as cathode materials for 5 V lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2014;247(2):794.
Mo MY, Guo JS, Ye CC, Chen HY. Preparation of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for high cathode materials by a gelatin-assisted solid state method. J South China Univ Technol Nat Sci Ed. 2015;47(4):69.
Gao ZG, Sun K, Cong LN, Zhao Q, Wang RS, Xie HM, Sun LQ, Su ZM. High performance 5 V LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel cathode materials synthesized by an improved solid-state method. J Alloys Compd. 2016;654(37):257.
Liu YZ, Zhang MH, Xia YG, Qiu B, Liu ZP, Li X. One-step hydrothermal method synthesis of core-shell LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel cathodes for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2014;256(12):66.
Wu HM, Belharouak I, Abouinrane A, Sun YK, Amine K. Surface modification of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by ZrP2O7 and ZrO for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2010;195(9):2909.
Yang TY, Sun KN, Lei ZY, Zhang NQ, Lang Y. The influence of Li sources on physical and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem. 2011;15(2):391.
Zhang MH, Wang J, Xia YG, Liu ZP. Microwave synthesis of spherical spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd. 2012;518(2):68.
Zhao QL, Ye NQ, Li L, Yan F. Oxalate coprecipitation process synthesis of 5 V cathode material LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 and its performance. Rare Met Mater Eng. 2010;39(10):1715.
Huang Y, Wang ZX, Li XH, Guo HJ, Wang JX. Synthesis of Ni0.8Co0.1Mn0.1(OH)2 precursor and electrochemical performance of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cathode material for lithium batteries. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2015;25(7):2253.
Sun Q, Li XH, Wang ZX, Ji Y. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of 5 V spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 prepared by solid-state reaction. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2009;19(1):176.
Zhong SK, Li W, Li YH, Zou ZG, Tang X. Synthesis and electrochemical performances of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cathode materials. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2009;19(6):1499.
Yao YL, Liu HC, Li GC, Peng HR, Chen KZ. Multi-shelled porous LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 microspheres as a 5 V cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Mater Chem Phys. 2014;143(2):867.
Zhan GC, Tang XC, Wang ZM. Preparation of LiCo1/3Ni1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode material by improved co-precipitation method. J Cent South Univ. 2012;43(10):3780.
Yang Y, Xu SM, Weng YQ, Huang GY, Li LY. Preparation and characterization of xLi2MnO3·(1−x) Li(Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3)O2(x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) cathode materials synthesized by hydroxide co-precipitation method. J Funct Mater. 2013;44(19):2878.
Jeon HJ, Monim SA, Kang CS, Son JT. Synthesis of Lix[Ni0.225Co0.125Mn0.65]O2 as a positive electrode for lithium-ion batteries by optimizing its synthesis conditions via a hydroxide co-precipitation method. J Phys Chem Solids. 2013;74(9):1185.
Liang LW, Du K, Peng ZD, Cao YB, Duan JG, Jiang JB, Hu GR. Co-precipitation synthesis of Ni0.6Co0.2Mn0.2(OH)2 precursor and characterization of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cathode material for secondary lithium batteries. Electrochim Acta. 2014;130(1):82.
Kong X, Sun HY, Wang QB, Yi ZZ, Wang BS, Liu GY. Improvement in the electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 lithium-ion battery cathodes prepared by a modified low temperature solution combustion synthesis. Ceram Int. 2014;40(8):11611.
Zhong QM, Bonadarpour A, Zhang M, Gao Y, Dahn JR. Synthesis and electrochemistry of LiNi x Mn2−x O4. J Electrochem Soc. 1997;144(1):205.
Myung ST, Komaba S, Kumgai N, Yashiro H, Chung HT, Cho TH. Nano-crystalline LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 synthesized by emulsion drying method. Electrochim Acta. 2002;47(15):2543.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the funding from the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technologies for Comprehensive Utilization of Platinum Metals (No. SKL-SPM-201211) and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT13026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Yang, Y., Xie, M. et al. Synthesis and electrochemical performances of high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials prepared by hydroxide co-precipitation method. Rare Met. 36, 277–283 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0859-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0859-4