Abstract
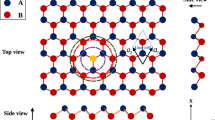
The effect of Cd impurity on the electronic structure and magnetic properties of hydrogen-terminated AlN nanoribbons with zigzag edges (ZAlNNRs) was investigate using the band structure results obtained through the full potential linearized augmented plane wave (FP-LAPW) method within the density functional theory (DFT). The exchange correlation potential was treated by the generalized gradient approximation within the Perdew scheme. The calculated results show that the H-terminated zigzag AlN nanoribbon is semiconducting and nonmagnetic material with a direct band gap of about 2.78 eV, while the Cd-doped H-terminated ZAlNNR structures show complete (100 %) spin polarization very close to the Fermi level, which will result in spin-anisotropic transport. The charge transport is totally dominated by Cd spin down electrons in the H-terminated ZAlNNR. These results suggest potential applications for the development of using the AlN nanoribbons in nanoelectronics and magnetoelectronic devices as a base.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science. 2004;306(5696):666.
Geim AK, Novoselov KS. The rise of graphene. Nat Mater. 2007;6(3):183.
Novoselov KS, Jiang Z, Zhang Y, Morozov SV, Stormer HL, Zeitler U, Maan JC, Boebinger GS, Kim P, Geim AK. Room-temperature quantum hall effect in graphene. Science. 2007;315(5817):1379.
Morozov SV, Novoselov KS, Katsnelson MI, Schedin F, Elias DC, Jaszczak JA, Geim AK. Giant intrinsic carrier mobilities in graphene and its bilayer. Phys Rev Lett. 2008;100(1):016602.
CastroNeto AH, Guinea F, Peres NMR, Novoselov KS, Geim AK. The electronic properties of graphene. Rev Mod Phys. 2009;81(1):109.
Zhou J, Wang Q, Sun Q, Jena P. Stability and electronic structure of bilayer graphone. Appl Phys Lett. 2011;98(6):063108.
Son YW, Cohen ML, Louie SG. Half-metallic graphene nanoribbons. Nature. 2006;444(7117):347.
Slotman GJ, Fasolino A. Structure, stability and defects of single layer h-BN in comparison to graphene. J Phys Cond Matter. 2011;25(4):045009.
Ataca C, Şahin H, Aktürk E, Ciraci S. Mechanical and electronic properties of MoS2 nanoribbons and their defects. J Phys Chem C. 2011;115(10):3934.
Li YR, Liu XZ, Zhu J, Zhang JH, Qian LX, Zhang WL. Dielectric thin films for GaN-based high-electron-mobility transistors. Rare Met. 2015;. doi:10.1007/s12598-015-0451-3.
Zhang YP, Liu W, Liu BD, Wang RM. Morphology–structure diversity of ZnS nanostructures and their optical properties. Rare Met. 2014;33(1):1.
Ruterana P, Albrecht M, Neugebauer J. Nitride Semiconductors: Handbook on Materials and Devices. New York: Wiley; 2006. 22.
Strite S, Morkoc H. GaN, AlN, InN: a review. J Vac Sci Tech B Microelectron Nanomater Struct. 1992;10(4):1237.
Wang AJ, Shang SL, Du Y, Kong Y, Zhang LJ, Chen L, Zhao DD, Liu ZK. Sturctural and elastic properties of cubic and hexagonal TiN and AlN from first-principles calculations. Comput Mater Sci. 2010;48(3):705.
Luan HX, Zhang CW, Yan SS. Novel electronic and magnetic properties in AlN nanoribbons: first-principles prediction. Eur Phys Lett. 2013;103(3):37009.
Zhang D, Zhang RQ. Theoretical prediction on aluminum nitride nanotubes. Chem Phys Lett. 2003;371(3–4):426.
Du AJ, Zhu ZH, Chen Y, Lu GQ, Smith Sean C. First principle studies of zigzag AlN nanoribbon. Chem Phys Lett. 2009;469(1–3):183.
Blaha P, Schwarz K, Madsen GKH, Kvasnicka D, Luitz J. WIEN2K, an augmented plane wave + local orbitals program for calculating crystal properties. Austria, Vienna: Vienna University of Technology; 2001. 1.
Perdew P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett. 1997;78(4):1396.
Blöchl PE, Jepsen O, Andersen OK. Improved tetrahedron method for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys Rev B. 1994;49(23):16223.
Maruska HP, Tietjen JJ. The preparation and properties of vapor-deposited single-crystal-line GaN. Appl Phys Lett. 1969;15(10):327.
Zheng FL, Zhang JM, Zhang Y, Ji V. First-principles study of the perfect and vacancy defect AlN nanoribbon. Phys B Cond Matter. 2010;405(17):3775.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Research of the Ayatollah Alozma Boroujerdi University (No. 92-1012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beiranvand, R. Electronic and magnetic properties of Cd-doped zigzag AlN nanoribbons from first principles. Rare Met. 35, 771–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0471-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-015-0471-z