Abstract
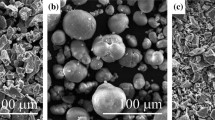
In this study, porous titanium-10 wt% bioglass (BG) composites were fabricated by the process of combining mechanical alloying with space holder sintering. The pore morphology and phase constituents of the milled powders and porous compacts were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffractometry (XRD), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The mechanical properties were determined by running compression test. The porosity of the sintered samples shows a downward trend with the increase of milling time. As the porosity increases, both the compressive strength and elastic modulus decrease. The results illustrate that the fabricated porous compacts with high porosity and suitable mechanical properties have the potential application in bone tissue engineering.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niinomi M, Nakai M, Hieda J. Development of new metallic alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(11):3888.
Liu R, Hui SX, Ye WJ, Li CL, Fu YY, Yu Y. Dynamic stress-strain properties of Ti–Al–V titanium alloys with various element contents. Rare Met. 2013;32(6):555.
Ma W, Chen B, Liu FS, Xu Q. Phase transformation behaviors and mechanical properties of Ti50Ni49Fe1 alloy with severe plastic deformation. Rare Met. 2013;32(5):448.
Dong BH, Wu F, Alajmi Z, Zhang C, Fu T, Ge Y. Sol-gel derived Ta-containing TiO2 films on surface roughened NiTi alloy. Rare Met. 2014;33(1):21.
Geetha M, Singh AK, Asokamani R, Gogia AK. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants: a review. Prog Mater Sci. 2009;54(3):397.
Wang YQ, Tao J, Zhang JL, Wang T. Effects of addition of NH4HCO3 on pore characteristics and compressive properties of porous Ti-10 % Mg composites. Trans Nonferr Met Soc China. 2011;21(5):1074.
Jurczyk M, Jurczyk K, Niespodziana K, Miklaszewski A. Hybrid Ti-ceramic bionanomaterials for dental engineering. Eur Cells Mater. 2010;19(S):1.
Jurczyk MU, Jurczyk K, Niespodziana K, Miklaszewski A, Jurczyk M. Titanium–SiO2 nanocomposites and their scaffolds for dental applications. Mater Charact. 2013;77(3):99.
Ning CQ, Zhou Y. In vitro bioactivity of a biocomposite fabricated from HA and Ti powders by powder metallurgy method. Biomaterials. 2002;23(14):2909.
Jurczyk MU, Jurczyk K, Miklaszewski A, Jurczyk M. Nanostructured titanium-45S5 bioglass scaffold composites for medical applications. Mater Des. 2011;32(10):4882.
Suryanarayana C. Synthesis of nanocomposites by mechanical alloying. J Alloys Compd. 2011;509(S):S229.
Yadav TP, Yadav RM, Singh DP. Mechanical milling: a top down approach for the synthesis of nanomaterials and nanocomposites. Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012;2(3):22.
Nouri A, Hodgson PD, Wen C., Biomimetic Porous Titanium Scaffolds for Orthopedic and Dental Applications, edited by Amitava M., Biomimetics Learning from Nature. Intech. 2010. 251.
Chen YJ, Feng B, Zhu YP, Weng J, Wang JX, Lu X. Fabrication of porous titanium implants with biomechanical compatibility. Mater Lett. 2009;63(30):2659.
Niu WJ, Bai CG, Qiu GB, Wang Q. Processing and properties of porous titanium using space holder technique. Mater Sci Eng A. 2009;506(1–2):148.
Mansourighasri A, Muhamad N, Sulong AB. Processing titanium foams using tapioca starch as a space holder. J Mater Process Technol. 2012;212(1):83.
Wen CE, Yamada Y, Hodgson PD. Fabrication of novel TiZr alloy foams for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2006;26(8):1439.
Jurczyk K, Niespodziana K, Jurczyk MU, Jurczyk M. Synthesis and characterization of titanium-45S5 bioglass nanocomposites. Mater Des. 2011;32(5):2554.
Chen YY, Wang XP, Xu LJ, Liu ZG, Kee DW. Tribological behavior study on Ti–Nb–Sn/hydroxyapatite composites in simulated body fluid solution. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;10(1):97.
Khoshakhlagh P, Moztarzadeh F, Rabiee SM, Moradi R, Heidari P, Ravarian R, Amanpour S. Bioglass/chitosan composite as a new bone substitute. Adv Bioceram Porous Ceram. 2010;31(6):39.
Li YH, Chen RB, Qi GX, Wang ZT, Deng ZY. Powder sintering of porous Ti–15Mo alloy from TiH2 and Mo powders. J Alloys Compd. 2009;485(1–2):215.
Williamson GK, Hall HW. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953;1(1):22.
Fuse M, Shirakawa Y, Shimosaka A, Hidaka J. Mechanically strain-induced modification of selenium powders in the amorphization process. J Nanopart Res. 2003;5(1–2):97.
Razavi M, Rahimipour MR, Mansoori R. Synthesis of TiC–Al2O3 nanocomposite powder from impure Ti chips, Al and carbon black by mechanical alloying. J Alloys Compd. 2008;450(1–2):463.
Webster TJ, Ejiofor Ju. Increased osteoblast adhesion on nanophase metals: Ti, Ti6Al4V, and CoCrMo. Biomaterials. 2004;25(19):4731.
Smith LJ, Swaim JS, Yao C, Haberstroh KM, Nauman EA, Webster TJ. Increased osteoblast cell density on nanostructured PLGA-coated nanostructured titanium for orthopedic applications. Int J Nanomed. 2007;2(3):493.
Rabiee SM, Moztarzadeh F, Solati-Hashjin M. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite cement. J Mol Struct. 2010;969(1–3):172.
Nabian N, Jahanshahi M, Rabiee SM. Synthesis of nano-bioactive glass–ceramic powders and its in vitro bioactivity study in bovine serum albumin protein. J Mol Struct. 2011;998(1–3):37.
Khodsiani Z, Mansuri H, Mirian T. The effect of cryomilling on the morphology and particle size distribution of the NiCoCrAlYSi powders with and without nano-sized alumina. Powder Technol. 2013;245(4):7.
Mousavi T, Karimzadeh F, Abbasi MH. Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline NiTi intermetallic by mechanical alloying. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008;487(1–2):46.
He J, Schoenung JM. Review nanostructured coatings. Mater Sci Eng A. 2002;336(1–2):274.
Wang XP, Chen YY, Xu LJ, Xiao SL, Kong FT, Woo KD. Ti–Nb–Sn–hydroxyapatite composites synthesized by mechanical alloying and high frequency induction heated sintering. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4(8):2074.
German RM. Particle Packing Characteristics. Princeton: Metal Powder Industries Federation; 1998. 401.
Moore JJ, Feng HJ. Combustion synthesis of advanced materials. Prog Mater Sci. 1995;39(4):243.
Nouri A, Hodgson PD, Wen C. Effect of ball-milling time on the structural characteristics of biomedical porous Ti–Sn–Nb alloy. Mater Sci Eng C. 2011;31(5):921.
Khayati GR, Janghorban K. An investigation on the application of process control agents in the preparation and consolidation behavior of nanocrystalline silver by mechanochemical method. J Adv Powder Technol. 2012;23(6):808.
Nouri A, Hodgson PD, Wen CE. Effect of process control agent on the porous structure and mechanical properties of a biomedical Ti–Sn–Nb alloy produced by powder metallurgy. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(4):1630.
Sharma M, Gupta GK, Modi OP, Prasad BK, Gupta Ak. Titanium foam through powder metallurgy route using acicular urea particles as space holder. Mater Lett. 2011;65(21–22):3199.
Naddaf Dezfuli S, Sadrnezhaad SK, Shokrgozar MA, Bonakdar S. Fabrication of biocompatible titanium scaffolds using space holder technique. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(10):2483.
Ghasemi A, Hosseini SR, Sadrnezhaad SK. Pore control in SMA NiTi scaffolds via space holder usage. Mater Sci Eng C. 2012;32(5):1266.
Ma PX, Choi JW. Biodegradable polymer scaffolds with well-defined interconnected spherical pore network. Tissue Eng. 2011;7(1):23.
Lu JX, Flautre B, Anselme P, Hardouin P, Gallur A, Descamps M, Thierry B. Role of interconnections in porous bioceramics on bone recolonization in vitro and vivo. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1999;10(2):111.
Esen Z, Bor S. Processing of titanium foams using magnesium spacer particles. Scr Mater. 2007;56(5):341.
Wen CE, Mabuchi M, Yamada Y, Shimojima K, Chino Y, Asahina T. Processing of biomedical porous foam of Ti and Mg. Scr Mater. 2001;45(10):1147.
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF. Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1997. 528.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the use of the facilities at Materials and Energy Research Center, Babol Noshirvani University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riahi, S., Rajabi, M. & Rabiee, S.M. Characterization of porous Ti-bioglass composite produced by mechanical milling and space holder sintering. Rare Met. 34, 638–644 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0414-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0414-0