Abstract
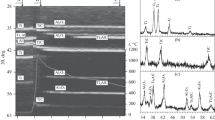
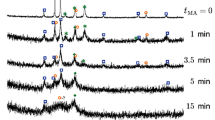
In this paper, Ti–Cr–Al–C materials were investigated by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) according to the experimental study and numerical simulation results. The highest adiabatic combustion temperature T ad of 2,467.45 K indicates that the 2Ti–0Cr–Al–C is the highest exothermic reaction system in the Ti–Cr–Al–C system. The adiabatic combustion temperature decreases with the increase of the Cr content. And a higher exothermal reaction would result in higher porosity which is induced by the high temperature and pressure of C reducing atmosphere and Al vapor. Combustion characterization of the products shows that the geometrical alternating layers result in the high exothermal reaction and flame-front propagating velocity. The higher the T ad is, the thinner the layer is. To demonstrate the process of the microscopic characterization and show the detailed combustion process closed to the experimental observations, the flame-front propagating velocity and temperature distribution were simulated numerically.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ge ZB, Chen KX, Guo JM, Zhou HP, Ferreira JMF. Combustion synthesis of ternary carbide Ti3AlC2 in Ti–Al–C system. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2003;23(3):567.
Liu GH, Chen KX, Zhou HP, Guo JM, Ren KG, Ferreira JMF. Layered growth of Ti2AlC and Ti3AlC2 in combustion synthesis. Mater Lett. 2007;61(3):779.
Yeh CL, Shen YG. Effects of Al content on formation of Ta2AlC by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. J Alloy Compd. 2009;482(1–2):219.
Yeh CL, Shen YG. Combustion synthesis of Ti3AlC2 from Ti/Al/C/TiC powder compacts. J Alloy Compd. 2008;466(1–2):308.
Riley DP, Kisi EH, Wu E, McCallum A. Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of Ti3SiC2 from 3Ti + SiC + C reactants. J Mater Sci Lett. 2003;22(15):1101.
Ying G, Wu Y, He X, Zhu C, Du S, Wang C, Li G. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and properties of Ti3AlC2–Cr2AlC–TiC composite. Rare Metal Mater Eng. 2013;42(1B):618.
Levashov EA, Pogozhev YS, Shtansky DV, Petrzhik MI. Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of ceramic materials based on the M n+1AX n phases in the Ti–Cr–Al–C system. Russ J Non-Ferr Met. 2009;50(2):151.
Ying GB, He XD, Li MW, Li YB, Du SY. Synthesis and mechanical properties of nano-layered composite. J Alloy Compd. 2010;506(2):734.
Gennari S, Tamburini UA, Maglia F, Spinolo G, Munir ZA. A new approach to the modeling of SHS reactions: combustion synthesis of transition metal aluminides. Acta Mater. 2006;54(9):2343.
Ying GB, Wang X. Numerical simulation of the SHS temperature fields of Al–Ti–C system based on plane propagating pattern. Int J Mod Phys C. 2009;20(7):1087.
Gennari S, Maglia F, Anselmi-Tamburini U, Spinolo G. Dynamic behavior in self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of intermetallic compounds. J Alloys Compd. 2006;413(1–2):232.
Sekhar JA, Li HP, Dey GK. Decay-dissipative Belousov–Zhabotinsky nanobands and nanoparticles in NiAl. Acta Mater. 2010;58(3):1056.
Merzhanov AG. Fluid dynamics phenomena in the processes of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Combust Sci Technol. 1995;105(4–6):295.
Makino A, Law CK. On the correspondence between the homogeneous and heterogeneous theories of SHS. Combust Flame. 2001;124(1–2):268.
Shafirovich E, Teoh SK, Varma A. Combustion of levitated titanium particles in air. Combust Flame. 2008;152(1–2):262.
Aldushin AP, Matkowsky BJ, Volpert VA. Interaction of gasless and filtration combustion. Combust Sci Technol. 1994;99(1–3):75.
Huque Z, Kanury AM. A theoretical-analysis of combustive synthesis of titanium carbide and a comparison of predictions with measurements. Combust Sci Technol. 1993;89(1–4):27.
Shteinberg AS, Shcherbakov VA, Munir ZA. Kinetics of combustion in the layered Ni–Al system. Combust Sci Technol. 2001;169:1.
Li YHY, Zhang W, Dong C, Makino A. Effects of Cu, Fe and Co addition on the glass-forming ability and mechanical properties of Zr–Al–Ni bulk metallic glasses. Sci China Phys Mech Astron. 2012;55(12):2367.
Zhao HL, Yue JS, Gao Y, Weng KR. Grain and dendrite refinement of A356 alloy with Al–Ti–C–RE master alloy. Rare Met. 2013;32(1):12.
Fang YZ, Xu QM, Zheng JJ, Wu FM, Ye HQ, Si JX, Zheng JL, Fan XZ, Yang XH. Highly sensitive giant magnetoimpedance in a solenoid containing FeCo-based ribbon. Chin Phys B. 2012;21(3):037501.
Fu GS, Wang XZ, Lu WB. Structural and band tail state photoluminescence properties of amorphous SiC films with different amounts of carbon. Chin Phys B. 2012;21(10):107802.
Hu GX, Zhang LX. Numerical investigation of sintering porous NiTi shape memory alloy by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Comput Mater Sci. 2008;42(4):558.
Li HP. The numerical simulation of the porosity effect on the unstable propagation during micropyretic synthesis. Scr Mater. 2004;50(7):999.
Li HP. A numerical study of the heterogeneous porosity effect on self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS). Mater Res Bull. 2004;39(12):1881.
Mossino P. Some aspects in self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Ceram Int. 2004;30(3):311.
Ge ZB, Chen KX, Guo JM, Zhou HP, Ning XS. Formation mechanism of ternary carbide Ti3AlC2 by combustion synthesis. J Inorg Mater. 2003;18(2):427.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11302068 and 51172057) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2013M541261).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ying, GB., He, XD., Du, SY. et al. Kinetics and numerical simulation of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis in Ti–Cr–Al–C systems. Rare Met. 33, 527–533 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-013-0205-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-013-0205-z