Abstract
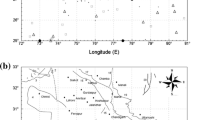
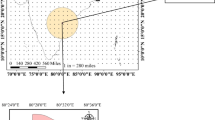
Gemsa has been chosen as the site for one of a new generation of power stations along the south-western margin of the Gulf of Suez. This site has been affected by a number of destructive earthquakes (Mw> 5), in addition to large number of earthquakes with magnitudes of less than 5. In this study seismic activities in the region were collected and re-evaluated, and the main earthquake prone zones were identified. It is indicated that this site is affected by the southern Gulf of Suez, northern Red Sea and Gulf of Aqaba source zones. The southern Gulf of Suez source zone is the nearest to the proposed site. The stochastic simulation method has been applied to estimate the Peak GroundAcceleration at the site of the proposed Gemsa power plant. It was noticed that the pseudo-spectral acceleration (PSA) reaches 175 cm/sec2 resulting from the southern Gulf of Suez seismic source. In addition, the response spectrum was conducted with a damping value of 5% of the critical damping, and the predominant period reached 0.1sec at the site. These results should be taken into consideration by civil engineers and decision-makers for designing earthquake resistant structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Rahman, K., Al-Amri, A. and Abdel-Moneim, E. (2009) Seismicity of Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Arab. Jour. Geosci., v.2, pp.103–118. DOI 10.1007/ s12517-008-0014-0
Al-Amri, A.M., Al-Dail, M.A. and Al-Haddad, M.S. (1996) Recent swarm activity in the Gulf of Aqaba region. Eleventh World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Paper No. 1945.
Al-Tarazi, E. (2000) The major Gulf of Aqaba earthquake, 22 November 1995-Maximum intensity distribution. Natural Hazards, v.22, pp.17–27.
Ambraseys, N.N., Melville, C.P. and Adams, R.D. (1994) The seismicity of Egypt, Arabia and the Red Sea: A historical review. Cambridge University Press, 181p.
Atkinson, G.M. (1993b) Earthquake source spectra in eastern North America, Bull. Seism. Soc. Amer., v.83, pp.1778–1798.
Atkinson, G.M. and Boore, D.M. (1995) Ground motion relations for eastern North America, Bull. Seism. Soc. Amer., v.85, pp.17–30.
Ben-Avraham, Z. (1985) Structural framework of the Gulf of Elat (Aqaba)-northern Red Sea. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.90, pp.703–726.
Ben-Avraham, Z., Almagor, G. and Garfunkel, Z. (1979a) Sediments and structure of the Gulf of Elat (Aqaba)-northern Red Sea. Sediment. Geol., v.23, pp.239–267.
Ben-Avraham, Z., Garfunkel, Z., Almagor, G. and Hall, J.K. (1979b.) Continental breakup by a leaky transform: The Gulf of Elat (Aqaba). Science, v.206, pp.214–216.
Men-Menahem, A. and Aboodi, E. (1971) Tectonic patterns in the Red Sea region. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.76, pp.2674–2689.
Boore, D.M. (1983) Stochastic simulation of high frequency ground motions based on seismological models of the radiated spectra. Bull. Seism. Soc. Amer., v.73, pp.1865–1894.
Boore, D.M. (2003) Simulation of ground motion using the stochastic method. Pure Appld. Geophys., v.160, pp.635–676.
Brune, J.N. (1970) Tectonic stress and the spectra of seismic shear waves from earthquakes. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.75, pp.4997–5009.
Bosworth, W. and McClay, K.R. (2001) Structural and stratigraphic evolution of the Gulf of Suez Rift, Egypt: a synthesis. In: Ziegler P.A., Cavazza W., Robertson A.H.F. & Crasquin-Soleau (Eds.), Peri-Tethyan Rift/Wrench Basins and Passive Margins. Mem. Mus. natn. Hist. nat. Peri-Tethys Memoir 6. Paris. pp.567–606. Retrieved 2010-04-27.
Coleman, R.G. (1974) Geologic Background of the Red Sea. In: C.A. Burke & C.L Drake (Eds.), the Geology of Continental Margins. Springer, Berlin, pp.743–751.
Daggett, P., Morgan, P., Boulos, F., Hennin, S., El-Sherif, A., Basta, N. and Melek, Y. (1986) Seismicity and active tectonics of the Egyptian Red Sea Margin and the northern Red Sea. Tectonophysics, v.125, pp.313–324.
Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation (1976) Stratigraphic Committee: Oligocene and Miocene rock-stratigraphy of the Gulf of Suez region, 142p
Egyptian National Seismological Network (ENSN, 2014). Earthquake Bulletin.
European Mediterranean Seismological Center (EMSC, 2015). On-line earthquake catalogue (http://www.emsc-csem.org/Earthquake/)
Freund, R., Garfunkel, Z., Zak, I., Goldberg, M., Weissbrod, T., Derin, B., Bender, F., Wellings, F. and Girdler, R. (1970) The Shear along the Dead Sea Rift. Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. London, Series A, Math Phys. Sci., v.267(1181), 107p.
Gardner, J.K. and Knopoff, L. (1974) Is the sequence of earthquake in Southern California, with aftershocks removed, Poissonian? Bull. Seism. Soc. Amer., v.64, pp.1363–1367.
Garfunkel, Z. (1981) Internal structure of the Dead Sea leaky transform (rift) in relation to plate kinematics. Tectonophysics, v.80(1–4), pp.81–108
Girdler, R.W. and Styles, P. (1976) Opening of the Red Sea with two poles of rotation-some comments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 33, 169–172.
Hempton, M. (1987) Constraints on Arabian Plate Motion and Extensional History of the Red Sea. Tectonics, v.6(6), pp.687–705.
Hussein, H.M., Abou Eleanean, K.M., Ibrahim, E.M. and Abu El Ata, A.S. (1998) Spectral magnitudes and source parameters for recent damaging earthquakes in Egypt. Bull. IISEE, no.34, pp.1–24.
International Seismological Center (ISC, 2015) Online earthquake catalogue (http://www.isc.ac.uk/gtevents/search/catalogue/)
Jennings, P.C. (1983) Engineering Seismology. In: H. Kanamori and E. Boschi (Eds.), Earthquakes: Observations, Theory and Interpretation. pp. 138–173. North Holland, Amsterdam-New York-Holland.
Khalil, S.M. and McClay K.R. (2001) Tectonic evolution of the NW Red Sea-Gulf of Suez rift system. In: Wilson, R.C.L., Whitmarsh, R.B., Taylor, B. & Froitzheim, N. (Eds.), Non-Volcanic Rifting of Continental Margins:A Comparison of Evidence from Land and Sea. Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., no.187, pp.453–473. ISBN 978-1-86239-091-1.
Maamoun, M. and El Khashab, H.M. (1978) Seismic studies of the Shedwan (Red Sea) earthquake. Helwan Inst. Astron. Geophys. Bull. v.171.
Maamoun, M., Megahed, A., and Allam, A. (1984) Seismicity of Egypt. Helwan Inst. Astron. and Geophys. Bull., v.4, ser. B, pp.109–162.
Meshref, W. M. (1990) In: R. Said (Ed.), (Geology of Egypt). Tectonic framework. A. A. Balkema, Rotterdam, Netherlands, pp.113–155.
Moustafa, A.R. (1996) Internal structure and deformation of an accommodation zone in the northern part of the Suez rift. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.18(1), pp.93–107.
Moustafa, A.R. and Fouda, H.G. (1988) Gebel Surf El Dara accommodation zone, southwestern part of the Suez rift. Middle East Research Center, Ain Shams Univ., Earth Sciences Series, no.2, pp.227–239.
Moustafa, S.R. (2002) Assessment of ground motion variation for seismic hazard mitigation in the vicinity of Cairo metropolitan area. Ph.D. Thesis, Fac. Sci., Ain ShamsUniv., Cairo, Egypt.
National earthquake Information center (NEIC, 2015) Online earthquake catalogue (http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes).
Riad S., Taeleb A.A., Salah El Hadidy, N. Z. Basta, Abuo El-Ela A. Mohamed, Mohamed A. Abdel Aziz and Khalil H. A. (2004) Ancient Earthquakes from Some Arabic Sources and Catalogue of Middle East Historical Earthquakes. EGSMA, NARSS, UNDP, UNESCO, pp.71–91.
Said, R. (1962) The geology of Egypt. Elsevier Pub. Co., Amesterdam, 377p.
Scordilis, E.M. (2006) Empirical global relations converting Msand Mb to moment magnitude. Jour. Seismology, v.19, pp.225–236.
Younes, A.I. and McClay K. (2002) Development of Accommodation Zones in the Gulf of Suez-Red Sea Rift, Egypt. AAPG Bulletin 86 (6), 1003–1026. Doi:10.1306/61EEDC10-173E-11D7-8645000102C1865D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelrahman, K., Al-Amri, A., Al-Arifi, N. et al. Seismic risk assessment at the proposed site of Gemsa wind power station, southwestern coast of Gulf of Suez, Egypt. J Geol Soc India 89, 192–196 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0583-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0583-1