Abstract
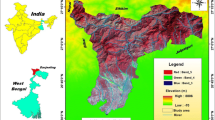
Remote Sensing and GIS, potential tools for facilitating the generation and use of thematic information, has been applied to assess the ground water potentiality of Baghain watershed falling in parts of the Panna and Satna districts, M.P. The role of various parameters namely drainage, lineament, lithology and geomorphology have been emphasized for delineation of ground water potential zones. IRS-1C, LISS III imagery (FCC) on 1:50,000 scale and topographic maps (63 D/5 and 63 D/6) along with field survey have been used as the data source. The various thematic maps have been integrated with the help of GIS applying Index Overlay model to demarcate different groundwater prospects. The resultant map indicates that high prospects is in fractured valley (FV) and pediplain-shallow (PPS) and the moderate prospects in pediment (PD), moderately dissected plateau (PLM) and slightly dissected plateau (PLS), while bute (B), escarpment slope (ES) and mesa (M) show poor prospects for ground water. The groundwater prospect units have been correlated with the discharge of well within the units and it has been found that values match with the units derived from this approach. This study shall be useful in targeting recharge sites as well as drilling sites. The present result shows that integration of all weighted attributes provides more accurate results in groundwater prospects identification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M.I., Jahan, C.S., Mazumdar, Q.H., Hossain M.M.A. and Haque, A. (2010) Study of Groundwater Recharge Potentiality of Barind Tract, Ragshahi District, Bangladesh Using GIS and Remote Sensing Technique. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.75, pp.432–438.
Avtar, R., Singh, C.K., Shashtri, S., Singh, A. and Mukherjee, S. (2010) Identification and analysis of groundwater potential zones in Ken-Betwa river linking area using remote sensing and geographic information system. Geocarto Int., v.25, pp.379–396.
Bahuguna, I. M., Nayak, S., Tamilarasan, V. and Moses, J. (2003) Groundwater prospective zones in basaltic terrain using remote sensing, Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.31(2), pp.101–105.
Baldev, S., Bhattacharya, A. and Hedge, V.S. (1991) IRS-IA application for ground water targeting. Curr. Sci., v.61(3&4), pp.172–179.
Basappa Reddy, M. and Gaikwad, R.L. (1985) Use of Remote Sensing techniques for targeting ground water in fractured crystalline rocks: two case studies from Karnataka. Proceedings, Sixth Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Hyderabad; pp.322–327. (Japan: Asian Association on Remote Sensing)
Benerji, I. (2000) Hydrogeology and Groundwater Resources of Dhanbad District, Unpublished CGWB report.
Chatterjee, R., Tarafder, G. and Paul, S. (2010) Groundwater Quality Assessment of Dhanbad District, Jharkhand, India. Bull. Engg. Geol. Environ., v.69, pp.137–141.
Chaturvedi, R.S., Bhattacharya, D.C., Kamal, P., Krishnamurthy, J. and Sunder Raman, N. (1983) Integrating Remote Sensing techniques in ground water exploration–a typical case study from Bundelkhand region in Uttar Pradesh. In: Baldev Sahai, R.S Chaurvedi and H.S. Iyer (Eds.), Proceedings, National Symposium on Remote Sensing in Development and Management of Water Resources. Indian Society of Photo-interpretation and Remote Sensing, Dehradun, pp.267–276.
Chowdhury, A., Jha, M.K., Chowdary, V.M. and Mal, B.C. (2009) Integrated Remote Sensing and GIS-Based Approach for Assessing Groundwater Potential in West Mednipur District, West Bengal, India. Internat. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.30, pp.231–250.
Das, S., Behera, S.C., Kar, A., Narendra, P. and Guha, S. (1997) Hydrogeomorphological mapping in groundwater exploration using remotely sensed data–A case study in Keonjhar district, Orissa. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.25, pp.247–259.
Dasgupta, S. (1994) Physico Chemical studies on Water Resources and its relation to lithology to Dhanbad District, Bihar India. Indian Jour. Earth Sci., v.21(2), pp.69–78.
Dinesh Kumar, P.K., Gopinath, G. and Seralathan, P. (2007) Application of remote sensing and GIS for the demarcation of groundwater potential zones of a river basin in Kerala, southwest coast of India. Internat. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.28, pp.5583–5601.
Greenbaum, D. (1992) Structural influences on the occurrence of ground water in SE Zimbabwe. In: E.P. Wright and W.G. Burges (Eds.), Hydrology of crystalline basement aquifers in Africa. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., no.66, pp.77–85.
Narendra, K., Nageswara Rao, K. and Swarna Latha, P. (2013) Integrating Remote Sensing and GIS for Identification of Groundwater Prospective Zones in the arava Basin, Visakhapatnam Region, Andhra Pradesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.81, pp.248–260.
Murthy, K.S.R., Amminedu, E. and Venkateswara Rao, V. (2003) Integration of Thematic Maps through GIS for Identification of Groundwater Potential Zones. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.31, pp.197–210.
Krishnamurthy, J. and Srinivas, G. (1995) Role of geological and Geo-morphological factors in ground water exploration in a hard rock terrain. Internat. Jour. Remote Sensing, v.13(15), pp.2925–2942.
Lokesh, N., Gopalakrishna, G.S., Gowda, H.H. and Gupta, A.K. (2005) Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones in a Hard Rock Terrain of Mysore District, Karnataka Using IRS Data and GIS Techniques. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.33(3), pp.405–412.
Manavalan, P., Krishnamurthy, J., Manikiam, B., Adiga, S., Radhakrishnan, K. and Chandrasekhar, M.G. (1993) Watershed analysis response using digital data integration techniques. Advance Space Res., v.13(5), pp.(5)177–(5)180.
Mondal, M.S., Pandey, A.C. and Garg, R.D. (2007) Groundwater Prospect Evaluation Based on Hydrogeomorphological Mapping using High Resolution Satellite Images: A case study in Uttarakahand. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.36(1), pp.69–76.
Mukherjee, S. (1996) Targeting Saline Aquifer by Remote Sensing and Geophysical Methods in a part of Hamirpur-Kanpur, India. Jour. Hydrology, v.19(1), pp.5364.
Murthy, K.S. (2000), Groundwater potential in a semi-arid region of Andhra Pradesh: a geographical information system approach. Internat. Jour. Remote Sensing v.21(9), 1867–1884.
Nag, S.K. (2005) Application of lineament density and hydrogeomorphology to delineate groundwater potential zones of Baghmundi block in Prulia district, West Bengal. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.33, pp.521–529.
Prabu Pothiraj and Baskaran Rajagopalan (2012), A GIS and remote sensing based evaluation of groundwater potential zones in a hard rock terrain of Vaigai sub-basin, India. Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.6(7), pp.2391–2407.
Pradeep Kumar, G.N., Srinivas, P., Jaya Chandra, K. and Sujatha, P. (2010) Delineation of Groundwater Potential Zones Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Kurmapalli Vagu Basin in Andhra Pradesh, India. Internat. Jour. Water Resources and Environ. Engg., v.2(3), pp.70–78.
Preeja, K.R., Joseph, S., Thomas, J. and Vijith, H. (2011) Identification of Groundwater Potential Zones of a Tropical River Basin (Kerala, India) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.39(1), pp.83–94.
Raj, S. and Sinha, A.K. (1989) An integral approach for the delineation of potential groundwater zones using satellite data: case study, Udaipur District, Rajasthan. Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing Jour., v.2(I), pp 61–64.
Ranna, S.S. (1998) Application of Directional filtering in Lineament mapping for ground water prospecting around Bhinmal-a semi-arid part of Thar desert, Photonirvachak. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.26(1&2), pp.35–44.
Mondal, M.S., Pandey, A.C. and Garg, R.D. (2007) Groundwater Prospect Evaluation Based on Hydrogeomorphological Mapping using High Resolution Satellite Images: A case study in Uttarakahand. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.36(1), pp.69–76.
Ravindran, K.V. and Jeyaram, A. (1997) Groundwater prospectus of Shahba Teshil, Baran district, eastern Raiasthan; A remote sensing approach. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.25(4), pp.239–246.
Roy, A.K. (1991) Hydromorphogeology for Ground Water Targeting and Development in Dehradun Valley, U.P., “Mountain Resource Management and Remote Sensing” Surya Publications, Dehradun.
Senthil Kumar, G.R. and Shankar, K. (2014) Assessment of Groundwater Potential Zones Using GIS, FG v.2(1), pp.1–10.
Sabale, S.M., Ghodake, V.R. and Narayanpethkar, A.B. (2009), Electrical Resistivity Distribution Studies for artificial recharge of groundwater in the Dhubdhubi Basin, Solapur District, Maharashtra, India. Jour. Indian Geophys. Union, v.13(4), pp.201–207.
Srivastava, V.K. (2000) Water Resources Management through Remote Sensing and GIS: A Case Study of Dhanbad Watershed. Proc. National Seminar on Geoinformatics, Coimbatore, pp.238–243
Suja Rose, R.S. and Krishnan, N. (2009), Spatial Analysis of Groundwater Potential Using Remote Sensing and GIS in the Kanyakumari and Nambiyar Basins, India, Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.37, pp.681–692.
Toleti, B.V.M.R., Chowdhary, B.S., Kumar, K.E.M., Saroha, G.P., Yadav, M., Singh, A., Sharma, M.P., Pandey, A.C. and Singh, P.K. (2000) Integrated Groundwater Resource Mapping in Gurgaon District, India Using RS and GIS Techniques. Proc. 21st Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Taipei, Taiwan, 4–8 December, 2000.
Vasanthavigar, M., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Vijayaragavan, K., Gopinath, S. and Sarma, S. (2011) Groundwater Potential Zoning in Thirumanimuttar Sub-Basin Tamil Nadu, India—A GIS and Remote Sensing Approach. Geospatial Information Sci., v.14(1) pp.17–26.
Vijith, H. (2007) Groundwater Potential in the Hard Rock Terrain of Western Ghats—a Case Study from Kottayam District, Kerala Using Resource Sat (IRS-P6) Data and GIS Techniques. Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing, v.35(2), pp.171–179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A.K., Shukla, J.P. A remote sensing and GIS based approach to evaluate the ground water prospects of Baghain watershed, Panna and Satna districts of M.P., India: A case study. J Geol Soc India 86, 733–741 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0366-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0366-5