Abstract
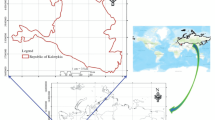
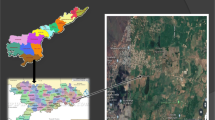
The present work accentuated the expediency of remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS) applications in groundwater studies, especially in the identification of groundwater potential zones in Ithikkara River Basin (IRB), Kerala, India. The information on geology, geomorphology, lineaments, slope and land use/land cover was gathered from Landsat ETM + data and Survey of India (SOI) toposheets of scale 1:50,000 in addition, GIS platform was used for the integration of various themes. The composite map generated was further classified according to the spatial variation of the groundwater potential. Four categories of groundwater potential zones namely poor, moderate, good and very good were identified and delineated. The hydrogeomorphological units like valley fills and alluvial plain and are potential zones for groundwater exploration and development and valley fills associated with lineaments is highly promising area for groundwater extraction. The spatial variation of the potential indicates that groundwater occurrence is controlled by geology, structures, slope and landforms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acworth, R. I. (1987). The development of crystalline basement aquifers in a tropical environment. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology, 20, 265–272.
Barker, R. D., White, C. C., &and Houston, J. F. T. (1992). Borehole siting in an African accelerated drought relief project. In: E. P. Wright, & W. G. Burgess (Eds.), The hydrogeology of crystalline basement aquifers in Africa. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., 66:183–201.
Bobba, A. G., Bukata, R. P., & Jerome, J. H. (1992). Digitally processed satellite data as a tool in detecting potential groundwater flow systems. Journal of Hydrology, 131(1–4), 25–62.
Davis, S. N., & De Wiest, R. J. M. (1966). Hydrogeology. New York: Wiley.
Engman, E. T., & Gurney, R. J. (1991). Remote Sensing in Hydrology. London: Chapman and Hall.
Farnsworth, R. K., Barret, E. C., & Dhanju, M. S. (1984). Application of Remote Sensing to Hydrology including Ground Water. Paris: UNESCO.
Harinarayana, P., Gopalakrishna, G. S., & Balasubramanaian, A. (2000). Remote sensing data for groundwater development and management in Keralapura watersheds of Cauvery basin, Karnataka, India. Indian Mineral, 34(2), 11–17.
Krishnamurthy, J., & Srinivas, G. (1996). Demarcation of geological and geomorphological features of parts of Dharwar Craton, Karnataka, using IRS LISS-II data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(16), 3271–3288.
Krishnamurthy, J., Kumar, N. V., Jayaraman, V., & Manivel, M. (1996). An approach to demarcate groundwater potential zones through remote sensing and a geographic information system. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17, 1867–1885.
Kukillaya, J. P., Padmanbhan, K., & Krishnan, E. (1999). Use and limitations of short and medium duration pumping tests in understanding hard rock aquifers—an example from Kerala. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 54, 267–277.
Mabee, S. B., Hardcastle, K. C., & Wise, D. U. (1994). A method of collecting and analyzing lineaments for regional scale fractured bedrock aquifer studies. Ground Water, 32, 884–894.
Magowe, M., & Carr, J. R. (1999). Relationship between lineaments and groundwater occurrence in Western Botswana. Ground Water, 37(2), 282–286.
McFarlane, M. J., Chilton, P. J., & Lweis, M. A. (1992). Geomorphological controls on borehole yields: a statistical study in an area of basement rocks in central Malawi. In: E. P. Wright, & W. G. Burgess (Eds.), The hydrogeology of crystalline basement aquifers in Africa. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., 66:131–154.
Meijerink, A. M. J. (2000). Groundwater. In G. A. Schultz & E. T. Engman (Eds.), Remote sensing in hydrology and water management (pp. 305–325). Berlin: Springer.
NRSA. (1995). Integrated Mission for Sustainable Development (IMSD). National Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderabad: Technical guidelines.
Owen, R., Maziti, A., & Dahlin, T. (2007). The relationship between regional stress field, fracture orientation and depth of weathering and implications for groundwater prospecting in crystalline rocks. Hydrogeology Journal, 15, 1231–1238.
Pradeep, J. K. (1998). Remote sensing techniques to locate groundwater potential zones in upper Urmil river basin, Chhatarpur distict—Central India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 26(3), 135–147.
Sander, P. (1996). Remote Sensing and GIS for Groundwater Assessment in Hard Rocks: Applications to Water Well Siting in Ghana and Botswana. PhD thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden.
Saraf, A. K., & Choudhury, P. R. (1998). Integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater exploration and identification of artificial recharge sites. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19, 1825–1841.
Shahid, S., & Nath, S. K. (2002). GIS integration of remote sensing and electrical sounding data for hydrogeological exploration. Journal of Spatial Hydrology, 2(1), 1–10.
Singh, A.K. and Prakash, S.R. (2002). An integrated approach of remote sensing, geophysics and GIS to evaluation of groundwater potentiality of Ojhala sub-watershed, Mirjapur district, U.P., India (Online). Available from http://www.GISdevelopment.net (accessed 25 June 2003).
Subba Rao, N. (1992). Factors affecting optimum development of groundwater in crystalline terrain of the Eastern Ghats, Visakhapatnam area, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 40(5), 462–467.
Subba Rao, N. (2006). Groundwater potential index in a crystalline terrain using remote sensing data. Environmental Geology, 50, 1067–1076.
Subba Rao, N., & Prathap, R. R. (1999). Groundwater prospects in a developing satellite township of Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 27(4), 193–203.
Subba Rao, N., Chakradhar, G. K. J., & Srinivas, V. (2001). Identification of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing techniques in and around Guntur town, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 29(1&2), 69–78.
Todd, D. K., & Mays, L. W. (2005). Groundwater hydrology (3rd ed.). New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
Vijith, H. (2007). Groundwater potential in the hard rock terrain of Western Ghats—a case study from Kottayam district, Kerala using Resourcesat (IRS-P6) data and GIS techniques. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 35(2), 171–179.
Waters, P., Greenbaum, P., Smart, L., & Osmaston, H. (1990). Applications of remote sensing to groundwater hydrology. Remote Sensing Review, 4, 223–264.
Wright, E. P. (1992). Hydrogeology of crystalline basement aquifers. In: E. P. Wright, & W. G. Burgess (Eds.), The hydrogeology of crystalline basement aquifers in Africa. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ., 66:1–27.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Arunkumar, K.S., Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment (KSCSTE), Thiruvananthapuram for his outstanding help with this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Preeja K. R., Joseph, S., Thomas, J. et al. Identification of Groundwater Potential Zones of a Tropical River Basin (Kerala, India) Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 39, 83–94 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0075-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0075-5