Abstract
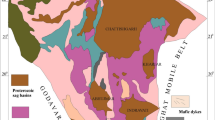
Felsic magmatisms in the north of Indus-Tsangpo Suture Zone (ITSZ) in Ladakh range of northwest Indian Himalaya, referred herein Ladakh granitoids (LG), and associated magmatic rocks constitute the bulk of the Ladakh batholith. They have been characterized as Andean-type, calc-alkaline, largely metaluminous (I-type) to a few peraluminous (S-type) granitoids derived from partial melting of subducting materials. The LG can be broadly classified into coarsegrained facies with abundant mafics (hbl-bt), medium-grained facies with low content of mafics, and fine-grained leucocratic facies with very low amount of mafics. Mesocratic to melanocratic, rounded to elliptical, fine to medium grained, mafic to hybrid microgranular enclaves (ME) are ubiquitous in medium to coarse-grained LG. ME are absent or rare in the leucocratic variety of LG. In this paper different types of ME, and their field relation and microstructures with respect to felsic host LG are documented from northwestern, central, southeastern parts of the Ladakh batholith. Rounded to elongate ME of variable sizes (a few cm to metres across, mostly d<30 cm) commonly having sharp, crenulate, and occasionally diffuse contacts of ME with felsic host LG suggest that several pulses of crystal-charged mafic and felsic magmas coexisted, hybridized, and co-mingled into subvolcanic settings. Occurrence of composite ME (several small mafic ME enclosed into large porphyritic ME) strongly point to multiple mafic to hybrid magma intrusions into partly crystalline LG magma chambers. Synplutonic mafic dykes disrupted to form subrounded to angular (brecciated) mafic ME swarms commonly disposed in strike-length suggest mafic magma injections at waning stage of felsic magma evolution with large rheological contrasts. Pillowing of mafic melt against leucocratic (aplitic) residual melt strongly suggests mafic magma intrusion in nearly-crystallized condition of pluton. Although common mineral asemblages (hblbt-pl-kfs-qtz-ap-zrn-mt±ilm) of ME (diorite, quartzdiorite) and host LG (granodiorite, monzogranite) may relate to their cogenetic relation, fine to medium grained porphyritic (hybrid) nature and lack of cumulate texture of ME strongly oppose cognate origin for ME. Presence of plagioclase xenocrysts, quartz ocelli and accicular apatite in porphyritic ME strongly indicate mingling and undercooling of hybridized ME globules into relatively crystal-charged cooler host LG magma. Grain size differences of some ME, except to those of porphyritic ones, appear related to varying degrees of undercooling of ME most likely controlled by their variable sizes. Several smaller ME, however, lack fine-grained chilled margin probably because of their likely disaggregation from a large size ME during the course of progressive hybridization (mingling to mixing) leaving behind trails of mafic schlieren. Field and microstructural evidences at least suggest that Ladakh granitoids and their microgranular enclaves are products of multistage magma mingling and mixing processes concomitant fractional differentiation of several batches of mafic and felsic magmas formed in open magma chamber(s) of subduction setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, T., Thakur, V.C., Islam., R., Khanna, P.P. and Mukherjee, P.K. (1998) Geochemistry and geodynamic implications of magmatic rocks from the Trans Himalayan arc. Geochem. Jour., v.32, pp.383–404.
Ahmad, T., Sivaprabha, S., Balakrishnan, S., Thanh, N.X., Itaya, T., Sachan, H.K., Mukhopadhyay, D.K. and Khanna, P.K. (2008a) Geochemical-isotopic characteristics and K-Ar ages of magmatic rocks from Hunder valley, Shyok suture zone, Ladakh. Abstract, 23-HKT workshop, Him. Jour. Sci., v.5, pp.18.
Ahmad, T., White, L., Forster, M., Ireland, T.R. and Lister, G. (2008b) New SHRIMP ages for Ladakh and Karakoram batholiths-inherited zircons indicate involvement of older crust. Abstract, 23-HKT workshop, Him. Jour. Sci., v.5, pp.19.
Auden, J.B. (1935) Traverses in the Himalaya. Rec. Geol. Surv. India, v.69, pp.123–167.
Asrat, A., Gleizes, G., Barbey, P. and Ayalew, D. (2003) Magma emplacement and mafic-felsic magma hybridization: structural evidenc from the Pan-African Nagash pluton, Northern Ethiopia. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.25, pp.1451–1469.
Bacon, C.R. (1986) Magmatic inclusions in silicic and intermediate volcanic rocks. Jour. Geophys. Res. v.91, pp.6091–6112.
Ban, M., Takahashi, K., Horie, T. and Toya, N. (2005) Petrogenesis of mafic inclusions in rhyolitic lavas from Narugo volcano, northeastern Japan. Jour. Petrol., v.46, pp.1543–1563.
Barbarin, B. (1990) Plagioclase xenocrysts and mafic magmatic enclaves in some granitoids of the Sierra Nevada batholith, California. Jour. Geophys. Res. v.95, pp.17747–17756.
Barbarin, B. and Didier, J. (1992) Genesis and evolution of mafic microgranular enclaves through various types of interaction between co-existing felsic and mafic magmas. Tran. Roy. Soc. Edin. Earth Sci., v.83, pp.145–153.
Blundy, J.D. and Sparks, R.S.J. (1992) Petrogenesis of mafic inclusions in granitoids of the Adamelo Massif, Italy. Jour. Petrol., v.33, pp.1039–1104.
Browne, B.L., Eichelberger, J.C., Patino, L.C., Vogel, T.A., Dehn, J., Uto, K. and Hoshizumi, H. (2006) Generation of porphyritic and equigranular mafic enclaves during magma recharge events at Unzen Volcano, Japan. Jour. Petrol., v.47, pp.301–328.
Campbell, I.H. and Turner, J.S. (1985) Turbulent mixing between fluids with different viscosities. Nature, v.313, pp.39–42.
Castro, A. (2001) Plagioclase morphologies in assimilation experiments. Implication for disequilibrium melting in the generation of granodiorite rocks. Mineral. Petrol., v.71, pp.31–49.
Castro, A., Moreno-ventas, I. and Dela Rosa, J.D. (1991) Multistage crystallization of tonalitic enclaves in granitoid rocks (Hercynian belt, Spain): implication for magma mixing. Geol. Runds., v.80, pp.109–120.
Chappell, B.W., White, A.J.R. and Wyborn, D. (1987) The importance of residual source material (restite) in granite petrogenesis. Jour. Petrol., v.28, pp.1111–1138.
Chen, Y.D., Price, R.C. and White, A.J.R. (1989) Inclusions in three S-type granites from southeastern Australia. Jour. Petrol., v 30, pp 1181–1218.
Clemens, J.D. (1990) The granulite-granite connection. In: D. Vielzeuf and P. Vidal (Eds.), Granulites and crustal evolution. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp.25–36.
Coombs, M.L., Eichelberger, J.C. and Rutherford, M.J. (2002) Experimental and textural constraints on mafic enclave formation in volcanic rocks. Jour. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., v.119, pp.125–144.
Didier, J. (1973) Granites and their enclaves: The Bearing of Enclaves on the Origin of Granites. Developments in Petrology, v. 3, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 393p.
Didier, J. (1984) The problem of enclaves in granitic rocks: A reviews of recent ideas on their origin. Proceed. Internat. Symp., on “Geology of granites and their metallogenetic relations”. Nanjing Univ., Nanjing, China, pp.137–144.
Dorais, M. J., Whitney, J. A. and Roden, M. F. (1990) Origin of mafic enclaves in the Dinkey Creek Pluton, Central Sierra Neveda Batholith, California. Jour. Petrol., v.31, pp.853–881.
Eichelberger, J.C., Izbekov, P.E. and Browne, B.L. (2006) Bulk chemical trends at arc volcanoes are not liquid line of descent. Lithos, v.87, pp.135–154.
Elburg, M.A. and Nicholls, I.A. (1995) Origin of microgranitoid enclaves in the S-type Wilson’s Promontory Batholith, Victoria: evidence for magma mingling. Austral. Jour. Earth Sci., v.52, pp.423–435.
Flinders, J. and Clamens, J.D. (1996) Non-linear diagrams, chaos, complexity and enclaves in granitoid magmas. Trans. Roy. Soc. Edin. Earth Sci., v.87, pp.217–223.
Frank, W., Thoni, M. and Purtscheller, F. (1977) Geology and petrography of Kullu-south Lahul area. Sci. Terre. Himalaya, CNRS, v.268, pp.147–160.
Frost, T.P. and Mahood, G.A. (1987) Field, chemical and physical constraints on mafic-felsic interaction in the Lamarck Granodiorite, Sierra Neveda, California. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.99, pp.272–291.
Furman, T. and Spera, F.J. (1985) Co-mingling of acid and basic magma with implication for the origin of mafic I-type xenoliths, field and petrological relations of an usual dyke complex at Eagle Peak Lake, Sequoia National Park, California, USA. Jour. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., v.24, pp.151–178.
Gansser, A. (1977) The great suture zone between Himalaya and Tibet: a preliminary account. Sci. Terre. Himalaya CNRS, v.268, pp.181–192.
Hibbard, M.J. (1981) The magma mixing origin of mantled feldspar. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.76, pp.158–170.
Hibbard, M.J. (1991) Textural anatomy of twelve magma-mixed granitoid systems. In: J. Didier and B. Barbarin (Eds.), Enclaves and granite petrology, Developments in Petrology 13, Elsevier, Amsterdam: pp431–444.
Hibbard, M.J. (1995) Petrography to petrogenesis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 575p.
Honegger, K., Dietrich, V., Frank, W., Gansser, A., Thoni, M. and Trommsdorff, V. (1982) Magmatism and metamorphism in the Ladakh Himalaya, the Indus Tsongpo Suture Zone. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.60, pp.253–292.
Huppert, H.E., Sparks, R.S.J. and Turner, J.S. (1982) Effects of volatiles on mixing in calc-alkaline magma systems. Nature, v.297, pp.554–557.
Huppert, H.E., Sparks, R.S.J. and Turner, J.S. (1984) Some effects of viscosity on the dynamics of replenished magma chamber. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.89, pp.6857–6877.
Jain, A.K., Singh, S., Manickavasagam, R.M., Joshi, M. and Verma, P.K. (2003) Himprobe Programme: Integrated studies on geology, petrology, geochronology and geophysics of the Trans-Himalaya and Karakoram. Mem. Geol. Soc. India, no53, pp.1–56.
Jayananda, M, Peucat, J-J, Martin, H. and Mahabaleswar, B. (1994) Magma mixing in plutonic environment: geochemical and isotopic evidences from Closepet batholith, southern India. Curr. Sci., v.66, pp.928–933.
Jayananda, M., Miyazaki, T., Gireesh, R. V., Mahesha, N. and Kano, T. (2009) Synplutonic mafic dykes from Late Archean granitoids in the Eastern Dharwar craton, Southern India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.73, pp.117–130.
Kretz, R. (1983) Symbols for rock forming minerals. Amer. Mineral., v.68, pp.277–279.
Kumar Santosh (1995) Microstructural evidence of magma quenching inferred from enclaves hosted in the Hodruša Granodiorites, Western Carpathians. Geol. Carpath., v.46, pp.379–382.
Kumar Santosh and Rino, V. (2006) Mineralogy and geochemistry of microgranular enclaves in Palaeoproterozoic Malanjkhand granitoids, Central India: evidences of magma mixing, mingling, and chemical equilibration. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.152, pp.591–609.
Kumar, Santosh, Pieru, T., Rino, V. and Lyngdoh, B.C. (2005) Miocrogranular enclaves in Neoproterzoic granitoids of south Khasi Hills, Meghalaya plateau, Northeast India: field evidences of interacting coeval mafic and felsic magmas. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.65, pp.629–633.
Kumar Santosh, Rino, V. and Pal, A.B. (2004) Field evidence of magma mixing from microgranular enclaves hosted in Palaeoproterozoic Malanjkhand granitoids, central India. Gondwana Res., v.7, pp.539–548.
Mahéo, G., Bertrand, H., Guillot, S., Villa, I.M., Keller, F. and Capiez, P. (2004) The south Ladakh ophiolites (NW Himalaya, India): an intra-oceanic tholeiitic origin with implication for the closure of the Neo-Tethys. Chem. Geol., v.203, pp.273–303.
Mahéo, G., Fayoux, X., Guillot, S., Gazzauti, E., Capiez, P. and Mascle, G. (2006) Relicts of an intra-oceanic arc in the Sapi-Shergol mélange zone (Ladakh, NW Himalaya, India): implications for the closure of the Neo-Tethys ocean. Jour. Asia. Earth Sci., v.26, pp.695–707.
Mason, D.R. (1986) Magmatic ferromagnesian inclusions in granitoid plagioclase cores, Barrington Tops granitoids, New South Wales, Australia. Amer. Mineral., v.71, pp.1314–1321.
Montel, J.M., Didier, J. and Pichavant, M. (1991) Origin of surmicaceous enclaves in intrusive granites. In: J. Didier and B. Barbarin (Eds.), Enclaves and Granite Petrology. Developments in Petrology, v.13, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp.509–528.
Patterson, M.G. and Windley, B.F. (1991) Changing source regions of magmas and central growth in the Trans-Himalayas: evidences from the Cholt volcanics and Kohistan batholith, Kohistan, northern Pakistan. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.102, pp.326–341.
Perugini, D. and Poli, G. (2000) Chaotic dynamics and fractals in magmatic interaction of mafic microgranular enclaves. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.175, pp.93–103.
Perugini, D. and Poli, G. (2005) Viscous fingering during replenishment of felsic magma chambers by continuous inputs of mafic magmas: field evidences and fluid mechanics experiments. Geology, v.3, pp. -8.
Perugini, D., Poli, G., Christofides and Eleftheriadis, G. (2003) Magma mixing in the Sithonia plutonic Complex, Greece: evidence from mafic microgranular enclaves. Mineral. Petrol., v.78, pp.173–200.
Perugini, D., Valentini, L. and Poli, G. (2007) Insights into magma chamber processes from the analysis of size distribution of enclaves in lava flows: a case study from Vucano Island (southern Italy). Jour.Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., v.166, pp.193–203.
Pitcher, W.S. (1991) Synplutonic dykes and mafic enclaves. In: J. Didier and B. Barbarin (Eds.), Enclaves and Granite Petrology. Developments in Petrology, v.13, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp.383–391.
Poli, G. and Tommasini, S. (1991) Origin and significance of microgranular inclusions in calc-alkaline granitoids: a proposed working model. Jour. Petrol., v.32, pp.657–666.
Poli, G. E., Tommasini, S. and Halliday, A.N. (1996) Trace element and isotopic exchange during acid-basic magma interaction processes. Trans. Roy. Soc. Edinburg: Earth Sci., v.87, pp.225–232.
Pons, J., Barbey, P., Nachit, H. and Burg, J. - P. (2006) Development of igneous layering during growth of pluton: the Tarçouate lacolith (Morocco). Tectonophysics, v.413, pp.271–286.
Rai, H. (1980) Origin and emplacement of Ladakh batholith: present day knowledge. Him. Geol., v.10, pp.78–93.
Ravikant, V., Wu, Fu-Yuan and Ji, Wei-Qiang (2009) Zircon UPb and Hf isotopic constraints on the petrogenesis of the Cretaceous-Tertiary granites in eastern Karakoram and Ladakh. Lithos, v.110, pp.153–166.
Rolland, Y., Pecher, A. and Picard, C. (2000) Middle Cretaceous back-arc formation and arc evolution along the Asian margin: the Shyok suture zone on northern Ladakh (NW Himalaya). Tectonophysics, v.325, pp.145–173.
Sharma, K.K. and Choubey, V.M. (1983) Petrology, geochemistry, and geochronology of the southern margin of the Ladakh batholith between Upshi and Chumathang. In: V.C. Thakur and K. K. Sharma (Eds.), Geology of Indus Suture Zone of Ladakh, 204p, Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Deharadun (India), pp 41–60.
Singh, S., Kumar, R., Barley, M.E. and Jain, A.K. (2007) SHRIMP U-Pb ages and depth of emplacement of Ladakh batholith, Eastern Ladakh, India. Jour. Asia. Earth Sic., v.30, pp.490–503.
Sisson, T.W. and Bacon, C.R. (1999) Gas-driven filter pressing in magmas. Geology, v.27, pp.613–616.
Sparks, R.J.S. and Marshall, L.A. (1986) Thermal and mechanical constraints on mixing between mafic and silicic magmas. Jour. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., v.29, pp.99–124.
Thakur, V.C. (1987) Plate tectonic interpretation of the western Himalaya. Tectonophysics, v.134, pp.91–102.
Thakur, V.C. and Misra, D.K. (1984) Tectonic framework of Indus and Shyok Suture Zones in eastern Ladakh, northwest Himalaya. Tectonophysics, v.101, pp.207–220.
Upadhyay, R., Frisch, W. and Siebel, W. (2008) Tectonic implication of U-Pb zircon ages of the Ladakh batholith, Indus suture zone, northwest Himalaya, India. Terra Nova, v.20, pp.309–317.
Valli, F., Leloup, P. H., Paquette, J-L., Arnanad, N., Li, H., Tapponnier, P., Lacassin, R., Guillot, S., Liu, D., Deloule, E., Xu, Z. and Mahço, G. (2008) New U-th/Pb constraints on timming of shearing and long-term slip-rate on the Karakorum fault. Tectonics, v.27, TC5007, doi: 10.1029/2007TC002184.
Van Der Laan, S.R. and Wyllie, P.J. (1993) Experimental interaction of granitic and basaltic magmas and implications for mafic enclaves. Jour. Petrol, v.34, pp.491–517.
Vernon, R.H. (1983) Restite, xenoliths and microgranitoid enclaves in granites. Clarke Memorial Lecture, Jour. Proc. Royal Soc. N.S.W., v.116, pp.77–103.
Vernon, R.H. (1986) K-feldspar megacrysts in granitesphenocrysts, not porphyroblasts. Earth Sci. Rev., v.23, pp.157–167.
Vernon, R.H. (1990) Crystallization and hybridism in microgranitoid enclave magmas: microstructural evidence. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.95, pp.17849–17859.
Vernon, R.H. (1991) Interpretation of microstructures of microgranitoid enclaves. In: J. Didier and B. Barbarin (Eds.), Enclaves and Granite Petrology. Developments in Petrology, v. 13, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp.277–291.
Vernon, R. H. and Paterson, S. R. (2008) How late are K-feldspar megacrysts in granites? Lithos, v.104, pp.327–336.
Vernon, R.H., Etheridge, M.A. and Wall, V. J. (1988) Shape and microstructures of microgranitoid enclaves: indicators of magma mingling and flow. Lithos, v.22, pp.1–11.
Wadia, D.N. (1937) The Cretaceous volcanic series of Astor-Deosai Kashmir and is intrusion. Rec. Geol. Surv. India, v.72, pp.151–161.
Wiebe, R.A. (1980) Comingling of contrasted magmas in the plutonic environment: examples from the Nain anorthositic complex. Jour. Geol., v.88, pp.197–209.
Wiebe, R.A. (1994) Silicic magma chambers a traps for basaltic magmas: The Cadillac mountain intrusive complex, Mount Desert island, Maine. Jour. Geol., v.102, pp.423–427.
Wiebe, R.A., Smith, D., Sturn, M., King, E.M. and Seckler, M.S. (1997) Enclaves in the Cadillac Mountain granite (Coastal Maine): samples of hybrid magma from the base of the chamber. Jour. Petrol., v.38, pp.393–426.
Wiebe, R.A., Manon, M.R., Hawkins, D.P. and Mcdonough, W.F. (2004) Late-stage mafic injection and thermal rejuvenation of the Vinalhaven granite, Coastal Maine. Jour. Petrol., v.45, pp.2133–2153.
Wiebe, R.A., Jellinek, M., Markley, M.J., Hawkins, D.P. and Snyder, D. (2007) Steep schlieren and associated enclaves in the Vinalhaven granite, Maine: possible indicators for granite rheology. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.153, pp.121–138.
Weinberg, R.F. (1997) The disruption of a diorite magma pool by intruding granite: the Sobu body, Ladakh batholith, Indian Himalayas. Jour. Geol., v.105, pp.87–98.
Weinberg, R.F. and Dunlap, W.J. (2000) Growth and deformation of the Ladakh batholith, northwest Himalayas: implications for timing of continental collision and origin of calc-alkaline batholith. Jour. Geol., v.108, pp.303–320.
Wyllie, P.J., Cox, K.G. and Biggar, G. M. (1962) The habit of apatite in synthetic systems and igneous rocks. Jour. Petrol., v.3, pp.238–243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S. Mafic to hybrid microgranular enclaves in the Ladakh batholith, northwest Himalaya: Implications on calc-alkaline magma chamber processes. J Geol Soc India 76, 5–25 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0080-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0080-2