Abstract
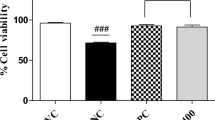
This study investigated the anti-allergic effect of a diethyl ether fraction from dried Sargassum fusiforme. In vivo experiments showed that percutaneous administration of this fraction suppressed mouse ear swelling induced by three types of sensitizers (arachidonic acid, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and oxazolone). At a dose of 0.1 mg/mouse, the suppression ratios were from 47 to 61 %. Oral administration of the fraction also suppressed mouse ear swelling. At a dose of 1 mg/mouse, the suppression ratios were from 69 to 92 % which were comparable to those obtained by the typical natural inhibitor, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). In vitro experiments were performed to elucidate the inhibitory effects of the fraction on the enzymatic activities (phospholipase A2, cyclooxygenase-2, lipoxygenase and hyaluronidase) involved in inflammation and degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia (RBL)-2H3 cells to understand the mechanism that underlies the suppression of mouse ear swelling. Similar to EGCG, the fraction inhibited the enzymatic activities tested and suppressed degranulation in RBL cells in a dose-dependent manner. Therefore, the active components present in this S. fusiforme fraction achieve the anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the enzymatic activities and degranulation in the ear of mice. Thus, S. fusiforme and its diethyl ether fraction could be useful ingredients in functional foods.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brownlee IA, Allen A, Pearson JP, Dettmar PW, Havler ME, Atherton MR, Onsøyen E (2005) Alginate as a source of dietary fiber. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 45:497–510
Li B, Lu F, Wei X, Zhao R (2008) Fucoidan: structure and bioactivity. Molecules 13:1671–1695
Nishino T, Nagumo T (1987) Sugar constituents and blood-anticoagulant activities of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides in nine brown seaweed species. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 61:361–363 (in Japanese)
Yoon MO, Lee SC, Rhim JW, Kim JM (2004) Comparison of alginic acid yields and viscosity by different extraction conditions from various seaweeds (Laminaria religiosa, Hizikia fusiforme, and Undaria pinnatifida). J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 33:747–752 (in Korean)
Nakamura T, Nagayama K, Uchida K, Tanaka R (1996) Antioxidant activity of phlorotannins isolated from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis. Fish Sci 62:923–926
Ragan MA, Glombitza KW (1986) Phlorotannins, brown algal polyphenols. Prog Phycol Res 4:129–241
Oka Y, Kiriyama S, Yoshida A (1973) Sterol composition of fruits, fungi, marine algae and tea, coffee and cocoa. J Jpn Soc Food Nutr 26:317–327 (in Japanese)
Dobashi K, Nishino T, Fujihara M, Nagumo T (1989) Isolation and preliminary characterization of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides with blood-anticoagulant activity from the brown seaweed Hizikia fusiforme. Carbohydr Res 194:315–320
Choi EY, Hwang HJ, Kim IH, Nam TJ (2009) Protective effects of a polysaccharide from Hizikia fusiformis against ethanol toxicity in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 47:134–139
Choi EY, Hwang HJ, Nam TJ (2010) Protective effect of a polysaccharide from Hizikia fusiformis against ethanol-induced cytotoxicity in IEC-6 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 24:79–84
Okai Y, Higashi-Okai K, Ishizaka S, Ohtani K, Matsui-Yuasa I, Yamashita U (1998) Possible immunodulating activities in an extract of edible brown alga, Hijikia fusiforme (Hijiki). J Sci Food Agric 76:56–62
Jeong SC, Jeong YT, Lee SM, Kim JH (2015) Immune-modulating activities of polysaccharides extracted from brown algae Hizikia fusiforme. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 79:1362–1365
Jang MS, Park HY, Nam KH (2014) Whitening effects of 4-hydroxyphenethyl alcohol isolated from water boiled with Hizikia fusiformis. Food Sci Biotechnol 23:555–560
Kim TY, Jin CY, Kim GY, Choi IW, Jeong YK, Nam TJ, Kim SK, Choi YH (2009) Ethyl alcohol extracts of Hizikia fusiforme sensitize AGS human gastric adenocarcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis. J Med Food 12:782–787
Huh GW, Lee DY, In SJ, Lee DG, Park SY, Yi TH, Kang HC, Seo WD, Baek NI (2012) Fucosterols from Hizikia fusiformis and their proliferation activities on osteosarcoma-derived cell MG63. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 55:551–555
Lee KH, Kim HJ, Kim HB, Kim ST, Choi YR, Seo DW, Yu JM, Jang SK, Kim SM, Lee DI, Joo SS (2013) Hizikia fusiformis fractions successfully improve atopic dermatitis indices in anti-CD3-stimulated splenocytes and 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-treated BALB/c mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 66:466–476
Hwang E, Park SY, Shin HS, Lee DG, Yi TH (2014) Effect of oral administration of fucosterol from Hizikia fusiformis on DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Food Sci Biotechnol 23:593–599
Jung KH, Ha E, Uhm YK, Park HJ, Kim MJ, Kim HK, Baik HH, Hong MS, Yang JS, Yim SV (2007) Suppressive effect by Hizikia fusiforme on the production of tumor necrosis factor in BV2 murine microglial cells. Neurol Res 29:88–92
Funk CD (2001) Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science 294:1871–1875
Kakegawa H, Matsumoto H, Satoh T (1985) Activation of hyaluronidase by metallic salts and compound 48/80, and inhibitory effect of anti-allergic agents on hyaluronidase. Chem Pharm Bull 33:642–646
Meurer R, Opas EE, Humes JL (1988) Effects of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase inhibitors on inflammation associated with oxazolone-induced delayed hypersensitivity. Biochem Pharmacol 37:3511–3514
Rao TS, Currie JL, Shaffer AF, Isakson PC (1993) Comparative evaluation of arachidonic acid (AA)- and tetradecanoylphorbol acetate (TPA)-induced dermal inflammation. Inflammation 17:723–741
Xu H, Diluio NA, Fairchild KL (1996) T cell populations primed by hapten sensitization in contact sensitivity are distinguished by polarized patterns of cytokine production: interferon-γ producing (Tcl) effector CD8+ T cells and interleukin (IL) 4/IL-10-producing (Th2) negative regulatory CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med 183:1001–1012
Bursumian EL, Isersky C, Petorino MG, Siraganian RP (1981) IgE-induced histamine release from rat basophilic leukemia cell lines: isolation of releasing and nonreleasing clones. Eur J Immunol 11:317–323
Yoshino K, Kawaguchi T, Yamazaki K, Sano M (2010) Preventive effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate on mouse type IV allergy induced by oxazolone and its antiinflammatory activities. J Technol Educ 17:57–65
Tachibana H (2011) Green tea polyphenol sensing. Proc Jpn Acad B Phys 87:66–80
Sugiura Y, Torii T, Tanaka R, Matsushita T (2012) Inhibitory effect of extracts from the brown alga, Ecklonia stolonifera, on enzymes responsible for allergic reactions and degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells. Food Sci Technol Res 18:467–471
Young JM, Spires DA, Bedord CJ, Wagner B, Ballaron SJ, Young LM (1984) The mouse ear inflammatory response to topical arachidonic acid. J Invest Dermatol 82:367–371
Suzuki M, Yoshino K, Maeda-Yamamoto M, Miyase T, Sano M (2000) Inhibitory effects of tea catechins and O-methylated derivatives of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate on mouse type IV allergy. J Agric Food Chem 48:5649–5653
Sugiura Y, Matsuda K, Okamoto T, Yamada Y, Imai K, Ito T, Kakinuma M, Amano H (2009) The inhibitory effects of components from a brown alga, Eisenia arborea, on degranulation of mast cells and eicosanoid synthesis. J Funct Foods 1:387–393
Kawakami Y, Nakamura T, Hosokawa T, Suzuki-Yamamoto T, Yamashita H, Kimoto M, Tsuji H, Yoshida H, Hada T, Takahashi Y (2009) Antiproliferative activity of guava leaf extract via inhibition of prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthase isoforms. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 80:239–245
Komoda T, Morimitsu Y, Hirota H, Hirota A (1995) USF-19A, a new lipoxygenase inhibitor from Streptomyces sp. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:924–926
Schwartz LB, Lewis RA, Seldin D, Austen KF (1981) Acid hydrolases and tryptase from secretory granules of dispersed human lung mast cells. J Immunol 126:1290–1294
Kujubu DA, Fletcher BS, Varnum BC, Lim RW, Herschman HR (1991) TIS10, a phorbol ester tumor promoter-inducible RNA from Swiss 3T3 cells, encodes a novel prostaglandin synthase/cyclooxygenase homologue. J Biol Chem 266:12866–12872
Ferreri NR, Millet I, Paliwal V, Herzog W, Solomon D, Ramabhadran R, Askenase PW (1991) Induction of macrophage TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, and PGE2 production by DTH-initiating factors. Cell Immunol 137:389–405
Ishizaka T, Ishizaka K, Tomioka H (1972) Release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) by IgE-anti-IgE reactions on monkey mast cells. J Immunol 108:513–520
Siriwardhana N, Lee KW, Jeon YJ (2005) Radical scavenging potential of hydrophilic phlorotannins of Hizikia fusiformis. Algae 20:69–75
Folin O, Denis W (1915) A colorimetric method for the determination of phenols (and phenol derivatives) in urine. J Biol Chem 22:305–308
Kidowaki S, Tanaka T, Nishiyama Y, Hayashi Y, Takatsuto S (2001) Laboratory experiment for natural products chemistry: isolation and determination of fucosterol in kelp (Laminaria religiosa Miyabe). Chem Educ 49:647–650 (in Japanese)
Katayama M, Sugawa-Katayama Y (2007) Effect of temperature on the diminution of retained arsenic in dried Hijiki, Sargassum fusiforme (Harvey) Setchell, by water-soaking. J Home Econ Jpn 58:75–80
Sakurai T, Kaise T, Matsubara C (1998) Inorganic and methylated arsenic compounds induce cell death in murine macrophages via different mechanisms. Chem Res Toxicol 11:273–283
Hanaoka K, Miyamoto S, Usui M (2012) Effect of hot water washing and soaking on the arsenic content of the brown alga Akamoku, Sargassum horneri. J Natl Fish Univ 61:23–26 (in Japanese)
Siriwardhana N, Kim KN, Lee KW, Kim SH, Ha JH, Song CB, Lee JB, Jeon YJ (2008) Optimization of hydrophilic antioxidant extraction from Hizikia fusiformis by integrating treatments of enzymes, heat and pH control. Int J Food Sci Technol 43:587–596
Choi JI, Kim JH, Chun BS, Ahn DH, Kim GH, Lee JW (2011) Enhancement of the physiological activities of cooking drip of Hizikia fusiformis by electron-beam irradiation. J Food Biochem 35:1058–1070
Li C, Wang C, Wang S, Qian G, Zhu Q, Liu Y, Wang W (2013) Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction technology of Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharides and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Food Sci Technol Res 19:157–162
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a research project promotion grant from the National Fisheries University and by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 23880036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugiura, Y., Kinoshita, Y., Abe, M. et al. Suppressive effects of the diethyl ether fraction from a brown alga Sargassum fusiforme on allergic and inflammatory reactions. Fish Sci 82, 369–377 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-016-0969-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-016-0969-9