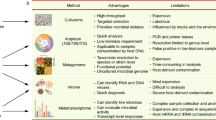
Abstract
The study of the microbial community—the microbiome—associated with a human host is a maturing research field. It is increasingly clear that the composition of the human’s microbiome is associated with various diseases such as gastrointestinal diseases, liver diseases and metabolic diseases. Using high-throughput technologies such as next-generation sequencing and mass spectrometry–based metabolomics, we are able to comprehensively sequence the microbiome—the metagenome—and associate these data with the genomic, epigenomics, transcriptomic and metabolic profile of the host. Our review summarises the application of integrating host omics with microbiome as well as the analytical methods and related tools applied in these studies. In addition, potential future directions are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Aziz MA, Cooper A, Weyrich LS (2016) Exploring relationships between host genome and microbiome: new insights from genome-wide association studies. Front Microbiol 7:1611. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01611
Barko PC, McMichael MA, Swanson KS, Williams DA (2018) The gastrointestinal microbiome: a review. J Vet Intern Med 32:9–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvim.14875
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Blekhman R, Goodrich JK, Huang K et al (2015) Host genetic variation impacts microbiome composition across human body sites. Genome Biol 16:191. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-015-0759-1
Bonder MJ, Kurilshikov A, Tigchelaar EF et al (2016) The effect of host genetics on the gut microbiome. Nat Genet 48:1407–1412. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3663
Breitwieser FP, Lu J, Salzberg SL (2017) A review of methods and databases for metagenomic classification and assembly. Brief Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx120
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Castro-Nallar E, Shen Y, Freishtat RJ et al (2015) Integrating microbial and host transcriptomics to characterize asthma-associated microbial communities. BMC Med Genet 8:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-015-0121-1
Chierico FD, Nobili V, Vernocchi P et al (2017) Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology 65:451–464. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28572
Cho I, Blaser MJ (2012) The human microbiome: at the interface of health and disease. Nat Rev Genet 13:260–270. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3182
Chong J, Xia J (2017) Computational approaches for integrative analysis of the metabolome and microbiome. Metabolites 7(4):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7040062
Chun H, Keleş S (2010) Sparse partial least squares regression for simultaneous dimension reduction and variable selection. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 72:3–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9868.2009.00723.x
Conti G, Frühwirth-Schnatter S, Heckman JJ, Piatek R (2014) Bayesian exploratory factor analysis. J Econom 183:31–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2014.06.008
Davenport ER, Cusanovich DA, Michelini K et al (2015) Genome-wide association studies of the human gut microbiota. PLoS One 10:e0140301. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140301
Devoid S, Overbeek R, DeJongh M et al (2013) Automated genome annotation and metabolic model reconstruction in the SEED and Model SEED. Methods Mol Biol 985:17–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-299-5_2
Dixon P (2003) VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J Veg Sci 14:927–930. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1654-1103.2003.tb02228.x
Dray S, Dufour A-B (2017) The ade4 package: implementing the duality diagram for ecologists. J Stat Softw. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v022.i04
de Steenhuijsen Piters WAA, Heinonen S, Hasrat R et al (2016) Nasopharyngeal microbiota, host transcriptome, and disease severity in children with respiratory syncytial virus infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 194:1104–1115. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201602-0220OC
Dong X, Yambartsev A, Ramsey SA et al (2015) Reverse enGENEering of regulatory networks from big data: a roadmap for biologists. Bioinforma Biol Insights 9:61–74. https://doi.org/10.4137/BBI.S12467
Ge T, Chen C-Y, Neale BM et al (2017) Phenome-wide heritability analysis of the UK Biobank. PLoS Genet 13:e1006711. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006711
Genomes Project (2012) An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 491:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11632
Gilbert JA, Blaser MJ, Caporaso JG et al (2018) Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat Med 24:392–400. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4517
Goodrich JK, Waters JL, Poole AC et al (2014) Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 159:789–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.053
Goodrich JK, Davenport ER, Beaumont M et al (2016) Genetic determinants of the gut microbiome in UK twins. Cell Host Microbe 19:731–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2016.04.017
Gower JC (1975) Generalized procrustes analysis. Psychometrika 40:33–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291478
Hall AB, Tolonen AC, Xavier RJ (2017) Human genetic variation and the gut microbiome in disease. Nat Rev Genet 18:690–699. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2017.63
Harris RA, Shah R, Hollister EB et al (2016) Colonic mucosal epigenome and microbiome development in children and adolescents. J Immunol Res 2016:9170162. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9170162
Hill CJ, Lynch DB, Murphy K et al (2017) Evolution of gut microbiota composition from birth to 24 weeks in the INFANTMET cohort. Microbiome 5:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-016-0213-y
Hua X, Song L, Yu G, et al (2015) MicrobiomeGWAS: a tool for identifying host genetic variants associated with microbiome composition. https://doi.org/10.1101/031187
Huang Y, Ma S-F, Espindola MS et al (2017) Microbes are associated with host innate immune response in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 196:208–219. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201607-1525OC
Igartua C, Davenport ER, Gilad Y et al (2017) Host genetic variation in mucosal immunity pathways influences the upper airway microbiome. Microbiome 5:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-016-0227-5
iHMP Research Network Consortium (2014) The integrative human microbiome project: dynamic analysis of microbiome-host omics profiles during periods of human health and disease. Cell Host Microbe 16:276–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2014.08.014
Imhann F, Vila AV, Bonder MJ et al (2018) Interplay of host genetics and gut microbiota underlying the onset and clinical presentation of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 67:108–119. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312135
Jolliffe IT, Cadima J (2016) Principal component analysis: a review and recent developments. Phil Trans R Soc A 374:20150202. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2015.0202
Kellermayer R (2017) Challenges for epigenetic research in inflammatory bowel diseases. Epigenomics 9:527–538. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2016-0155
Knights D, Silverberg MS, Weersma RK et al (2014) Complex host genetics influence the microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease. Genome Med 6:107. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-014-0107-1
Kostic AD, Gevers D, Siljander H et al (2015) The dynamics of the human infant gut microbiome in development and in progression toward type 1 diabetes. Cell Host Microbe 17:260–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2015.01.001
Kreznar JH, Keller MP, Traeger LL et al (2017) Host genotype and gut microbiome modulate insulin secretion and diet-induced metabolic phenotypes. Cell Rep 18:1739–1750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.062
Kroemer G, Zitvogel L (2018) Cancer immunotherapy in 2017: the breakthrough of the microbiota. Nat Rev Immunol 18:87–88
Kumar H, Lund R, Laiho A et al (2014) Gut microbiota as an epigenetic regulator: pilot study based on whole-genome methylation analysis. mBio 5:e02113–e02114. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02113-14
Kurilshikov A, Wijmenga C, Fu J, Zhernakova A (2017) Host genetics and gut microbiome: challenges and perspectives. Trends Immunol 38:633–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2017.06.003
Lam KC, Vyshenska D, Hu J et al (2018) Transkingdom network reveals bacterial players associated with cervical cancer gene expression program. PeerJ 6:e5590
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinf 9:559. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Larsen PE, Collart FR, Field D et al (2011) Predicted relative metabolomic turnover (PRMT): determining metabolic turnover from a coastal marine metagenomic dataset. Microb Inform Exp 1:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/2042-5783-1-4
Li D, Xie Z, Le Pape M, Dye T (2015) An evaluation of statistical methods for DNA methylation microarray data analysis. BMC Bioinf 16:217. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-015-0641-x
Lippert C, Listgarten J, Liu Y et al (2011) FaST linear mixed models for genome-wide association studies. Nat Methods 8:833–835. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1681
Lowe R, Shirley N, Bleackley M et al (2017) Transcriptomics technologies. PLoS Comput Biol 13:e1005457. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005457
Lozupone CA, Knight R (2008) Species divergence and the measurement of microbial diversity. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:557–578. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00111.x
Lynch J, Tang K, Priya S et al (2017) HOMINID: a framework for identifying associations between host genetic variation and microbiome composition. GigaScience 6:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/gix107
McGeachie MJ, Sordillo JE, Gibson T et al (2016) Longitudinal prediction of the infant gut microbiome with dynamic Bayesian networks. Sci Rep 6:20359. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20359
McHardy IH, Goudarzi M, Tong M et al (2013) Integrative analysis of the microbiome and metabolome of the human intestinal mucosal surface reveals exquisite inter-relationships. Microbiome 1:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-2618-1-17
Meng C, Zeleznik OA, Thallinger GG et al (2016) Dimension reduction techniques for the integrative analysis of multi-omics data. Brief Bioinform 17:628–641. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbv108
Molyneaux PL, Willis-Owen SAG, Cox MJ et al (2017) Host–microbial interactions in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 195:1640–1650. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201607-1408OC
Moore LD, Le T, Fan G (2013) DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:23–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.112
Morgan XC, Kabakchiev B, Waldron L et al (2015) Associations between host gene expression, the mucosal microbiome, and clinical outcome in the pelvic pouch of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Genome Biol 16:67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-015-0637-x
Morgun A, Dzutsev A, Dong X et al (2015) Uncovering effects of antibiotics on the host and microbiota using transkingdom gene networks. Gut 64:1732–1743. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308820
Nakatsu G, Li X, Zhou H et al (2015) Gut mucosal microbiome across stages of colorectal carcinogenesis. Nat Commun 6:8727. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9727
Nguyen N-P, Warnow T, Pop M, White B (2016) A perspective on 16S rRNA operational taxonomic unit clustering using sequence similarity. Npj Biofilms and Microbiomes 2:16004. https://doi.org/10.1038/npjbiofilms.2016.4
Noecker C, Eng A, Srinivasan S et al (2016) Metabolic model-based integration of microbiome taxonomic and metabolomic profiles elucidates mechanistic links between ecological and metabolic variation. mSystems 1:e00013–e00015. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00013-15
Nugent JL, McCoy AN, Addamo CJ et al (2014) Altered tissue metabolites correlate with microbial dysbiosis in colorectal adenomas. J Proteome Res 13:1921–1929. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr4009783
Org E, Parks BW, Joo JWJ et al (2015) Genetic and environmental control of host-gut microbiota interactions. Genome Res 25:1558–1569. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.194118.115
Pan W (2001) Akaike’s information criterion in generalized estimating equations. Biometrics 57:120–125
Pedersen HK, Gudmundsdottir V, Nielsen HB et al (2016) Human gut microbes impact host serum metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature 535:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18646
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM et al (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38:904–909. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1847
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575. https://doi.org/10.1086/519795
Qin Y, Wade PA (2018) Crosstalk between the microbiome and epigenome: messages from bugs. J Biochem (Tokyo) 163:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvx080
Rakyan VK, Down TA, Balding DJ, Beck S (2011) Epigenome-wide association studies for common human diseases. Nat Rev Genet 12:529–541. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3000
Ramanan D, Bowcutt R, Lee SC et al (2016) Helminth infection promotes colonization resistance via type 2 immunity. Science 352:608–612. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf3229
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D et al (2015) limma powers differential expression analyses for RNAsequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e47–e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Rodrigues RR, Shulzhenko N, Morgun A (2018) Transkingdom networks: a systems biology approach to identify causal members of host-microbiota interactions. Methods Mol Biol 1849:227–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8728-3_15
Rothschild D, Weissbrod O, Barkan E et al (2018) Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 555:210–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25973
Schaefer J, Opgen-Rhein R, Strimmer and K (2015) GeneNet: Modeling and Inferring Gene Networks. R package version 1.2.13 https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=GeneNet. Accessed 28 Dec 2018
Schwartz S, Friedberg I, Ivanov IV et al (2012) A metagenomic study of diet-dependent interaction between gut microbiota and host in infants reveals differences in immune response. Genome Biol 13:r32. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2012-13-4-r32
Shabalin AA (2012) Matrix eQTL: ultra fast eQTL analysis via large matrix operations. Bioinformatics 28:1353–1358. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts163
Shen Y, Rahman M, Piccolo SR et al (2015) ASSIGN: context-specific genomic profiling of multiple heterogeneous biological pathways. Bioinformatics 31:1745–1753. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv031
Shoaie S, Karlsson F, Mardinoglu A et al (2013) Understanding the interactions between bacteria in the human gut through metabolic modeling. Sci Rep 3:2532. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02532
Steinway SN, Biggs MB, Jr TPL et al (2015) Inference of network dynamics and metabolic interactions in the gut microbiome. PLoS Comput Biol 11:e1004338. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004338
Tahara T, Hirata I, Nakano N et al (2017) Potential link between Fusobacterium enrichment and DNA methylation accumulation in the inflammatory colonic mucosa in ulcerative colitis. Oncotarget 8:61917–61926. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18716
Tian Y, Nichols RG, Cai J et al (2018) Vitamin A deficiency in mice alters host and gut microbial metabolism leading to altered energy homeostasis. J Nutr Biochem 54:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.10.011
Trygg J, Wold S (2003) O2-PLS, a two-block (X–Y) latent variable regression (LVR) method with an integral OSC filter. J Chemom 17:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.775
Tsay J-CJ, Wu BG, Badri MH et al (2018) Airway microbiota is associated with up-regulation of the PI3K pathway in lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201710-2118OC
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Hamady M et al (2007) The human microbiome project: exploring the microbial part of ourselves in a changing world. Nature 449:804–810. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06244
Turpin W, Espin-Garcia O, Xu W et al (2016) Association of host genome with intestinal microbial composition in a large healthy cohort. Nat Genet 48:1413–1417. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3693
Wang W, Baladandayuthapani V, Morris JS et al (2013) iBAG: integrative Bayesian analysis of high-dimensional multiplatform genomics data. Bioinformatics 29:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts655
Wang J, Thingholm LB, Skiecevičienė J et al (2016) Genome-wide association analysis identifies variation in vitamin D receptor and other host factors influencing the gut microbiota. Nat Genet 48:1396–1406. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3695
Wang J, Kurilshikov A, Radjabzadeh D et al (2018) Meta-analysis of human genome-microbiome association studies: the MiBioGen consortium initiative. Microbiome 6:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-018-0479-3
Weir TL, Manter DK, Sheflin AM et al (2013) Stool microbiome and metabolome differences between colorectal cancer patients and healthy adults. PLoS One 8:e70803. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070803
Xie H, Guo R, Zhong H et al (2016) Shotgun metagenomics of 250 adult twins reveals genetic and environmental impacts on the gut microbiome. Cell Syst 3:572–584.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2016.10.004
Zhang X-S, Li J, Krautkramer KA et al (2018) Antibiotic-induced acceleration of type 1 diabetes alters maturation of innate intestinal immunity. ELife Sci 7:1–37. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.37816
Zhao Y, Johnson WE (2018) Exploring host-microbe interactions in lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201807-1225ED
Zhao N, Chen J, Carroll IM et al (2015) Testing in microbiome-profiling studies with MiRKAT, the microbiome regression-based kernel association test. Am J Hum Genet 96:797–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.04.003
Zhernakova A, Kurilshikov A, Bonder MJ et al (2016) Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity. Science 352:565–569. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad3369
Zhou X, Stephens M (2012) Genome-wide efficient mixed-model analysis for association studies. Nat Genet 44:821–824. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2310
Zierer J, Jackson MA, Kastenmüller G et al (2018) The fecal metabolome as a functional readout of the gut microbiome. Nat Genet 50:790–795. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0135-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Funding was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81330011, 81330014, 81790631, 81790633, 81570512 and 81121002), the Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81721091), and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 program) (grant no. 2013CB531401). This work was also supported in part by funds from the New South Wales Ministry of Health, a National Health and Medical Research Council Career Development Fellowship (1105271 to JWKH) and the National Heart Foundation (Future Leader Fellowship 100848 to JWKH and 101204 to EG).
Conflict of interest
Qing Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Kaicen Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Wenrui Wu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Eleni Giannoulatou declares that she has no conflict of interest. Joshua W. K. Ho declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lanjuan Li declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of a Special Issue on ‘Big Data’ edited by Joshua WK Ho and Eleni Giannoulatou.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, K., Wu, W. et al. Host and microbiome multi-omics integration: applications and methodologies. Biophys Rev 11, 55–65 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-018-0491-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-018-0491-7