Abstract
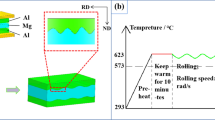
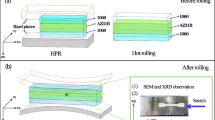
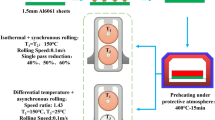
The long manufacturing process, difficult coordinated regulation of structural properties and interface bonding ability are some of the difficulties that restrict the rapid development of lightweight composite plate forming and manufacturing for a long time. In order to solve the above problems, this paper proposes adding hard plate to roll Al/Mg/Al composite plates. The thickness of Mg/Al is 10:1, and the hard-plate rolling process experiments were carried out by designing five groups of different temperatures. The influence of magnesium plate microstructure evolution on the interface bonding ability and mechanical behavior of composite plates is mainly studied. Under the same conditions, the matrix microstructure changes greatly from 200 to 350 °C. At 350 °C, the microstructure of Mg plate in ND is uniform without shear bands and twins. Its recrystallization ratio is 31.77%, which played a role in weakening the texture and reducing its anisotropy. Interestingly, in the process of three-point bending, the non-basal plane slip and the basal plane slip start simultaneously, the maximum bending strength of the composite plate reaches 504 MPa, and the interface was well bonded without obvious bending fatigue phenomenon. The tear test showed that the tear load reaches 0.42 kN, and the elastic elongation stage of Al is longer than the tear propagation stage, and the interface bonding was uniform. The hard plate rolling process provides scientific guidance for the forming and preparation of composite plates.
Graphic Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 February 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-023-01409-7
References
Z. Yan, Z. Zhang, X. Li, J. Xu, Q. Wang, G. Zhang, J. Zheng, H. Fan, K. Xu, J. Zhu, Y. Xue, J. Alloy. Compd. 822, 153698 (2020)
P. Wankhede, K. Suresh, Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 6, 458 (2020)
A. Ramesh, S. Sathian, V. Satheeshkumar, Mater. Today Proc. 5, 25255 (2018)
K. Hassan, A.S. Kang, C. Prakash, G. Singh, Mater. Today Proc. 50, 1043 (2022)
Y. He, H. Xu, M. Hu, B. Jiang, Z. Ji, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 53, 82 (2020)
Y. Wang, S. Zhang, R. Wu, N. Turakhodjaev, L. Hou, J. Zhang, S. Betsofen, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 61, 197 (2021)
J. Wang, L. Xu, R. Wu, J. Feng, J. Zhang, L. Hou, M. Zhang , Acta Metall. Sin.-Engl. 33, 490 (2020)
J. Tang, L. Chen, G. Zhao, C. Zhang, J. Yu, J. Alloy. Compd. 784, 727 (2019)
G. Chen, X. Chang, J. Zhang, Y. Jin, C. Sun, Q. Chen, Z. Zhao, Met. Mater. Int. 26, 1574 (2020)
X. Bi, Y. Hu, R. Li, H. Zhao, T. Li, J. Alloy. Compd. 900, 163417 (2022)
W.-W Yang, X.-Q Cao, L.-F Wang, Z.-Q. Chen, W.-X. Wang, D.-Y. Wang, Mat. Res. 21, e20180350 (2018)
Y. Yu, P. Yan, T. Chai, B. Yan, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 36, 2240056 (2022)
H.Y. Sun, D.H. Zhang, M. Ma, J.X. Zhang, W.C. Liu, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 31, 7624 (2022)
X.P. Zhang, T.H. Yang, S. Castagne, J.T. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 1954 (2011)
K. Wu, H. Chang, E. Maawad, W.M. Gan, H.G. Brokmeier, M.Y. Zheng, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 3073 (2010)
C.Z. Luo, W. Liang, X.R. Li, Y.J. Yao, Mater. Sci. Forum 747-748, 346 (2013)
K.S. Lee, D.H. Yoon, H.K. Kim, Y.-N. Kwon, Y.-S. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 556, 319 (2012)
X.P. Zhang, T.H. Yang, S. Castagne, J.T. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 1954 (2011)
P.D. Huo, F. Li, Y. Wang, X.M. Xiao, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 118, 55 (2022)
L. Chen, J. Tang, G. Zhao, C. Zhang, X. Chu, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 258, 165 (2018)
P.D. Huo, F. Li, Y. Wang, R.Z. Wu, R.H. Gao, A.X. Zhang, Mater. Design 219, 110696 (2022)
Z. Zhang, J. Zhang, J. Wang, Z. Li, J. Xie, S. Liu, K. Guan, R. Wu, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 281, 30 (2021)
J. Rong, P.-Y. Wang, M. Zha, C. Wang, X.-Y. Xu, H.-Y. Wang, Q.-C. Jiang, J. Alloy. Compd. 738, 246 (2018)
N. Wang, X. Chen, A. Li, Y. Li, H. Zhang, Y. Liu, T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 26, 359 (2016)
Y. Wang, F. Li, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, X.M. Xiao, J. Magnes. Alloy. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2021.05.007
Y. Wang, F. Li, N. Bian, H.Q. Du, P.D. Huo, J. Magnes. Alloy. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2021.08.035
H. Ding, X. Shi, Y. Wang, G. Cheng, S. Kamado, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 645, 196 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. JQ2022E004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate that they have no financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research. And the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
In the original version of this article, the given and family names of Rong He Gao were incorrectly structured. The correct name has been updated.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, R.H., Li, F., Niu, W.T. et al. Response Mechanism of Mechanical Behavior with Mg Plate Microstructure Evolution During Al/Mg/Al Composite Plate Rolled by hard Plate. Met. Mater. Int. 29, 2004–2016 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01348-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01348-9