Abstract
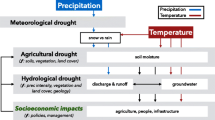
Drought assessment would be insufficient and unreliable when using the existing indicators based on a single variable (e.g., precipitation) or a combination of two variables (e.g., precipitation and runoff). Therefore, the entropy theory was utilized to develop a hybrid drought index (HDI) that combines meteorological, hydrological, and agricultural information based on precipitation, runoff, and soil moisture data, respectively, and it was applied to characterize the drought condition in Northwest China. Furthermore, the linkages between the atmospheric circulation anomaly/sunspot activities and the HDI series in Northwest China were explored through cross wavelet analysis. The results indicated that (1) HDI has a good performance to capture drought in Northwest China due to its consideration of multiple variables; (2) the annual HDI series in Northwest China was dominated by an insignificantly upward trend, except for Xinjiang, and this trend will be the opposite in the near future; and (3) generally, all of the sunspot activities, El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events, AMO (Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation), and PDO (Pacific Decadal Oscillation) had strong associations with the HDI series in Northwest China, in which sunspot activities had the strongest effects on drought conditions, whereas the AMO had the relatively lowest impacts. This study sheds new light on developing the hybrid drought index, and the findings are valuable for local drought mitigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AghaKouchak A (2015) A multivariate approach for persistence-based drought prediction: application to the 2010–2011 East Africa drought. J Hydrol 526:127–135
American Meteorological Society (1997) Meteorological drought—policy statement. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 78:847–849
Begueria S, Vicente-Serrano SM, Angulo-Martinez M (2010) A multiscalar global drought dataset: the SPEIbase: a new gridded product for the analysis of drought variability and impacts. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 91:1351–1354
Cai XL, Ye DX, Li Q et al (2013) Analysis of temporal-spatial variation characteristics of drought in Shaanxi Province based on compound meteorological drought index (CI). Agric Res Arid Areas 31(5):1–8 (in Chinese)
Chen LX, Zhu WQ, Wang W et al (1998) Studies on climate change in China in recent 45 years. Acta Meteor Sin 1:1–17 (in Chinese)
Cheng GD, Wang GX (2006) Changing trend of drought and drought disaster in northwest China and countermeasures. Earth Sci Front 13(1):3–14 (in Chinese)
Dai Y, Luo Y, Li XP (2010) Review of climate change in the journal Nature 2009. Adv Clim Chang Res 6(2):154–156 (in Chinese)
Dionisio A, Menezes R, Mendes DA (2007) Entropy and uncertainty analysis in financial markets. Appl Phys Finance Anal 4–7 July, Portugal
Dou RY, Yan JP (2013) Relationships between drought and flood disasters in Guanzhong plain and the activities of sunspot. J Arid Land Resour Environ 27(08):76–82 (in Chinese)
Ebrahimi N, Maasoumi E, Soofi ES (1999) Ordering univariate distributions by entropy and variance. J Econ 90(2):317–336
Edwards DC, McKee TB (1997) Characteristics of 20th century drought in the United States at multiple scales. Atmospheric Science Paper No. 634, May 1–30
Feng XL, Feng ZL, Luo LC et al (2008) Fractal analysis of climate change and Hurst index experiment in Tibetan Plateau in future. Arid Land Geogr 31(2):175–181 (in Chinese)
Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 2014. Climate change 2014: mitigation of climate change (vol. 3). Cambridge University Press
Gammel BM (1998) Hurst’s rescaled range statistical analysis for pseudorandom number generators used in physical simulations. Phys Rev E 58(2):2586–2597
Gao X, Bai HY, Zhang SH et al (2012) Climatic change tendency in Qinling Mountains from 1959 to 2009. Bull Soil Water Conserv 32(1):207–211 (in Chinese)
Glantz MH, Katz RW, Nicholls N (1991) Teleconnections linking world wide climatic anomalies, vol 535. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Griggs DJ, Noguer M (2002) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. Contribution of working group I to the third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Weather 57(8):267–269
Grinsted A, Moore JC, Jevrejeva S (2004) Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process Geophys 11(5/6):561–566
Guttman NB (1999) Accepting the standardized precipitation index: a calculation algorithm. J Am Water Resour Assoc 35(2):311–322
Hamed KH (2008) Trend detection in hydrologic data: the Mann–Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis. J Hydrol 349(3):350–363
Hamed KH (2009) Exact distribution of the Mann–Kendall trend test statistic for persistent data. J Hydrol 365(1):86–94
Hao Z, AghaKouchak A (2013) Multivariate standardized drought index: a parametric multi-index model. Adv Water Resour 57:12–18
Hayes MJ, Wilhelmi OV, Knutson CL (2004) Reducing drought risk: bridging theory and practice. Nat Hazard Rev 5(2):106–113
Heim Jr RR (2002) A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the United States. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83(8):1149
Hu NF, Wang AZ, Guan DX, Yuan FH, Jin CJ, Wu JB, Wang JJ (2010) Multiple time scale analysis of precipitation series in Changbai Mountain Region in 1959–2006. Chin J Appl Ecol 21(3):549–556 (in Chinese)
Huang SZ, Chang JX, Huang Q et al (2014) Spatio-temporal changes and frequency analysis of drought in the Wei river basin, China. Water Resour Manag 28(10):3095–3110
Huang SZ, Chang JX, Leng GY et al (2015a) Integrated index for drought assessment based on variable fuzzy set theory: a case study in the Yellow River basin, China. J Hydrol 527:608–618
Huang SZ, Huang Q, Chang JX, Zhu Y, Leng G, Xing L (2015b) Drought structure based on a nonparametric multivariate standardized drought index across the Yellow River basin, China. J Hydrol 530:127–136
Huang XY, Li YH, Feng JY et al (2015c) Climate characteristics of precipitation and extreme drought events in Northwest China. Acta Ecol Sin 35(5):1359–1370 (in Chinese)
Huang SZ, Huang Q, Leng GY, Liu SY (2016) A nonparametric multivariate standardized drought index for characterizing socioeconomic drought: a case study in the Heihe River basin. J Hydrol 542:875–883
Jevrejeva S, Moore JC, Grinsted A (2003) Influence of the Arctic Oscillation and El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) on ice conditions in the Baltic Sea: the wavelet approach. J Geophys Res: Atmos 108(D21):1–12
Kao SC, Govindaraju RS (2010) A copula-based joint deficit index for droughts. J Hydrol 380(1):121–134
Keyantash J, Dracup JA (2002) The quantification of drought: an evaluation of drought indices. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83(8):1167–1180
Kim Y, Kimball JS, Zhang K et al (2012) Satellite detection of increasing Northern Hemisphere non-frozen seasons from 1979 to 2008: implications for regional vegetation growth. Remote Sens Environ 121:472–487
Kim TW, Valdés JB, Yoo C (2003) Nonparametric approach for estimating return periods of droughts in arid regions. J Hydrol Eng 8(5):237–246
Knight JR, Folland CK, Scaife AA (2006) Climate impacts of the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. Geophys Res Lett 33(17):1–14
Kogan FN (2000) Contribution of remote sensing to drought early warning. Early warning systems for drought preparedness and drought management. pp 75–87
Li SS, Hong S, Liu XJ (2011) World climate change research trends. Adv Clim Chang Res 7(1):73–76 (in Chinese)
Li JF, Zhang Q, Chen XH et al (2012) SPI-based drought variations in Xinjiang, China. J Appl Meteorol Sci 23(3):322–330 (in Chinese)
Liang X, Lettenmaier DP, Wood EF, Burges SJ (1994) A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for GSMs. J Geophys Res: Atmos 99(D7):14415–14428
Liang X, Lettenmaier DP, Wood EF (1996) One-dimensional statistical dynamic representation of subgrid spatial variability of precipitation in the two-layer variable infiltration capacity model. J Geophys Res: Atmos 101(D16):21403–21422
Lin JK, Jiang YM, Zheng WH et al (2008) Automatic establishment of the initial black start schemes for power systems. Autom Electr Power Syst 32(2):72–75 (in Chinese)
Lin JK, Li TF, Zhao ZM et al (2012) Assessment on power system black-start schemes based on entropy-weighted fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model. Power Syst Technol 36(2):115–120 (in Chinese)
Liu GS, Guo AH, An SQ (2004) Research progress in Palmer drought severity index and it’s application. J Nat Disasters 13(4):21–27 (in Chinese)
Ma M, Ren L, Singh VP, Tu X, Jiang S, Liu Y (2015) Evaluation and application of the SPDI-JDI for droughts in Texas, USA. J Hydrol 521:34–45
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology. Boston, MA: American Meteorological Society 17(22):179–183
Mishra V, Cherkauer KA (2010) Retrospective droughts in the crop growing season: implications to corn and soybean yield in the Midwestern United States. Agric For Meteorol 150(7):1030–1045
Mishra AK, Singh VP (2010) A review of drought concepts. J Hydrol 391(1):202–216
Mishra AK, Singh VP, Desai VR (2009) Drought characterization: a probabilistic approach. Stoch Env Res Risk A 23(1):41–55
Mitchell JM, Dzerdzeevskii B, Flohn H et al (1966) Climate change. WHO Technical Note 79
Oliver R, Ballester JL (1996) Rescaled range analysis of the asymmetry of solar activity. Sol Phys 169(1):215–224
Palmer WC (1965) Meteorological drought, Rep. 45. U.S. Dept. of Commerce, Washington, D.C, pp 58
Palmer WC (1968) Keeping track of crop moisture conditions, nationwide: the new crop moisture index. Weatherwise 21:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/00431672.1968.9932814
Pandey RP, Ramasastri KS (2001) Relationship between the common climatic parameters and average drought frequency. Hydrol Process 15(6):1019–1032
Pasquini AI, Depetris PJ (2011) Southern patagonia’s perito moreno glacier, Lake Argentino, and Santa Cruz River hydrological system: an overview. J Hydrol 405(1):48–56
Rajsekhar D, Singh VP, Mishra AK (2015) Multivariate drought index: an information theory based approach for integrated drought assessment. J Hydrol 526:164–182
Sang YF, Wang D (2008) Wavelets selection method in hydrologic series wavelet analysis. Shuili Xuebao 39(3):295–300 (in Chinese)
Sharma A (2000) Seasonal to interannual rainfall probabilistic forecasts for improved water supply management: part 1—a strategy for system predictor identification. J Hydrol 239(1):232–239
Shukla S, Steinemann AC, Lettenmaier DP (2011) Drought monitoring for Washington State: indicators and applications. J Hydrometeorol 12(1):66–83
Torrence C, Compo GP (1998) A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79(1):61–78
Van Gee B, Raspopov OM, Renssen H et al (2002) The role of solar forcing upon climate change. Climate Change: Natural forcing factors for climate change timescales 10–1 to 10–5 years18, 100
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, López-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23(7):1696–1718
Wan JH, Tan XM, Liu CD (2013) Spatial-temporal pattern of drought hazards in China’s Qing dynasty based on Forbidden City archives. Adv Water Sci 24(1):18–23 (in Chinese)
Wan JH, Lyu J, Liu HP et al (2014) Drought-flood variation characteristics and trends in arid Northwestern China during 1470–2008. Adv Water Sci 25(5):625–631 (in Chinese)
Wang YM, Feng Q, Li ZX (2014) Analysis of low cloud amount variations in the Northwest China during 1960–2005. Sci Geogr Sin 34(5):635–640 (in Chinese)
Waseem M, Ajmal M, Kim TW (2015) Development of a new composite drought index for multivariate drought assessment. J Hydrol 527:30–37
Wei ZF, Ren ZY, Zhang C et al (2014) Changes of vegetation cover and its correlation with precipitation and temperature in Northwest China. Bull Soil Water Conserv 34(03):283–289 (in Chinese)
Wilhite DA (2000) Drought as a natural hazard: concepts and definitions. In: Wilhite DA (ed) Drought: a global assessment, hazards disasters Ser, vol I. Routledge, New York, pp 3–18
Xu J, Chen Y, Lu F, Li W, Zhang L, Hong Y (2011) The nonlinear trend of runoff and its response to climate change in the Aksu River, western China. Int J Climatol 31(5):687–695
Xu XY, Zhu JW, Xie JC et al (2015) Evolution characteristics of drought/flood disasters in Xi’an Region from 1951 to 2012 and their correlation to related multiple events. J Nat Disasters 24(6):64–71 (in Chinese)
Yang Q, Qin ZH, Wang T et al (2012) Characteristics of climate factor change in Yulin Region during 1970–2010. Arid Land Geogr 35(5):695–707 (in Chinese)
Yang D, Wang H, Cheng JQ et al (2013) Climate change in Qinghai and its relationship with ENSO in the recent 50 years. Ecol Environ Sci 22(4):547–553 (in Chinese)
Yu B, Zwiers FW (2007) The impact of combined ENSO and PDO on the PNA climate: a 1,000-year climate modeling study. Clim Dyn 29(7–8):837–851
Zargar A, Sadiq R, Naser B et al (2011) A review of drought indices. Environ Rev 19(NA):333–349
Zhang S, Fan BJ (1995) China disaster report (1949–1995) (in Chinese)
Zhang Q, Yao YB, Li YH et al (2015) Research progress and prospect on the monitoring and early warning and mitigation technology of meteorological drought disaster in northwest China. Adv Earth Science 30(2):196–213 (in Chinese)
Zhao CC, Wang Y, Ding YJ et al (2011) Spatial-temporal variations of temperature and precipitation in northern China in recent 50 years. Plateau Meteorol 30(2):385–390 (in Chinese)
Funding
This study has been partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51479160, 51709221) and the Project Supported by Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (2016JQ5061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Zhou, L. & Huang, S. A hybrid drought index combining meteorological, hydrological, and agricultural information based on the entropy weight theory. Arab J Geosci 11, 91 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3438-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3438-1