Abstract
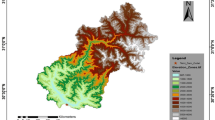
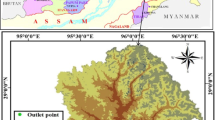
Basins located in Eastern Turkey are largely fed by snowmelt runoff during spring and early summer seasons. This study investigates the efficiency of artificial neural networks (ANNs) in snowmelt runoff generation. Although ANNs have been used for streamflow simulating/forecasting in the last two decades, using satellite-based snow-covered area (SCA) maps and meteorological observations as inputs to ANN provides a novel basis for estimating streamflow. The proposed methodology is implemented over Upper Euphrates River Basin in Eastern Turkey. SCA data was acquired from Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS) for an 8-year period from February 2004 to September 2011. Meteorological observations including daily cumulative precipitation and daily average air temperatures were obtained from Turkish State Meteorological Services. The simulation results are promising with coefficient of correlation varying from 0.67 to 0.98 among proposed models. Past days discharge was found to substantially improve the forecast accuracy. The paper presents the expected basin discharge for 2011 water year based on meteorological observations and SCA input.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abudu S, King JP, Bawazir AS (2011) Forecasting monthly streamflow of spring-summer runoff season in Rio Grande headwaters basin using stochastic hybrid modeling approach. J Hydrol Eng 16:384–390. doi:10.1061/(Asce)He.1943-5584.0000322
Akyurek Z, Surer S, Beser O (2011) Investigation of the snow-cover dynamics in the Upper Euphrates Basin of Turkey using remotely sensed snow-cover products and hydrometeorological data. Hydrol Process 25:3637–3648. doi:10.1002/Hyp.8090
Armstrong JS (1985) Long-range forecasting: from crystal ball to computer 2nd Edition. Wiley
Ataş M, Yardimci Y, Temizel A (2012) A new approach to aflatoxin detection in chili pepper by machine vision. Comput Electron Agric 87:129–141. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2012.06.001
Birikundavyi S, Labib R, Trung HT, Rousselle J (2002) Performance of neural networks in daily streamflow forecasting. J Hydrol Eng 7:392–398. doi:10.1061/(Asce)1084-0699(2002)7:5(392)
Bostan PA, Heuvelink GBM, Akyurek SZ (2012) Comparison of regression and kriging techniques for mapping the average annual precipitation of Turkey. Int J Appl Earth Obs 19:115–126. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2012.04.010
Breiman L, Spector P (1992) Submodel selection and evaluation in regression—the X-random case. Int Stat Rev 60:291–319. doi:10.2307/1403680
Chokmani K, Ouarda TBMJ, Hamilton S, Ghedira MH, Gingras H (2008) Comparison of ice-affected streamflow estimates computed using artificial neural networks and multiple regression techniques. J Hydrol 349:383–396. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.11.024
Crane RG, Anderson MR (1984) Satellite discrimination of snow cloud surfaces. Int J Remote Sens 5:213–223
Dozier J (1989) Spectral signature of alpine snow cover from the Landsat Thematic Mapper. Remote Sens Environ 28:9. doi:10.1016/0034-4257(89)90101-6
Gao Y, Xie HJ, Yao TD, Xue CS (2010) Integrated assessment on multi-temporal and multi-sensor combinations for reducing cloud obscuration of MODIS snow cover products of the Pacific Northwest USA. Remote Sens Environ 114:1662–1675. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2010.02.017
Gessel G (1989) An algorithm for snow and ice detection using AVHRR data. An extension to the APOLLO software package. Int J Remote Sens 10:897–905
Govindaraju RS, Rao AR (2000) Artificial neural networks in hydrology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Amsterdam
Hall DK, Riggs GA, Salomonson VV (1995) Development of methods for mapping global snow cover using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer data. Remote Sens Environ 54:127–140. doi:10.1016/0034-4257(95)00137-P
Hall DK, Riggs GA, Salomonson VV, DiGirolamo NE, Bayr KJ (2002) MODIS snow-cover products. Remote Sens Environ 83:181–194. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00095-0
Haykin S (1999) Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation. 2nd edition, Prentice-Hall
Helfrich SR, McNamara D, Ramsay BH, Baldwin T, Kasheta T (2007) Enhancements to, and forthcoming developments in the Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS). Hydrol Process 21:1576–1586. doi:10.1002/Hyp.6720
Kisi O (2007) Streamflow forecasting using different artificial neural network algorithms. J Hydrol Eng 12:532–539. doi:10.1061/(Asce)1084-0699(2007)12:5(532)
Kisi O (2008) River flow forecasting and estimation using different artificial neural network techniques. Hydrol Res 39:27–40. doi:10.2166/Nh.2008.026
Kisi O (2009) Neural networks and wavelet conjunction model for intermittent streamflow forecasting. J Hydrol Eng 14:773–782. doi:10.1061/(Asce)He.1943-5584.0000053
Kisi O (2013) Evolutionary neural networks for monthly pan evaporation modeling. J Hydrol 498:36–45. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.06.011
Kisi O, Tombul M (2013) Modeling monthly pan evaporations using fuzzy genetic approach. J Hydrol 477:203–212
Kisi O, Shiri J, Tombul M (2013) Modeling rainfall-runoff process using soft computing techniques. Comput Geosci-UK 51:108–117. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2012.07.001
Kormos PR, Marks D, McNamara JP, Marshall HP, Winstral A, Flores AN (2014) Snow distribution, melt and surface water inputs to the soil in the mountain rain-snow transition zone. J Hydrol 519:190–204. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.06.051
Legates DR, McCabe GJ (1999) Evaluating the use of “goodness-of-fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour Res 35:233–241. doi:10.1029/1998wr900018
Lohani AK, Jain SK, Kumar R., Singh RD (2012) Stream flow forecasting using ANN and fuzzy logic. India Water Week 2012, water, energy and food security: call for solutions, 10–14 April 2012, New Delhi
Mazari N, Tekeli AE, Xie HJ, Sharif HO, El Hassan AA (2013) Assessment of ice mapping system and moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer snow cover maps over Colorado Plateau. J Appl Remote Sens 7 doi: 10.1117/1.Jrs.7.073540
McCulloch W, Pitts W (1943) A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5:115–133. doi:10.1007/bf02478259
Mognard N (2003) Snow cover dynamics. In: Bobylev LP, Kondratyev KY, Johannessen OM (eds) Arctic environment variability in the context of global change. Praxis-Springer, Chichester
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10(3):282–290
NSIDC, (2013) http://nsidc.org/data/docs/noaa/g02156_ims_snow_ice_analysis/index.html (last access 02 August 2014)
Papa F, Legresy B, Mognard NM, Josberger EG, Remy F (2002) Estimating terrestrial snow depth with the Topex-Poseidon altimeter and radiometer. IEEE T Geosci Remote 40:2162–2169. doi:10.1109/Tgrs.2002.802463
Parajka J, Bloschl G (2008) Spatio-temporal combination of MODIS images—potential for snow cover mapping. Water Resour Res 44 doi: 10.1029/2007wr006204
Parent AC, Anctil F, Cantin V, Boucher MA (2008) Neural network input selection for hydrological forecasting affected by snowmelt. J Am Water Resour Assoc 44:679–688. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.2008.00198.x
Pearson K (1895) Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc R Soc Lond 58:240–242
Ramsay BH (1998) The interactive multisensor snow and ice mapping system. Hydrol Process 12:1537–1546. doi:10.1002/(Sici)1099-1085(199808/09)12:10/11<1537::Aid-Hyp679>3.0.Co;2-A
Rees WG (2006) Remote sensing of snow and ice. Taylor and Francis, Cambridge University, London
Robinson DA, Dewey KF, Heim RR (1993) Global snow cover monitoring: an update. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 74:1689–1696. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1993)074<1689:GSCMAU>2.0.CO;2
Romanov P, Gutman G, Csiszar I (2000) Automated monitoring of snow cover over North America with multispectral satellite data. J Appl Meteorol 39:1866–1880. doi:10.1175/1520-0450(2000)039<1866:Amosco>2.0.Co;2
Rumelhart DE, Hinton GE, Williams RJ (1986) Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323:533–536. doi:10.1038/323533a0
Salas JD (1993) Analysis and modeling of hydrologic time series. In: Maidment DR (ed) Handbook of hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 19.1–19.71
Ṣensoy A, Uysal G (2012) The value of snow depletion forecasting methods towards operational snowmelt runoff estimation using MODIS and Numerical Weather Prediction Data. Water Resour Manag 26:3415–3440. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0079-0
Simic A, Fernandes R, Brown R, Romanov P, Park W (2004) Validation of VEGETATION, MODIS, and GOES plus SSM/I snow-cover products over Canada based on surface snow depth observations. Hydrol Process 18:1089–1104. doi:10.1002/Hyp.5509
Singh P, Spitzbart G, Hubl H, Weinmeister HW (1997) Hydrological response of snowpack under rain-on-snow events: a field study. J Hydrol 202:1–20. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(97)00004-8
Sönmez İ, Tekeli AE, Erdi E (2014) Snow cover trend analysis using Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System data over Turkey. Int J Climatol 34:2349–2361. doi:10.1002/Joc.3843
Şorman AA, Tekeli AE, Ṣensoy A, Ṣorman AÜ (2004) Forecasting the early snowmelt flood event of 2004—a case study from Upper Euphrates Basin. 6th International Congress on Advances in Civil Engineering, 6–8 October 2004 Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkiye
Ṣorman AA, Sensoy A, Tekeli AE, Sorman AU, Akyurek Z (2009) Modelling and forecasting snowmelt runoff process using the HBV model in the eastern part of Turkey. Hydrol Process 23:1031–1040. doi:10.1002/Hyp.7204
Surfleet CG, Tullos D (2013) Variability in effect of climate change on rain-on-snow peak flow events in a temperate climate. J Hydrol 479:24–34. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.021
Tekeli AE (2008) Early findings in comparison of AMSR-E/Aqua L3 global snow water equivalent EASE-grids data with in situ observations for Eastern Turkey. Hydrol Process 22:2737–2747. doi:10.1002/Hyp.7093
Tekeli Y, Tekeli AE (2012) A technique for improving MODIS standard snow products for snow cover monitoring over Eastern Turkey. Arab J Geosci 5:353–363. doi:10.1007/s12517-010-0274-3
Tekeli AE, Akyurek Z, Sorman AA, Sensoy A, Sorman AU (2005a) Using MODIS snow cover maps in modeling snowmelt runoff process in the eastern part of Turkey. Remote Sens Environ 97:216–230. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2005.03.013
Tekeli AE, Akyurek Z, Sensoy A, Sorman AA, Sorman U (2005b) Modelling the temporal variation in snow-covered area derived from satellite images for simulating/forecasting of snowmelt runoff in Turkey. Hydrol Sci J 50:669–682. doi:10.1623/hysj.2005.50.4.669
Tekeli AE, Sensoy A, Sorman A, Akyurek Z, Sorman U (2006) Accuracy assessment of MODIS daily snow albedo retrievals with in situ measurements in Karasu basin, Turkey. Hydrol Process 20:705–721. doi:10.1002/Hyp.6114
Tokar AS, Johnson PA (1999) Rainfall-runoff modeling using artificial neural networks. J Hydrol Eng 4:232–239. doi:10.1061/(Asce)1084-0699(1999)4:3(232)
Tokar AS, Markus M (2000) Precipitation-runoff modeling using artificial neural networks and conceptual models. J Hydrol Eng 5:156–161. doi:10.1061/(Asce)1084-0699(2000)5:2(156)
Wang X, Xie H (2007) New multi-day snow cover products from combination of Terra and Aqua MODIS daily snow cover data. AGU Fall meeting, San Francisco, CA, December 10–14
Wassenaar HJ, Chen W, Cheng J (2004) Sujianto A (2004) Enhancing discrete choice demand modeling for decision-based design. J Mech Des 127(4):514–523. doi:10.1115/1.1897408
Willimot CJ (1981) On the validation of the models. Phys Geogr 2:184–194
Yadav D, Naresh R, Sharma V (2011) Stream flow forecasting using Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm approach. Int J Water Resour Environ Eng 3(1):30–40
Yilmaz AG, Imteaz MA, Jenkins G (2011) Catchment flow estimation using Artificial Neural Networks in the mountainous Euphrates Basin. J Hydrol 410:134–140
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Research Center,College of Engineering, King Saud University, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Authors thank Turkish State Meteorological Services for providing the data. The valuable remarks and solid guidelines of the anonymous reviewers improved the text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ataṣ, M., Tekeli, A.E., Dönmez, S. et al. Use of interactive multisensor snow and ice mapping system snow cover maps (IMS) and artificial neural networks for simulating river discharges in Eastern Turkey. Arab J Geosci 9, 150 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2074-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2074-2