Abstract
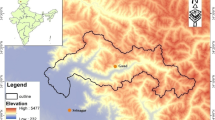
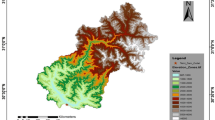
Forecasting streamflow mainly due to snowmelt in the mountainous eastern part of Turkey is important in terms of effective management of water resources at the headwaters of Euphrates River, where large dam reservoirs are located. Monitoring Snow Covered Area (SCA) and modeling snowmelt forms the backbone of the forecasting studies as the snowmelt dominating runoff constitutes approximately 2/3 of total annual volume of runoff during spring and early summer. Two main motivations of the study are; firstly, to assess the methodologies to forecast SCA using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data and derive Snow Depletion Curve (SDC) for each elevation zone. Secondly, to forecast 1 day ahead daily discharges using the derived SDCs and Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) data corrected specifically for the area. The Upper Euphrates Basin (10,275 km2) is selected as the pilot basin and MODIS daily snow cover products are analyzed for the snowmelt season. Four different methodologies are proposed and assessed to forecast SDCs; simple averaging, temperature based, stochastic modeling and probabilistic approach. SDCs are derived for the water years 2006–2010, 4 years data are used to derive the equations of the methodologies and 1 year is used to verify their skills. Forecasting discharges 1 day ahead with Snowmelt Runoff Model using NWP data is the second part of the study. Impact of forecasted SDCs with different methodologies is examined with the model. Model applications provide promising results both for the forecasting of SCA and runoff with an overall Model Efficiency higher than 0.60 and 0.85, respectively.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreadis KM, Lettenmaier DP (2006) Assimilating remotely sensed snow observations into a macroscale hydrology model. Adv Water Resour 29:872–886. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.08.004
Bales RC, Molotch NP, Painter TH, Dettinger MD, Rice R, Dozier J (2006) Mountain hydrology of the Western United States. Water Resour Res 42. doi:10.1029/2005wr004387
Bitner D, Carroll T, Cline D, Romanov P (2002) An assessment of the differences between three satellite snow cover mapping techniques. Hydrol Process 16:3723–3733. doi:10.1002/Hyp.1231
Box GEP, Jenkins GM (1970) Time series analysis: Forecasting and control: San Francisco; Holden-Day
Clark MP, Slater AG, Barrett AP, Hay LE, McCabe GJ, Rajagopalan B, Leavesley GH (2006) Assimilation of snow covered area information into hydrologic and land-surface models. Adv Water Resour 29:1209–1221. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.10.001
Dressler KA, Leavesley GH, Bales RC, Fassnacht SR (2006) Evaluation of gridded snow water equivalent and satellite snow cover products for mountain basins in a hydrologic model. Hydrol Process 20:673–688. doi:10.1002/Hyp.6130
Ferguson RI (1999) Snowmelt runoff models. Progr Phys Geogr 23(2):205–227
Forsythe N, Fowler HJ, Kilsby CG, Archer DR (2012) Opportunities from remote sensing for supporting water resources management in village/valley scale catchments in the upper Indus basin. Water Resour Manag 26:845–871. doi:10.1007/s11269-011-9933-8
Gafurov A, Bárdossy A (2009) Cloud removal methodology from MODIS snow cover product. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 13(7):1361–1373
Garen DC, Johnson GL, Hanson CL (1994) Mean areal precipitation for daily hydrologic modeling in mountainous regions. Water Resour Bull 30(3):481–491
Gómez-Landesa E, Rango A (2002) Operational snowmelt runoff forecasting in the Spanish Pyrenees using the snowmelt runoff model. Hydrol Process 16:1583–1591. doi:10.1002/Hyp.1022
Hall DK, Martinec J (1985) Remote sensing of ice and snow. Chapman and Hall Ltd, London, p 189
Hall DK, Riggs GA, Salomonson VV, DiGirolamo NE, Bayr KJ (2002) MODIS snow-cover products. Remote Sens Environ 83:181–194
Jain S, Lall U (2000) Magnitude and timing of annual maximum floods: trends and large-scale climatic associations for the Blacksmith Fork River, Utah. Water Resour Res 36(12):3641–3651
Jain SK, Goswami A, Saraf AK (2009) Role of elevation and aspect in snow distribution in western Himalaya. Water Resour Manag 23:71–83. doi:10.1007/s11269-008-9265-5
Jain SK, Goswami A, Saraf AK (2010a) Snowmelt runoff modelling in a Himalayan basin with the aid of satellite data. Int J Remote Sens 31(24):6603–6618
Jain SK, Goswami A, Saraf AK (2010b) Assessment of snowmelt runoff using remote sensing and effect of climate change on runoff. Water Resour Manag 24(9):1763–1777. doi:10.1007/s11269-009-9523-1
Jain SK, Thakural LN, Singh RD, Lohani AK, Mishra SK (2011) Snow cover depletion under changed climate with the help of remote sensing and temperature data. Nat Hazards 58(3):891–904. doi:10.1007/s11069-010-9696-1
Kaya HI (1999) Application of snowmelt runoff model using remote sensing and GIS. Msc. Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Turkey
Klein AG, Barnett AC (2003) Validation of daily MODIS snow cover maps of the Upper Rio Grande River Basin for the 2000–2001 snow year. Remote Sens Environ 86:162–176. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(03)00097-X
Lee SW, Klein AG, Over TM (2005) A comparison of MODIS and NOHRSC snow-cover products for simulating stream flow using the Snowmelt Runoff Model. Hydrol Process 19(15):2951–2972. doi:10.1002/Hyp.5810
Martinec J (1975) Snowmelt-runoff model for stream flow forecasts. Nord Hydrol 6:145–154
Maurer EP, Rhoads JD, Dubayah RO, Lettenmaier DP (2003) Evaluation of the snow-covered area data product from MODIS. Hydrol Process 17(1):59–71. doi:10.1002/Hyp.1193
McGuire M, Wood AW, Hamlet AF, Lettenmaier DP (2006) Use of satellite data for streamflow and reservoir storage forecasts in the snake river basin. J Water Res Pl-Asce 132(2):97–110. doi:10.1061/(Asce)0733-9496
Nash JC, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10(3):282–290
Parajka J, Blöschl G (2006) Validation of MODIS snow cover images over Austria. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 10(5):679–689
Parajka J, Blöschl G (2008a) The value of MODIS snow cover data in validating and calibrating conceptual hydrologic models. J Hydrol 358(3–4):240–258. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.06.006
Parajka J, Blöschl G (2008b) Spatio-temporal combination of MODIS images—potential for snow cover mapping. Water Resour Res 44(3), 10.1029/2007WR006204
Pu ZX, Xu L, Salomonson VV (2007) MODIS/Terra observed seasonal variations of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys Res Lett 34(6), 10.1029/2007GL029262
Rango A, Martinec J (1979) Application of a snowmelt-runoff model using landsat data. Nord Hydrol 10:225–238. doi:10.2166/nh.1979.015
Rango A, Vankatwijk V (1990) Development and testing of a snowmelt-runoff forecasting technique. Water Resour Bull 26:135–144
Richer EE (2009) Snowmelt runoff analysis and modelling for the upper cache La Poudre River basin, Colorado. MsS Thesis, Colorado State University Fort Collins, USA
Seidel K, Martinec J (2004) Remote sensing in snow hydrology. Springer and Praxis, Chichester
Şensoy A, Şorman AA, Tekeli AE, Şorman AÜ, Garen DC (2006) Point-scale energy and mass balance snowpack simulations in the upper Karasu basin, Turkey. Hydrol Process 20(4):899–922. doi:10.1002/Hyp.6120
Şensoy A, Uysal G, Şorman AA, Şorman AÜ (2010) Topographic effects on snow depletion curves of upper Euphrates River Basin, Turkey. Paper presented at the BALWOIS 2010 on water observation and information systems, Ohrid, FYROM, 25–29 May 2010
Simic A, Fernandes R, Brown R, Romanov P, Park W (2004) Validation of VEGETATION, MODIS, and GOES plus SSM/I snow-cover products over Canada based on surface snow depth observations. Hydrol Process 18(6):1089–1104. doi:10.1002/Hyp.5509
Singh P, Bengtsson L, Berndtsson R (2003) Relating air temperatures to the depletion of snow covered area in a Himalayan basin. Nord Hydrol 34(4):267–280
Şorman AA, Yamankurt E (2011) Modified satellite products on snow covered area in upper Euphrates basin, Turkey. Geophysical Research Abstracts Vol. 13: EGU2011-7887. European Geosciences Union, General Assembly 2011, Vienna, 03–08 April 2011
Şorman AA, Şensoy A, Tekeli AE, Şorman AÜ, Akyürek Z (2009) Modelling and forecasting snowmelt runoff process using the HBV model in the eastern part of Turkey. Hydrol Process 23(7):1031–1040. doi:10.1002/Hyp.7204
Şorman AÜ, Akyürek Z, Şensoy A, Şorman AA, Tekeli AE (2007) Commentary on comparison of MODIS snow cover and albedo products with ground observations over the mountainous terrain of Turkey. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 11:1353–1360
Tekeli AE (2005) Operational hydrological forecasting of snowmelt runoff by remote sensing and geographic information systems integration. PhD Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Turkey
Tekeli AE, Akyurek Z, Şensoy A, Şorman AA, Şorman AÜ (2005a) Using MODIS snow cover maps in modeling snowmelt runoff process in the eastern part of Turkey. Remote Sens Environ 97:216–230. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2005.03.013
Tekeli AE, Akyürek Z, Şorman AA, Şensoy A, Şorman AÜ (2005b) Modelling the temporal variation in snow-covered area derived from satellite images for simulating/forecasting of snowmelt runoff in Turkey. Hydrolog Sci J 50(4):669–682
Tong J, Dery SJ, Jackson PL (2009) Topographic control of snow distribution in an alpine watershed of western Canada inferred from spatially-filtered MODIS snow products. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 13:319–326
Wang XW, Xie HJ, Liang TG, Huang XD (2009) Comparison and validation of MODIS standard and new combination of Terra and Aqua snow cover products in northern Xinjiang, China. Hydrol Process 23(3):419–429. doi:10.1002/Hyp.7151
WinSRM (2008) WinSRM users manual. Available at: http://aces.nmsu.edu/pubs/research/weather_climate/SRMSpecRep100.pdf Accessed on 1thAugust 2011
Zhou XB, Xie HJ, Hendrickx JMH (2005) Statistical evaluation of remotely sensed snow-cover products with constraints from streamflow and SNOTEL measurements. Remote Sens Environ 94:214–231. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2004.10.007
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) 108Y161 and Anadolu University Scientific Research Project BAP070212. The valuable contributions of A.Ünal Şorman, Emmanuel Roulin and A.Arda Şorman to the improvement of this paper is gratefully acknowledged. The authors would like thank to A.Arda Şorman and his group (E. Yamankurt and E. Gözel) for SCA preprocessing of MODIS. The support of TSMS and EIE for providing hydrological and meteorological data is also appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şensoy, A., Uysal, G. The Value of Snow Depletion Forecasting Methods Towards Operational Snowmelt Runoff Estimation Using MODIS and Numerical Weather Prediction Data. Water Resour Manage 26, 3415–3440 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0079-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0079-0