Abstract
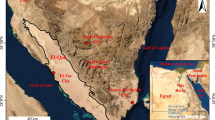
Uncertainty assessment of groundwater modeling is important for sustainable groundwater management and planning. The purpose of this study is to assess parameter uncertainty of groundwater modeling in the Birjand plain, Iran. This arid aquifer was modeled using MATLAB-based MODFLOW to avoid propagating uncertainty associated with hydraulic conductivity and recharge parameters. So, the aquifer was divided into 17 hydraulic conductivity homogenous zones; besides, 9 recharge zones were considered separately. Parameter uncertainty was evaluated using the Monte Carlo (MC) sampling technique, namely, the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation (GLUE). The results indicated that the performance of the GLUE based on the inverse error variance likelihood function was satisfied, because it gave the higher bracketing of observations equal to 86 %. Parameter uncertainty is well defined in the zones where they are not influenced directly by an inflow or outflow stream while hydraulic conductivity parameters of these zones follow approximately a normal distribution. In addition, groundwater modeling leads to a uniform exponential distribution in the zones with inflow or outflow streams.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Maximum Likelihood Bayesian Model Averaging
Kashyap Information Criteria
Bayesian Information Criteria
Akaike Information Criterion
References
Beven K (2001) Rainfall-runoff modelling: the primer. Wiley-Blackwell, England
Beven K (2006) A manifesto for the equifinality thesis. J Hydrol 320:18–36. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.07.007
Beven K, Binley A (1992) The future of distributed models: model calibration and uncertainty prediction. Hydrol Process 6:279–298. doi:10.1002/hyp.3360060305
Beven K, Freer J (2001) Equifinality, data assimilation, and uncertainty estimation in mechanistic modeling of complex environmental systems using the GLUE methodology. J Hydrol 249:11–29. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00421-8
Beven K, Smith PJ, Freer J (2008) So just why would a modeller choose to be incoherent? J Hydrol 354:15–32. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.02.007
Buckley KM, Binley A, Beven K (1995) Calibration and predictive uncertainty estimation of groundwater quality models: application to the Twin Lake Tracer Test. In: Groundwater Quality Management: Proceedings of the GQM 3 Conference Held in Tallinn, Estonia, September 1993. IAHS Publ 220: 205–214
Feyen L, Beven KJ, De Smedt F, Freer J (2001) Stochastic capture zone delineation within the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation methodology: conditioning on head observations. Water Resour Res 37(3):625–638. doi:10.1029/2000WR900351
Freer J, Beven K, Ambroise B (1996) Bayesian estimation of uncertainty in runoff prediction and the value of data: an application of the GLUE approach. Water Resour Res 32(7):2161–2173. doi:10.1029/95WR03723
Ghoochanian E, Etebari B, Akbarpour A (2013) Integrating groundwater management with WEAP and MODFLOW models (Case study: Birjand Plain, east of Iran). MODFLOW and More 2013: Translating Science into Practice – Conference, June 2–5, 2013, Colorado
Hassan AE, Bekhit HM, Chapman JB (2008) Uncertainty assessment of a stochastic groundwater flow model using GLUE analysis. J Hydrol 362:89–109. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.08.017
He J, Jones JWJ, Graham WWD, Dukes MMD (2010) Influence of likelihood function choice for estimating crop model parameters using the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation method. Agric Syst 103:256–264. doi:10.1016/j.agsy.2010.01.006
Humphrey S (2008) Astochastic approach to a groundwater flow model of southern honey lake valley in Lassen county, CA and Washoe county, NV. Thesis, University of Nevada
Ijiri Y, Saegusa H, Sawada A, Ono M, Watanabe K, Karasaki K, Doughty C, Shimo M, Fumimura K (2009) Evaluation of uncertainties originating from the different modeling approaches applied to analyze regional groundwater flow in the Tono area of Japan. J Contam Hydrol 103(3–4):168–181. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2008.10.010
Izady A, Davary K, Alizadeh A, Ziaei AN, Alipoor A, Joodavi A, Brusseau ML (2014) A framework toward developing a groundwater conceptual model. Arab J Geosci 7:3611–3631. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-0971-9
Izady A, Davary K, Alizadeh A, Ziaei AN, Akhavan S, Alipoor A, Joodavi A, Brusseau ML (2015) Groundwater conceptualization and modeling distributed SWAT-based recharge for semi-arid agricultural Neishaboor plain, Iran. Hydrogeol J 23(1):47–68. doi:10.1007/s10040-014-1219-9
JiChun WU, XianKui Z (2013) Review of the uncertainty analysis of groundwater numerical simulation. Chin Sci Bull 25:3044–3052. doi:10.1007/s11434-013-5950-8
Jin X, XU CY, Zhang Q, Sing VP (2010) Parameter and modeling uncertainty simulated by GLUE and a formal Bayesian method for a conceptual hydrological model. J Hydrol 383:147–155. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.12.028
Keesman K, van Straten G (1989) Identification and prediction propagation of uncertainty in models with bounded noise. Int J Control 49(6):2259–2269. doi:10.1080/00207178908559771
Li X, Tsai F (2009) Bayesian model averaging for groundwater head prediction and uncertainty analysis using multimodel and multimethod. Water Resour Res 45:W09403. doi:10.1029/2008WR007488
Li L, Xia J, Xu C-Y, Singh VP (2010) Evaluation of the subjective factors of the GLUE method and comparison with the formal Bayesian method in uncertainty assessment of hydrological models. J Hydrol 390:210–221. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.06.044
Makowski D, Wallach D, Tremblay M (2002) Using a Bayesian approach to parameter estimation: comparison of the GLUE and MCMC methods. Agronomie 22:191–203. doi:10.1051/agro:2002007
Mansouri B, Salehi J, Etebari B, Kardanmoghadam H (2012) Metal concentrations in the groundwater in Birjand Flood Plain, Iran. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:138–142. doi:10.1007/s00128-012-0630-y
McDonald MG, Harbaugh AW (1988) A modular three-dimensional finite-difference ground-water flow model. U.S. Geological Survey, USA
McKay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ (1979) Comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 21(2):239–245. doi:10.1080/00401706.1979.10489755
Mirarabi A, Nakhaei M (2009) Groundwater level Fluctuation forcasting in birjand aquifer using artificial neural network. EGU General Assembly 2009, held 19–24 April, 2009 in Vienna, Austria
Moore C, Wöhling T, Doherty J (2010) Efficient regularization and uncertainty analysis using a global optimization methodology. Water Resour Res 46:W08527. doi:10.1029/2009WR008627
Morse BS, Pohll G, Huntington J, Rodrigues-Castillo R (2003) Stochastic capture zone analysis of arsenic-contaminated well using the generalized likelihood uncertainty estimator (GLUE) methodology. Water Resour Res 39(6):1151. doi:10.1029/2002WR001470
Mousavi SJ, Abbaspour KC, Kamali B, Amini M, Yang H (2012) Uncertainty-based automatic calibration of HEC-HMS model using sequential uncertainty fitting approach. J Hydroinform 14(2):286–309. doi:10.2166/hydro.2011.071
Olsthoorn T N (2013) mfLab: Environmet for MODFLOW suite groundwater modeling.http://code.google.come/p/mfLab. Accessed 19 Dec 2013
Pourtaghi ZS, Pourghasemi HR (2014) GIS-based groundwater spring potential assessment and mapping in the Birjand Township, southern Khorasan Province, Iran. Hydrogeol J 22(3):643–662. doi:10.1007/s10040-013-1089-6
Rahnama B, Naseri M, Zahraie B (2014) Identifying optimized structure and uncertainty analysis of monthly water balance model. IWRJ 8(14):77–86 (in Farsi)
Refsgaard JC, Christensen S, Sonnenborg TO, Seifert D, Hojberg AL, Trodborg L (2012) Review of strategies for handling geological uncertainty in groundwater flow and transport modeling. Adv Water Resour 36:36–50. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2011.04.006
Rojas R, Feyen L, Dassargues A (2008) Conceptual model uncertainty in groundwater modeling: combining generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation and Bayesian model averaging. Water Resour Res 44:1–16. doi:10.1029/2008WR006908
Rojas R, Kahunde S, Peeters L, Batelaan O, Feyen L, Dassargues A (2010) Application of a multimodel approach to account for conceptual model and scenario uncertainties in groundwater modeling. J Hydrol 394:416–435. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.09.016
Romanowicz R, Beven KJ, Tawn J (1994) Evaluation of predictive uncertainty in non-linear hydrological models using a Bayesian approach. In: Barnettand V, Turkman KF (eds) Statistics for the environment: water related issues. Wiley, NewYork, pp 297–317
Singh A, Mishra S, Ruskauff G (2010) Model averaging techniques for quantifying conceptual model uncertainty. Ground Water 48:701–715. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.2009.00642.x
Troldborg L, Refsgaard J, Jensen K, Engesgaard P (2007) The importance of alternative conceptual models for simulation of concentrations in a multi–aquifer system. Hydrogeol J 15(5):843–860. doi:10.1007/s10040-007-0192-y
Tsai FTC, Li X (2008) Inverse groundwater modeling for hydraulic conductivity estimation using Bayesian model averaging and variance window. Water Resour Res 44:W09434. doi:10.1029/2007WR006576
Vazquez RF, Beven K, Feyen J (2009) GLUE based assessment on the overall predictions of a MIKE SHE application. Water Resour Manag 23:1325–1349. doi:10.1007/s11269-008-9329-6
Wang X, He X, Williams JR, Izaurralde RC, Atwood JD (2005) Sensitivity and uncertainty analyses of crop yields and soil organic carbon simulated with EPIC. Trans ASAE 48(3):1041–1054. doi:10.13031/2013.18515
Wu JC, Lu L, Tang T (2011) Bayesian analysis for uncertainty and risk in a groundwater numerical model’s predictions. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 7:1310–1331. doi:10.1080/10807039.2011.618419
Ye M, Pohlmann KF, Chapman JB, Pohll GM, Reeves DM (2010) A model-averaging method for assessing groundwater conceptual model uncertainty. Ground Water 48:716–728. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.2009.00633
Yoon H, Hart DB, McKenna SA (2013) Parameter estimation and predictive uncertainty in stochastic inverse modeling of groundwater flow: comparing null-space Monte Carlo and multiple starting point methods. Water Resour Res 49:536–553. doi:10.1002/wrcr.20064
Zia H (2004) Hydrogeology and effect artificial recharge of ground water Birjand Plain. MSc Thesis, Tabriz University, Iran
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamraz, B., Akbarpour, A., Pourreza Bilondi, M. et al. On the assessment of ground water parameter uncertainty over an arid aquifer. Arab J Geosci 8, 10759–10773 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1935-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1935-z