Abstract
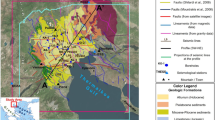
Ground magnetic and seismic refraction survey is carried out on an urban extension site in the southwest of Ahud Rufeidah town, southwest Saudi Arabia. The purpose of the survey was to map the surface topography of the bedrock and thickness of the alluvium overburden. The ground magnetic survey based on an assumption that the alluvial sediments is less or non-magnetic relative to the underlying gneiss basement rock. In this context, a total of 3,750 survey stations were measured along 40 east–west survey profiles, striking roughly perpendicular to the extension of the expected structures. In addition, 13 seismic refraction spreads were conducted along four seismic survey profiles across the expected pathways of buried alluvial channels in order to provide additional details about the depth and boundaries of the buried channels. The ground magnetic survey results show the presence of a basin combining two sub-basins filled with alluvium sediments that occupy the middle area of the investigated site. This basin is a closed basin that has no outlet, and there are four small and narrow channels that convey water and sediments from the eastern and southern hills into sub-basins. These channels are represented by narrow and elongated low magnetic anomalies extending towards the basinal area. The thickness of the alluvial sediments is verified using seismic refraction survey that indicates a greater thickness, exceeds 20 m, of low velocity sedimentary overburden inside the interpreted sub-basins and surrounding buried alluvial channels. These soft alluvial sediments can be deceptive and dangerous for urban foundations.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Garni MA (2004) Application of magnetic and electrical geophysical methods in exploration of groundwater resources of Wadi Malakan, Saudi Arabia. Journal of King AbdulAziz Univeristy: Earth Sciences 16:67–93
Al-Garni MA (2005) Investigating the groundwater occurrence in Wadi Rahjan and its potential contribution to Ain Zubaida using magnetic and electric methods, KSA. Journal of King AbdulAziz University: Earth Sciences 18:23–47
Al-Garni MA, Hassanein HI, Gobashy M (2005) Ground-magnetic survey and Schlumberger sounding for identifying the subsurface factors controlling the groundwater flow along Wadi Lusab, Makkah Al-Mukarramah, Saudi Arabia. J Appl Geophys 4:59–74
Benson RC, Yuhr L (2002) Site characterization strategies: old and new. Second Annual Conference on the Application of Geophysical and NDT Methodologies to Transportation Facilities, Federal Highway Administration, April 15–19, Los Angeles, California
Benson RC, Glaccum R, Noel M (1984) Geophysical techniques for sensing buried wastes and waste migration. NTIS PB84-198449
Berry MJ, West GF (1966) An interpretation of the first arrival data of the Lake Superior experiment by the time-term method. Bull Seism Soc Am 56:141–171
Blakely RJ (1995) Potential theory in gravity and magnetic applications. University Press, Cambridge, 441 pp
Coleman RG, Brown GF (1971) Volcanism in the southwest of Saudi Arabia. Geol Soc American Abs with programs 3(7):529
Dumbleton MJ, West G (1974) Guidance on planning, directing and reporting site investigation. TRRI, Laboratory Report 625. Transport and Road Research Laboratory, Crowthorne
Dutta NP (1984) Seismic refraction method to study the foundation rock of a dam. Geophys Prospect 32:1103–1110
Geometrics Inc. (2009) SeisImager/2DTM, version 3.3
Geosoft Inc. (2008) Geosoft Oasis Montaj, 2nd edition, version 7.0.1 (OL)
Goldstein NE (1994) Expedited site characterization geophysics: geophysical methods and tools for site characterization. Prepared for the US Department of Energy by Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, Univ. of California. 124 p
Hatherly PJ, Neville MJ (1986) Experience with the generalized reciprocal method of seismic refraction interpretation for shallow seismic engineering site investigation. Geophysics 51:276–288
Iwasaki T (2002) Extended time-term method for identifying lateral structural variations from seismic refraction data. Earth Planets Space 54:663–677
Kilty KT, Noriss RA, McLamore WR, Hennon KP, Euge K (1986) Seismic refraction at Horse Dam. An application of the generalized reciprocal method. Geophysics 51:266–272
McDowell PW (1981) Recent developments in geophysical techniques for the rapid location of near-surface anomalous conditions by geophysical methods. Ground Eng 14:20–30
Meru RF (1966) An iterative method for solving the time-term equations, J. S. Steinhart and T. J. Smith, Ed., Geophys. Monogr. 10: 495–497
Reynolds JM (1997) An introduction to applied and environmental geophysics. Wiley, NY, 806 pp
Scheidegger A, Willmore PL (1957) The use of a least square method for the interpretation of data from seismic surveys. Geophysics 22:9–22
Sjogren BO, Sandberg J (1979) Seismic classification of rock mass qualities. Geophys Prospect 27:409–442
Smith TJ, Steinhart JS, Aldrich LJ (1966) Lake Superior crustal structure. J Geophys Res 71:1141–1172
Verduzco B, Fairhead JD, Green CM, MacKenzie C (2004) New insights into magnetic derivatives for structural mapping. Lead Edge 23:116–119
Willmore PL, Bancroft AM (1960) The time-term approach to refraction seismology. Geophys J R Astron Soc 3(3):419–432
Yoshii T, Asano S (1972) Time-term analysis of explosion seismic data. J Phys Earth 20:47–57
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by King Saud University, Deanship of Scientific Research, College of Science Research Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almadani, S., Ibrahim, E., Abdelrahman, K. et al. Magnetic and seismic refraction survey for site investigation of an urban expansion site in Abha District, Southwest Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 8, 2299–2312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1342-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1342-x