Abstract
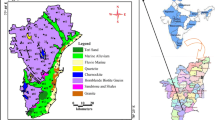
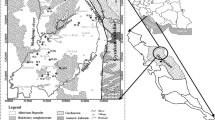
An attempt has been made to evaluate the water quality in the fast-growing coastal area of South Chennai. Groundwater samples were collected from selected locations and analyzed for major physico-chemical parameters. Experimental results show that the water has alkaline with pH varying from 7.2 to 8.2. Concentrations of Na and Cl were positively correlated with EC and elevated levels of these parameters near the coastal region, especially in the northern end of the study area, indicating the influence of seawater intrusion. Piper diagram identified Na–Cl as the dominant type of water in most of the samples. The presence of Ca–Cl facies in the groundwater suggests the possible ion exchange (Na with Ca) reaction in the aquifer. Molar ratios of Cl/HCO3 and Mg/Ca showed a higher value (>1) in many samples, which confirmed the influence of seawater intrusion on water quality. The Water Quality Index (WQI) of the study area ranged between 8 and 116, the highest recorded being at Thiruvanmiyur and the lowest at Muttukkadu. However, total hardness values show that 64% of the samples were hard or very hard in nature. The results of SAR, Na%, and PI show that majority of the samples are suitable for irrigation purposes. A comparison of spatial distribution maps of water quality parameters with those of WQI shows that groundwater quality has highly deteriorated in the Thiruvanmiyur region, located on the northeast part of the study area. Good-quality water is found at the southeast part of the study area, namely, Muttukkadu. This study indicates that urbanization and seawater intrusion have heavily affected the groundwater quality of South Chennai coastal area.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikary PP, Dash CJ, Chandrasekharan H, Rajput TBS, Dubey SK (2012) Evaluation of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking using GIS and geostatistics in a peri-urban area of Delhi, India. Arab J Geosci 5:1423–1434
Alobaidy AHMJ, Abid HS, Maulood BK (2010) Application of Water Quality Index for assessment of Dokan Lake ecosystem, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. J Water Res Prot 2:792–798
Al-Taani AA (2012) Seasonal variations in water quality of Al-Wehda Dam north of Jordan and water suitability for irrigation in summer. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0428-y
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (APHA)
BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) 10500 (1991) Indian Standard drinking water-specification. 1st rev pp. 1–8
Bordalo AA, Teixeira R, Wiebe WJ (2006) A Water Quality Index applied to an international shared river basin: the case of Douro River. Environ Manag 38:910–920
CGWB (2008) District groundwater brochure, Chennai,Tamil Nadu. Technical report series
Elango L, Ramachandran S, Choudary YSN (1992) Ground water quality in coastal region of South Madras. Indian J Environ Health 34:318–325
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Sci J 170:795–840
Gnanasundar D, Elango L (1999) Groundwater quality assessment of a coastal aquifer using geoelectrical techniques. J Environ Hydrol 7:21–33
Gurumoorthy C, Sasidhar P, Arunugham V, Nathur RK (2004) Sub-surface investigations on deep saline ground water of charnokite rock formation, Kalpakkam, India. Environ Monit Assess 91:211–222
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of chemical characteristics of natural water. US Geological Survey, Water Supply Paper No. 2254
Kashouty ME, Aziz AA, Soliman M, Mesbah H (2012) Hydrogeophysical investigation of groundwater potential in the El Bawiti, Northern Bahariya Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 5:953–970
Ketata M, Gueddari M, Bouhlila R (2012) Use of geographical information system and water quality index to assess groundwater quality in El Khairat deep aquifer (Enfidha, Central East Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 5:1379–1390
Lakshmanan E, Kannan K, Senthil Kumar M (2003) Major ion chemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical process of groundwater in part of Kancheepuram district, Tamilnadu, India. J Environ Geosci 10:157–166
Lermontov A, Yokoyama L, Lermontov M, Machado MAS (2009) River quality analysis using fuzzy water quality index: Ribeira do Iguape river watershed, Brazil. Ecol Indic 9:1188–1197
Manap MA, Sulaiman WNA, Ramli MF, Pradhan B, Surip N (2012) A knowledge driven GIS modelling technique for prediction of groundwater potential zones at the Upper Langat Basin, Malaysia. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0469-2
Mehrjardi TR, Jahromi ZM, Mahmodi SHA (2008) Spatial distribution of groundwater quality with geostatistics (case study: Yazd-Ardakan Plain). World Appl Sci J 4:9–17
Mitra BK (1998) Spatial and temporal variation of ground water quality in sand dune area of Aomori prefecture in Japan. Paper number 062023, 2006 ASAE annual meeting
Mondal NC, Singh VS, SaxenaVK SVP (2011) Assessment of seawater impact using major hydrochemical ions: a case study from Sadras, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 177:315–335
Mustapha A, Aris AZ, Juahir H, Ramli MF (2012) Surface water quality contamination source apportionment and physicochemical characterization at the upper section of the Jakara Basin, Nigeria. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-012-0731-2
Namibian M (2007) A new Water Quality Index for environmental contamination contributed by mineral processing: a case study of Amang (tin tailing) processing activity. J Appl Sci 7:2977–2987
Palanivelu K, Priya MN, Selvan AM, Natesan U (2006) Water quality assessment in the tsunami-affected coastal areas of Chennai. Curr Sci 91:5
Piper AM (1953) A graphic procedure in the geo-chemical interpretation of water analysis. USGS Groundwater Note No. 12
Pradhan B (2009) Ground water potential zonation for basaltic watersheds using satellite remote sensing data and GIS techniques. Cent Eur J Geosci 1:120–129
Pradhan B, Pirasteh S (2011) Hydro-chemical analysis of the ground water of the Basaltic catchments: upper Bhatsai Region, Maharastra. Open Hydrol J 5:51–57
Ragunath HM (1987) Groundwater. WileyEastern Ltd, New Delhi, pp 563
Ramakrishnaiah CR, Sadashivaiah C, Ranganna G (2009) Assessment of Water Quality Index for the groundwater in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. E-J Chem 6:523–530
Ravikumar P, Somashekar RK (2011) A geochemical assessment of coastal groundwater quality in the Varahi river basin, Udupi District, Karnataka State, India. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0470-9
Sadashivaiah C, Ramakrishnaiah CR, Ranganna G (2008) Hydrochemical analysis and evaluation of groundwater quality inTumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. Int J Environ Res Public Health 5:158–164
Sajil Kumar PJ, Jegathambal P, James EJ (2011) Multivariate and geostatistical analysis of groundwater quality in Palar river basin. Int J Geol 5:108–119
Sánchez E, Colmenarejo MF, Vicente J, Rubio A, García MG, Travieso L, Borja R (2007) Use of the Water Quality Index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watershed pollution. Ecol Indic 7:315–328
Sathish S, Elango L, Rajesh R, Sarma VS (2011) Assessment of seawater mixing in a coastal aquifer by high resolution electrical resistivity tomography. Int J Environ Sci Tech 8:483–492
Sawyer GN, McCarthy DL (1967) Chemistry of sanitary Engineers, 2nd edn. McGraw Hill, New York, p 518
Schoeller H (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In Methods and techniques of groundwater investigations and development (pp. 54–83). UNESCO
Schoeller H (1967) Geochemistry of groundwater—an international guide for research and practice (Chap. 15, pp. 1–18). UNESCO
Simoes FS, Moreira AB, Bisinoti MC, Gimenez SMN, Yabe MJS (2008) Water Quality Index as a simple indicator of aquaculture effects on aquatic bodies. Ecol Indic 8:476–484
Sisodia R, Moundiotiya C (2006) Assessment of the water quality index of wetland Kalakho lake, Rajasthan, India. J Environ Hydrol 14:1–11
Srinivasamoorthy K, Chidambaram M, Prasanna MV, Vasanthavigar M, John Peter A, Anandhan P (2008) Identification of major sources controlling Groundwater Chemistry from a hard rock terrain—a case study from Mettur taluk, Salem district, Tamilnadu, India. J Earth Syst Sci 117:49–58
Vasanthavigar M, Srinivasamoorthy K, Vijayaragavan K, Rajiv Ganthi R, Chidambaram S, Anandhan P, Manivannan R, Vasudevan S (2010) Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-1302-1
WHO (1984) Guidelines for drinking water quality V.1 Recommendations. Switzerland: Geneva pp. 130
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation water. US Geol Dep Agri Arc 969:19
Younger P, Casey V (2003) A simple method for determining the suitability of brackish groundwaters for irrigation. Waterlines 22:11–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajil Kumar, P.J., Elango, L. & James, E.J. Assessment of hydrochemistry and groundwater quality in the coastal area of South Chennai, India. Arab J Geosci 7, 2641–2653 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0940-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0940-3