Abstract
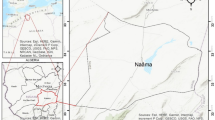
Groundwater is the most important natural resource used for drinking by many people around the world, especially in rural areas. In Tunisia, since the quantity and the quality of water available for different uses is variable from one place to another, groundwater quality in El Khairat deep aquifer was evaluated for its suitability for drinking purposes. To this end, an attempt has been made for the first time in order to determine spatial distribution of groundwater quality parameters and to identify places with the best quality for drinking within the study area based on: (1) an integrated analysis of physical–chemical parameters, (2) use of Geographical Information System, and (3) Water Quality Index (WQI) calculation. The physical–chemical results were compared with the World Health Organization (WHO) standards for drinking and public health, in order to have an overview of the present groundwater quality. According to the overall assessment of the basin, almost all the parameters analyzed are above the desirable limits of WHO. Using GIS contouring methods with Arcview 3.2a, spatial distribution maps of pH, TDS, EC, TH, Cl, HCO3, SO4, NO3, Ca, Mg, Na, and K have been created. The spatial analysis of groundwater quality patterns of the study area shows that the TDS value increases from north-west to south-east following the general trend of the Khairat aquifer flow direction. The spatial distribution map of TH shows that a majority of the groundwater samples falls in the very hard category. WQI was used to assess the suitability of groundwater from the study area for human consumption. From the WQI assessment, over 82% of the water samples fall within the “Poor” and “Very poor” categories, suggesting that groundwater from the south-eastern of the El Khairat deep aquifer is unsuitable for drinking purposes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abassi SA (1999). Water Quality Indices, State-of-the art. J.IPHE., No.1
Adak MDG, Purohit KM, Datta J (2001) Assessment of drinking water quality of river Brahmani. Indian J Environ Protect 8(3):285–291
Al-ahmadi ME, El-Fiky AA (2009) Hydrogeochemical evaluation of shallow alluvial aquifer of Wadi Marwani, western Saudi Arabia. Journal of King Saud University (Science) 21:179–190
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, USA
Asadi SS, Vuppala P, Anji Reddy M (2007) Remote sensing and GIS techniques for evaluation of groundwater quality in Municipal Corporation of Hyderabad (Zone-V). India Int J Environ Res Publ Health 4(1):45–52
Avvannavar SM, Shrihari S (2008) Evaluation of water quality index for drinking purposes for river Netravathi, Mangalore, South India. Environ Monit Assess 143:279–290
Bahar MM, Reza MS (2009) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in a coastal area of Southwest Bangladesh. Environmental Earth Science. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0427-4
Burrough PA, McDonnell RA (1998) Principles of Geographical Information Systems, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 352
Chadly B (2002) Impact de la recharge de la nappe d'oued El Khairat par les lâchés du barrage « Oued El Khairat ». Internal Report, General Direction of Water Resources, Tunisia, p.24
Challerjee R, Tarafder G, Paul S (2009) Groundwater quality assessment of Dhanbad district, Jharkhand, India. Bull Eng Geol Environ. doi:10.1007/s10064-009-0234-x
DGRE a (General Direction of Water Resources) (1960-2003). Pluviometric directories of Tunisia. Publi., DGRE, Minist. Agric., Tunis, Tunisia
DGRE b (1991-2004) Directories of exploitation of Tunisia. Publi., DGRE, Minist. Agric., Tunis, Tunisia
DGRE c (2000-2005) Piezometric directories of Tunisia. Publi., DGRE, Minist. Agric., Tunis, Tunisia
Dwivedi SL, Pathak V (2007) A preliminary assignment of water quality index to Mandakini river, Chitrakoot. Indian J Environ Protect 27:1036–1038
El Batti D (1974) Hydrogéologie de la plaine d'Enfidhaville. Doctorate Thesis, Faculty of Sciences of Tunis, p. 121
ESRI (1999) ARCVIEW GIS v.3.2, Environmental Systems Research, Institute Inc
Ferry LT, Akihiko K, Mohammed Aslam MA (2003) A Conceptual Database Design for Hydrology Using GIS. Proceedings of Asia Pacific Association of Hydrology and Water Resources. Kyoto, Japan
Horton RK (1965) An index number system for rating water quality. J Water Pollut Control Fed 37:300–305
Khan F, Husain T, Lumb A (2003) Water quality evaluation and trend analysis in selected watersheds of the Atlantic Region of Canada. Environ Monit Assess 88:221–242
Kumar M (2004) An integrated hydrogeochemical and isotopic study of NCR-Delhi, India [in English]. Mphil. Jawaharlal Nehru University, India
Kumar M, Kumari K, Ramanathan AL, Saxena R (2007) A comparative evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in two intensively cultivated districts of Punjab, India. Environ Geol 5:553–574
Manaa M (1991) Note sur l'hydrogéologie de la nappe d'Oued El Khairat (Gouvernorat de Sousse). Internal Report, General Direction of Water Resources, Tunisia, p. 199
Manaa M, Chaieb H, Amri R (1996) Etude par modèle hydrogéologique de la nappe alluviale d'Oued El Khairat. General Direction of Water Resources, Tunisia, p. 31
Mathes ES, Rasmussen TC (2006) Combining multivariate statistical analysis with geographic information systems mapping: a tool for delineating groundwater contamination. Hydrogeol J. doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0041-4
Mishra PC, Patel RK (2001) Study of the pollution load in the drinking water of Rairangpur, a small tribal dominated town of North Orissa. Indian J Environ Ecoplann 5(2):293–298
Naik S, Purohit KM (2001) Studies on water quality of river Brahmani in Sundargarh district, Orissa. Indian J Environ Ecoplann 5(2):397–402
Pradhan SK, Patnaik D, Rout SP (2001) Water quality index for the ground water in and around a phosphatic fertilizer plant. Indian J Environ Protect 21:355–358
Ramesh K, Elango L (2006) Groundwater quality assessment in Tondiar Basin. Int J Environ Pollut 26(6):497–504
Ravikumar P, Somashekar RK, Angami M (2010) Hydrochemistry and evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in the Markandeya River basin, Belgaum District, Karnataka State, India. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1399-2
Rodier J, Legube B, Merlet N (2009) L'analyse de l'eau. 9th edition, Dunod, p. 1530
Saeedi M, Abessi O, Sharifi F, Meraji H (2010) Development of groundwater quality index. Environ Monit Assess 163:327–335
Sahu P, Sikdar PK (2008) Hydrochemical framework of the aquifer in and around East Kolkata wetlands, West Bengal. India Environ Geol 55:823–835
Sargaonkar A, Deshpande V (2003) Development of an overall index of pollution for surfacewater based on a general classification scheme in Indian context. Environ Monit Assess 89:43–67
Sawyer GN, McCarthy DL (1967) Chemistry of sanitary engineers. McGrawHill, New York
Singh DF (1992) Studies on the water quality index of some major rivers of Pune, Maharashtra. Proc Acad Environ Biol 1(1):61–66
Srinivasamoorthy K, Chidambaram M, Prasanna MV, Vasanthavigar M, John Peter A, Anandhan P (2008) Identification of major sources controlling Groundwater Chemistry from a hard rock terrain-a case study from Mettur taluk, Salem district, Tamilnadu, India. Journal of Earth System Sciences 117(1):49–58
Subba Rao N (1997) Studies on water quality index in hard rock terrain of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. National Seminar on Hydrology of Precambrian Terrains and hard rock areas. pp. 129–134
Subramani T, Elango L, Damodarasamy SR (2005) Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use Chithar River Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Geol 47:1099–1110
Tiwari TN, Mishra MA (1985) A preliminary assignment of water quality index of major Indian rivers. Indian J Environ Protect 5:276–279
Vasanthavigar M, Srinivasamoorthy K, Vijayaragavan K, Rajiv Ganthi R, Chidambaram S, Anandhan P, Manivannan R, Vasudevan S (2010) Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-1302-1
Yidana SM, Yidana A (2010) Assessing water quality using water quality index and multivariate analysis. Environmental Earth Science 59:1461–1473
World Health Organization (1996a) Guidelines for drinking water quality. Health Criteria and Other Supporting Information, vol 2, 2nd edn. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland
WHO (1996b) Water quality monitoring: a practical guide to the design and implementation of freshwater quality studies and monitoring programmes. E&FN Spon, London, UK
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality: training pack. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ketata, M., Gueddari, M. & Bouhlila, R. Use of geographical information system and water quality index to assess groundwater quality in El Khairat deep aquifer (Enfidha, Central East Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 5, 1379–1390 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0292-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0292-9