Abstract
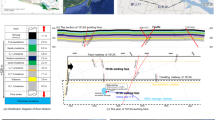
Under two rock strata combination conditions, over 10,000 microseismic events were received with microseismic location monitoring technology which possessed by the author’s studying team, used in fully mechanized coal face of Huafeng Mine of Xinwen Coal Mining Group Co., Shandong Province. On the basis of the achievement of the location results, the conclusions were drawn as follows: On the basis of the achievement of 3D strata fracturing situation and the section plane of microseimic events in different areas, the relationship between spatial structure of overlying strata and mining pressure field was found, and we might describe distribution range of dynamic pressure of advance pressure and lateral stress around long face, and range of structure ad-tivation. Quantitative guidance to prevent dynamic disasters was provided. The practice in coal mine got a effective results. According to the FLAC3D soft numerical simulation of diameter drilling hole (the diameter is 300 mm) to relieve pressure in specified geological condition in Huafeng Mine, the right distance of two dirlls is 2.5 m and the right depth is 12 m. The research pro-vided basic guiding and practical experiences for the underground microseismic monitoring and disaster prevention in side slopes or tunnels engineering.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bossart P, Meier P M, Moeri A, Trick T, Mayor J, 2002. Geological and hydraulic characterisation of the excavation disturbed zone in the Opalinus Clay of the Mont Terri Rock Laboratory. Eng. Geol., (66): 19–38.
Cai M, Kaiser P K, 2005. Assessment of excavation damaged zone using a micromechanics model. Tunneling and Underground Space Technology, 20(4): 301–310.
Cheng Y H, Jiang F X, Cheng J L, 2006. The primary study on microseismic locating and monitoring technology of shock bump caused by key stratum movement. Journal of China Coal Society, 31(3): 273–277.
Cheng Y H, Jiang F X, Zhang X M, 2007. C-sharped strata spatial structure and stress field in longwall face monitored by MS monitoring. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 26(1): 102–107.
Ge M, 2005. Efficient mine microseismic monitoring. International Journal of Coal Geology, 64(1/2): 44–56.
Jiang F X, Wang C W, Yang S H, 2007. Micro seismic monitoring and measuring technology for pumping presuure, coal and gas outburst and water in-rush. Coal Science and Technology, 35(1): 26–29.
Jiang F X, Yang S H, Cheng Y H, 2006a. A study on microseismic monitoring of rock burst in coal mine. Chinese Journal of Geo. Physcs., 49(5): 1 511–1 516.
Jiang F X, Zhang X M, Yang S H, 2006b. Discussion on overlying strata spatial structures of longwall in coal mine. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 25(5): 975–984.
Liu Z, Wu H, 2004. Several key problems research on the crustal stress measuring based on the Kaiser effect. Shanghai Geology, (3): 37–41.
Pang H D, 2005. Study on MS mode, location of rock mass and its collapse prediction. Ph.D.Thesis. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology, 6–35.
Qian M G, Miao X X, Xu J L, Mao X B, 2007. Key strata theory in ground control. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press, 17–28.
Xun L, Hatherly P, 1998. Application of microseismic monitoring to characterise geomechanical conditions in long wall mining. Exploration Geophysics, 29: 489–493.
Yang Y J, 2006. Basic experimental study on char acteristics of strength, deformation and MS of coal under compression. Ph.D.Thesis. Shandong University of Science and Technology, 41–75.
Zhang W B, 1991. Study on ground sound MS monitoring. Beijing Mining Research Branch of China Coal Research Institute. Symposium on Mining Hard Rocks Control. Beijing, 1991: 157–166.
Zhao J S, 2004. Fracture mechanics and fracture physical. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 91–178.
Zhuan Z, Jiang C P, 2004. Engineering fracture and damage. Beijing: Machinery Industry Publishing House, 6–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40674017, 50534080); the Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Coal Resources and Safe Mining(2007-04); the Open Doctor Innovation Fund of Shandong Province (200703020); the Chinese Postdoctoral Science Fundation (20080440304)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Yh., Jiang, Fx. & Zou, Yh. Research on inversion high mining pressure distribution and technology of preventing dynamic disasters by MS monitoring in longwall face. J Coal Sci Eng China 15, 252–257 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12404-009-0307-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12404-009-0307-2