Abstract
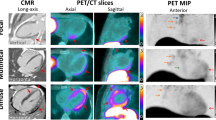
Recently, the applicability of somatostatin receptor-targeted (SSTR-t) radiotracers for post-ischemic myocardial inflammation imaging has been shown using PET. Currently, there are no studies which demonstrate ability of SPECT and technetium-99m SSTR-t radiotracers to detect inflammation, which appears in response to acute myocardial infarction (AMI). A case of 51-year-old male with acute anterior myocardial infarction (AMI) with ST elevation has been presented. This patient on 7th day after AMI onset underwent SPECT/CT (by cardiac cadmium-zinc-telluride gamma-camera) with 99mTc-Tectrotide, cardiac MRI with gadolinium and, on 9th day after AMI, myocardial perfusion scintigraphy (MPS) at rest. Clear myocardial uptake of 99mTc-Tectrotide, predominantly in apical and intermediate anterior wall of left ventricle was detected. The uptake matched with areas of hypoperfusion (by SPECT) and myocardial injury (by MRI). This case demonstrated the applicability of technetium-99m-labeled SSTR-t radiotracers for post-infarction inflammation imaging. Currently assumed, that SSTR-t radiotracers reflect an increased number of activated macrophages infiltrating infarcted myocardium, which is not possible using any other imaging technique. Thus, potentially, SSTR scintigraphy may be useful for diagnosis and monitoring of myocardial post-infarction inflammation as well as for anti-inflammatory image-guide therapy assessment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thackeray JT. PET Assessment of immune cell activity and therapeutic monitoring following myocardial infarction. Curr Cardiol Rep 2018;20:13.
Tarkin JM, Calcagno C, Dweck MR, Evans NR, Chowdhury MM, Gopalan D, et al. (68)Ga-DOTATATE PET identifies residual myocardial inflammation and bone marrow activation after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;73:2489-91.
Lapa C, Reiter T, Li X, Werner RA, Samnick S, Jahns R, et al. Imaging of myocardial inflammation with somatostatin receptor based PET/CT—A comparison to cardiac MRI. Int J Cardiol 2015;194:44-49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
S.I. Sazonova, A.G. Syrkina, O.V. Mochula, Zh.Zh. Anashbaev, E.V. Popov and V.V. Ryabov declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sazonova, S.I., Syrkina, A.G., Mochula, O.V. et al. Subacute myocardial infarction detected by technetium-99m-labeled somatostatin analog scintigraphy. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 29, 3586–3589 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-021-02644-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-021-02644-4