Abstract
Background
Chronic lower back pain (LBP) with or without leg pain (LP) is the most commonly reported anatomical site of pain among Canadian adults with chronic pain. A common cause for LBP and LP arises from dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint (SIJ) complex. When conventional medical management or rehabilitative efforts for SIJ-related LBP and LP fail to provide analgesia, pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) and/or radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of the dorsal entry root zone complex lesions (DREZC) and/or their more peripheral branches can also be a suitable means for treatment. Both PRF and RFA are interventional techniques that utilize heat to attenuate or ablate transmission of painful signals, respectively. The purpose of this chart review is to explore the clinical outcomes of patients experiencing SIJ-related pain who have undergone procedures with combined sensory nerve branch RFA and DREZC PRF lesions targeting the SIJ complex.
Methods
Following institutional review board approval, a retrospective chart review was performed from June 2018 to February 2021 for patients with LBP and/or LP refractory to physical rehabilitative efforts and medical management that underwent combined PRF and RF treatments for a diagnosis of SIJ complex pain. RF and PRF procedures were anatomically guided with the addition of sensory stimulation to ensure appropriate needle placement. Charts were reviewed for percentage of analgesia at final follow-up, duration of effect, degree of analgesia, patients’ functional improvements, and changes in medication use patterns.
Results
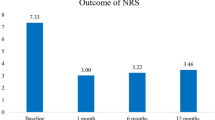
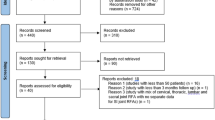
Data was reviewed from 180 patients with LBP or LP who underwent combined PRF and RF treatments for a diagnosis of SIJ complex pain. The group consisted of 69 men and 111 women with a mean age of 59 years. All patients had lesions to their dorsal roots and/or branches (lumbar medial and sacral lateral), as determined using their pain profile as well as sensory stimulation. In the sample of 180 patients a total of 276 SIJs were treated over the period of data collection. Overall, 85.0% (n = 234) of procedures were considered successful with more than 50% analgesic relief at final follow-up. Of 234 successful outcomes, 110 reported ongoing analgesia (mean = 80.3% pain relief, SD ± 18.0) on the last date of follow up (mean = 53.2 days, SD ± 41.8) prior to being lost to follow-up. For patients not lost to follow-up, the mean amount of analgesia was reported to be 83.9% with an average duration of 86.3 days. Among all treatments, 6.9% (n = 19) provided no analgesic effect. Among the successful procedure outcomes, 54.4% (n = 150) reported increased activity/mobility, 24.3% (n = 67) reported improved sleep, 49.3% (n = 136) reported improved mood, and 11.6% (n = 32) reported decreased medication usage. Nine patients reported complications following the procedure. Complications included transient soreness, bruising, tenderness, myofascial pain, and two mild vagal responses without lasting sequelae.
Conclusion
This review suggests that combined sensory nerve branch RFA and DREZC PRF lesions targeting the SIJ complex is a suitable intervention to treat SIJ-related LBP and/or LP refractory to physical rehabilitative efforts and medical management. Approximately 85% of these cases were successfully treated with the majority of patients report lasting analgesic effects with minimal complications, supporting the use of sensory stimulation-guided combined RF and PRF lesions for treatment of refractory SIJ complex pain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schopflocher D, Taenzer P, Jovey R. The prevalence of chronic pain in Canada. Pain Res Manage. 2011;16(6):445–50.
Oh DCs, First L, Rakesh N, Oh H, Gulati A. Inferior and intra‐/peri‐articular superior sacroiliac joint injection approaches under ultrasound guidance to treat metastasis‐related posterior pelvic bone pain. Pain Practice. 2020;20(7):769–76.
Cher D, Polly D, Berven S. Sacroiliac joint pain: burden of disease. Med Devices (Auckl). 2014;7:73.
Cavalli E, Mammana S, Nicoletti F, Bramanti P, Mazzon E. The neuropathic pain: an overview of the current treatment and future therapeutic approaches. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2019;33:2058738419838383.
Carter GT, Duong V, Ho S, Ngo KC, Greer CL, Weeks DL. Side effects of commonly prescribed analgesic medications. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2014;25(2):457–70.
Chen C-H, Weng P-W, Wu L-C, Chiang Y-F, Chiang C-J. Radiofrequency neurotomy in chronic lumbar and sacroiliac joint pain: a meta-analysis. Medicine. 2019;98(26).
Park J, Park JY, Kim S-H, Lim DJ, Kim S-D, Chung H. Long term results from percutaneous radiofrequency neurotomy on posterior primary ramus in patients with chronic low back pain. Adv Funct Reparat Neurosurg Springer. 2006;81–3.
Choi W-S, Kim J-S, Ryu K-S, Hur J-W, Seong J-H, Cho H-J. Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of the sacroiliac joint complex in the treatment of chronic low back pain: a preliminary study of feasibility and efficacy of a novel technique. BioMed Res Int. 2016;2016:2834259.
Yin W, Willard F, Carreiro J, Dreyfuss P. Sensory stimulation-guided sacroiliac joint radiofrequency neurotomy: technique based on neuroanatomy of the dorsal sacral plexus. Spine. 2003;28(20):2419–25.
Aydin SM, Gharibo CG, Mehnert M, Stitik TP. The role of radiofrequency ablation for sacroiliac joint pain: a meta-analysis. PM&R. 2010;2(9):842–51.
Visnjevac O, Ma F, Abd-Elsayed A. A literature review of dorsal root entry zone complex (DREZC) lesions: integration of translational data for an evolution to more accurate nomenclature. J Pain Res. 2021;14:1.
Yang AJ, McCormick ZL, Zheng PZ, Schneider BJ. Radiofrequency ablation for posterior sacroiliac joint complex pain: a narrative review. PM&R. 2019;11:S105–13.
Roberts SL, Stout A, Loh EY, Swain N, Dreyfuss P, Agur AM. Anatomical comparison of radiofrequency ablation techniques for sacroiliac joint pain. Pain Med. 2018;19(10):1924–43.
Fortin J. The anatomy of the lateral branches of the sacral dorsal rami: implications for radiofrequency ablation. Pain Physician. 2014;17:459–64.
Huang JH, Galvagno SM Jr, Hameed M, et al. Occipital nerve pulsed radiofrequency treatment: a multi-center study evaluating predictors of outcome. Pain Med. 2012;13(4):489–97.
Dutta K, Dey S, Bhattacharyya P, Agarwal S, Dev P. Comparison of efficacy of lateral branch pulsed radiofrequency denervation and intraarticular depot methylprednisolone injection for sacroiliac joint pain. Pain Physician. 2018;21(5):489–96.
Vallejo R, Benyamin RM, Kramer J, Stanton G, Joseph NJ. Pulsed radiofrequency denervation for the treatment of sacroiliac joint syndrome. Pain Med. 2006;7(5):429–34.
Laslett M, Young SB, Aprill CN, McDonald B. Diagnosing painful sacroiliac joints: a validity study of a McKenzie evaluation and sacroiliac provocation tests. Aust J Physiother. 2003;49(2):89–97.
Arnbak B, Jurik AG, Jensen RK, Schiøttz-Christensen B, Van der Wurff P, Jensen TS. The diagnostic value of three sacroiliac joint pain provocation tests for sacroiliitis identified by magnetic resonance imaging. Scand J Rheumatol. 2017;46(2):130–7.
Park H-W, Ahn S-H, Son J-Y, et al. Pulsed radiofrequency application reduced mechanical hypersensitivity and microglial expression in neuropathic pain model. Pain Med. 2012;13(9):1227–34.
Khalil KI. Evaluation of the effect of duration on the efficacy of pulsed radiofrequency in an animal model of neuropathic pain. Pain Physician. 2018;21:191–8.
Basbaum AI, Bautista DM, Scherrer G, Julius D. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell. 2009;139(2):267–84.
Ji R-R, Nackley A, Huh Y, Terrando N, Maixner W. Neuroinflammation and central sensitization in chronic and widespread pain. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(2):343–66.
Liu C-K, Liao W-T, Chu Y-C, et al. Pulsed radiofrequency attenuates complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced epigenetic suppression of potassium chloride cotransporter 2 expression. Pain Med. 2017;18(4):807–13.
Chen K-H, Yang C-H, Juang S-E, et al. Pulsed radiofrequency reduced complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced mechanical hyperalgesia via the spinal c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014;34(2):195–203.
Jiang R, Li P, Yao Y-X, et al. Pulsed radiofrequency to the dorsal root ganglion or the sciatic nerve reduces neuropathic pain behavior, decreases peripheral pro-inflammatory cytokines and spinal β-catenin in chronic constriction injury rats. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019;44(7):742–6.
Schmidt PC, Pino CA, Vorenkamp KE. Sacroiliac joint radiofrequency ablation with a multilesion probe: a case series of 60 patients. Anesth Analg. 2014;119(2):460–62. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000000282.
Chang MC, Ahn SH. The effect of intra-articular stimulation by pulsed radiofrequency on chronic sacroiliac joint pain refractory to intra-articular corticosteroid injection: a retrospective study. Medicine. 2017;96(26):e7367-e.
Cohen SP, Hurley RW, Buckenmaier CC, Kurihara C, Morlando B, Dragovich A. Randomized placebo-controlled study evaluating lateral branch radiofrequency denervation for sacroiliac joint pain. Anesthesiology. 2008;109(2):279–88.
Acknowledgements
Funding
No external funding was obtained for this manuscript. All contributions of time and effort by the authors were voluntary without monetary reimbursement.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Author Contributions
1. Conception or design of the work: JS, OV, FK, SM, AA, BV. 2. Data collection: JS, MP, LD, OV. 3. Data analysis and interpretation: JS, MP, LD, NV, BV, FM, FK, MS, OV, FK, SM, JSK. 4. Drafting the article. JS, MP, LD, NV, BV, FM, FK, MS, OV, FK, SM, JSK. 5. Critical revision of the article: JS, MP, LD, NV, BV, FM, FK, MS, OV, FK, SM, JSK. 6. Final approval of the version to be published: JS, MP, LD, NV, BV, FM, FK, MS, OV, FK, SM, JSK.
Disclosures
Authors Jordan Sam, Mila Pastrak, Larysa Duda, Nikola Vladicic, Bruce Vrooman, Frederick Ma, Farhan Khandwalla, Alaa Abd-ElSayed, Michael Catapano, Scott McGilvray, James S. Khan, Ognjen Visnjevac have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This study was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) approval from Veritas IRB (protocol ID 2021-2584-5272-1), an IRB accredited by the Human Research Accreditation Canada. Requirement for patient consent to participate in this study was waived by the IRB. This study was performed in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and its later amendments.
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article/as supplementary information files.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sam, J., Pastrak, M., Duda, L. et al. Clinical Radiofrequency Ablation Outcomes of Combined Sensory Nerve Branch and Dorsal Entry Root Zone Complex Lesions for Sacroiliac Joint Complex Pain. Adv Ther 39, 3539–3546 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-022-02183-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-022-02183-5