Abstract
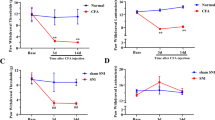
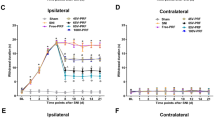
Pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) treatment involves the pulsed application of a radiofrequency electric field to a nerve. The technology offers pain relief for patients suffering from chronic pain who do not respond well to conventional treatments. We tested whether PRF treatment attenuated complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) induced inflammatory pain. The profile of spinal c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) phosphorylation was evaluated to elucidate the potential mechanism. Injection of CFA into the unilateral hind paw of rats induced mechanical hyperalgesia in both the ipsilateral and contralateral hind paws. We administered 500-kHz PRF treatment in 20-ms pulses, at a rate of 2 Hz (2 pulses per second) either to the sciatic nerve in the mid-thigh, or to the L4 anterior primary ramus just distal to the intervertebral foramen in both the CFA group and no-PRF group rats. Tissue samples were examined at 1, 3, 7, and 14 days following PRF treatments. Behavioral studies showed that PRF applied close to the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) significantly attenuated CFA-induced mechanical hyperalgesia compared to no-PRF group (P < .05). And western blotting revealed significant attenuation of the activation of JNK in the spinal dorsal horn compared to no-PRF group animals (P < .05). Application of PRF close to DRG provides an effective treatment for CFA-induced persistent mechanical hyperalgesia by attenuating JNK activation in the spinal dorsal horn.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu R, Ugur F, Bicer C, Menku A, Guler G, Madenoglu H, Canpolat DG, Boyaci A (2010) The efficiency of pulsed radiofrequency application on L5 and L6 dorsal roots in rabbits developing neuropathic pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med 35(1):11–15. doi:10.1097/AAP.0b013e3181c76c21
Al-Badawi EA, Mehta N, Forgione AG, Lobo SL, Zawawi KH (2004) Efficacy of pulsed radio frequency energy therapy in temporomandibular joint pain and dysfunction. Cranio 22(1):10–20
Bogduk N (2006) Pulsed radiofrequency. Pain Med 7(5):396–407. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2006.00210.x
Bonny C, Borsello T, Zine A (2005) Targeting the JNK pathway as a therapeutic protective strategy for nervous system diseases. Rev Neurosci 16(1):57–67
Byrd D, Mackey S (2008) Pulsed radiofrequency for chronic pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep 12(1):37–41
Cahana A, Vutskits L, Muller D (2003) Acute differential modulation of synaptic transmission and cell survival during exposure to pulsed and continuous radiofrequency energy. J Pain 4(4):197–202
Carlsson C (2002) Acupuncture mechanisms for clinically relevant long-term effects–reconsideration and a hypothesis. Acupunct Med 20(2–3):82–99
Chiang CY, Wang J, Xie YF, Zhang S, Hu JW, Dostrovsky JO, Sessle BJ (2007) Astroglial glutamate-glutamine shuttle is involved in central sensitization of nociceptive neurons in rat medullary dorsal horn. J Neurosci 27(34):9068–9076. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2260-07.2007
Chua NH, Vissers KC, Sluijter ME (2011) Pulsed radiofrequency treatment in interventional pain management: mechanisms and potential indications-a review. Acta Neurochir 153(4):763–771. doi:10.1007/s00701-010-0881-5
Cosman ER Jr, Cosman ER Sr (2005) Electric and thermal field effects in tissue around radiofrequency electrodes. Pain Med 6(6):405–424. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2005.00076.x
Erdine S, Yucel A, Cimen A, Aydin S, Sav A, Bilir A (2005) Effects of pulsed versus conventional radiofrequency current on rabbit dorsal root ganglion morphology. Eur J Pain 9(3):251–256. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2004.07.002
Eyigor C, Eyigor S, Korkmaz OK, Uyar M (2010) Intra-articular corticosteroid injections versus pulsed radiofrequency in painful shoulder: a prospective, randomized, single-blinded study. Clin J Pain 26(5):386–392. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181cf5981
Gao YJ, Ji RR (2008) Activation of JNK pathway in persistent pain. Neurosci Lett 437(3):180–183. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.03.017
Gao YJ, Xu ZZ, Liu YC, Wen YR, Decosterd I, Ji RR (2010) The c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in spinal astrocytes is required for the maintenance of bilateral mechanical allodynia under a persistent inflammatory pain condition. Pain 148(2):309–319. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2009.11.017
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Takeshima N, Noguchi T (2009) Mechanisms of analgesic action of pulsed radiofrequency on adjuvant-induced pain in the rat: roles of descending adrenergic and serotonergic systems. Eur J Pain 13(3):249–252. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2008.04.013
Hamann W, Abou-Sherif S, Thompson S, Hall S (2006) Pulsed radiofrequency applied to dorsal root ganglia causes a selective increase in ATF3 in small neurons. Eur J Pain 10(2):171–176. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2005.03.001
Higuchi Y, Nashold BS Jr, Sluijter M, Cosman E, Pearlstein RD (2002) Exposure of the dorsal root ganglion in rats to pulsed radiofrequency currents activates dorsal horn lamina I and II neurons. Neurosurgery 50(4):850–855 discussion 856
Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Woolf CJ (2003) Central sensitization and LTP: do pain and memory share similar mechanisms? Trends Neurosci 26(12):696–705
Ji RR, Kawasaki Y, Zhuang ZY, Wen YR, Decosterd I (2006) Possible role of spinal astrocytes in maintaining chronic pain sensitization: review of current evidence with focus on bFGF/JNK pathway. Neuron Glia Biol 2(4):259–269. doi:10.1017/S1740925X07000403
Ji RR, Gereau RWt, Malcangio M, Strichartz GR (2009) MAP kinase and pain. Brain Res Rev 60(1):135–148. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.011
Karaman H, Tufek A, Kavak GO, Yildirim ZB, Uysal E, Celik F, Kaya S (2011) Intra-articularly applied pulsed radiofrequency can reduce chronic knee pain in patients with osteoarthritis. JCMA 74(8):336–340. doi:10.1016/j.jcma.2011.06.004
Latremoliere A, Woolf CJ (2009) Central sensitization: a generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J Pain 10(9):895–926. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2009.06.012
Malik K, Benzon HT (2008) Radiofrequency applications to dorsal root ganglia: a literature review. Anesthesiology 109(3):527–542. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e318182c86e
Obata K, Noguchi K (2004) MAPK activation in nociceptive neurons and pain hypersensitivity. Life Sci 74(21):2643–2653. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2004.01.007
Ozsoylar O, Akcali D, Cizmeci P, Babacan A, Cahana A, Bolay H (2008) Percutaneous pulsed radiofrequency reduces mechanical allodynia in a neuropathic pain model. Anesth Analg 107(4):1406–1411. doi:10.1213/ane.0b013e31818060e1
Perret DM, Kim DS, Li KW, Sinavsky K, Newcomb RL, Miller JM, Luo ZD (2011) Application of pulsed radiofrequency currents to rat dorsal root ganglia modulates nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia. Anesth Analg 113(3):610–616. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e31821e974f
Podhajsky RJ, Sekiguchi Y, Kikuchi S, Myers RR (2005) The histologic effects of pulsed and continuous radiofrequency lesions at 42 °C to rat dorsal root ganglion and sciatic nerve. Spine 30(9):1008–1013
Protasoni M, Reguzzoni M, Sangiorgi S, Reverberi C, Borsani E, Rodella LF, Dario A, Tomei G, Dell’Orbo C (2009) Pulsed radiofrequency effects on the lumbar ganglion of the rat dorsal root: a morphological light and transmission electron microscopy study at acute stage. Eur Spine J 18(4):473–478. doi:10.1007/s00586-008-0870-z
Richebe P, Rathmell JP, Brennan TJ (2005) Immediate early genes after pulsed radiofrequency treatment: neurobiology in need of clinical trials. Anesthesiology 102(1):1–3
Sandkuhler J, Chen JG, Cheng G, Randic M (1997) Low-frequency stimulation of afferent Adelta-fibers induces long-term depression at primary afferent synapses with substantia gelatinosa neurons in the rat. J Neurosci 17(16):6483–6491
Schepers RJ, Mahoney JL, Gehrke BJ, Shippenberg TS (2008) Endogenous kappa-opioid receptor systems inhibit hyperalgesia associated with localized peripheral inflammation. Pain 138(2):423–439. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2008.01.023
Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2007) The neuropathic pain triad: neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat Neurosci 10(11):1361–1368. doi:10.1038/nn1992
Shabat S, Pevsner Y, Folman Y, Gepstein R (2006) Pulsed radiofrequency in the treatment of patients with chronic neuropathic spinal pain. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 49(3):147–149. doi:10.1055/s-2006-944238
Sluijter ME, Teixeira A, Serra V, Balogh S, Schianchi P (2008) Intra-articular application of pulsed radiofrequency for arthrogenic pain—report of six cases. Pain Pract 8(1):57–61. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2007.00172.x
Tanaka N, Yamaga M, Tateyama S, Uno T, Tsuneyoshi I, Takasaki M (2010) The effect of pulsed radiofrequency current on mechanical allodynia induced with resiniferatoxin in rats. Anesth Analg 111(3):784–790. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181e9f62f
Tsujino H, Kondo E, Fukuoka T, Dai Y, Tokunaga A, Miki K, Yonenobu K, Ochi T, Noguchi K (2000) Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) induction by axotomy in sensory and motoneurons: a novel neuronal marker of nerve injury. Mol Cell Neurosci 15(2):170–182. doi:10.1006/mcne 1999.0814
Van Zundert J, de Louw AJ, Joosten EA, Kessels AG, Honig W, Dederen PJ, Veening JG, Vles JS, van Kleef M (2005) Pulsed and continuous radiofrequency current adjacent to the cervical dorsal root ganglion of the rat induces late cellular activity in the dorsal horn. Anesthesiology 102(1):125–131
Van Zundert J, Patijn J, Kessels A, Lame I, van Suijlekom H, van Kleef M (2007) Pulsed radiofrequency adjacent to the cervical dorsal root ganglion in chronic cervical radicular pain: a double blind sham controlled randomized clinical trial. Pain 127(1–2):173–182. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.002
Werner MU, Bischoff JM, Rathmell JP, Kehlet H (2012) Pulsed radiofrequency in the treatment of persistent pain after inguinal herniotomy: a systematic review. Reg Anesth Pain Med 37(3):340–343. doi:10.1097/AAP.0b013e31824bea4e
Yang CH, Chen KH, Huang HW, Sheen-Chen SM, Lin CR (2013) Pulsed radiofrequency treatment attenuates increases in spinal excitatory amino acid release in rats with adjuvant-induced mechanical allodynia. NeuroReport 24(8):431–436. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e32836164f5
Zhuang ZY, Wen YR, Zhang DR, Borsello T, Bonny C, Strichartz GR, Decosterd I, Ji RR (2006) A peptide c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor blocks mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation: respective roles of JNK activation in primary sensory neurons and spinal astrocytes for neuropathic pain development and maintenance. J Neurosci 26(13):3551–3560. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5290-05.2006
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grant Nos. 880891, 880892, 880893, 891251, and 8A1011 from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Research, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, and by Grant Nos. 96-2628-B-182A-005-MY3, 98-2314-B-182A-035-MY2, 100-2314-B-182A-037, 101-2314-B-182A-014-, and 101-2314-B-182A-068-MY3 from the Taiwan National Science Council, Taipei, Taiwan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jiin-Tsuey Cheng and Chung-Ren Lin have contributed equally to this project and should be considered co-corresponding authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Fig. S1
Western blot analysis showing the time course of pERK1/2, ERK1/2, pp38 and p38 expressions in ipsilateral hindpaw after intraplantar CFA injection with/without PRF. Densitometric analysis of the immunoblots were presented (b , c and d). Data are normalized to the band intensity of GAPDH and presented as the fold change over the day 0 control. The pERK1, pERK2 and pp38 proteins were activated in the dorsal horn of the lumbar spinal cord, and their expression was maintained for the 14-day duration of the study in the ipsilateral and lumbar spinal cord. PRF applied proximal to DRG did not affect the induction of pERK1 (b), pERK2 (c) and pp38 (d). Each value is presented as means (SD); n = 5 for each group (JPEG 436 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, KH., Yang, CH., Juang, SE. et al. Pulsed Radiofrequency Reduced Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-induced Mechanical Hyperalgesia via the Spinal c-Jun N-terminal Kinase Pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34, 195–203 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-0003-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-0003-z