Abstract
Introduction
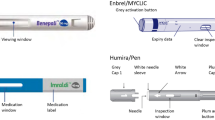
This study aimed to compare the usability of subcutaneous administration of SB4 (an etanercept biosimilar) via prefilled syringe (PFS) and autoinjector (AI) based on injection site pain, patient preference, and safety in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
This was an open-label, single-arm, multicenter study to evaluate the usability and safety of the AI and PFS of SB4. Adult patients with RA received two injections of SB4 via the PFS, followed by six injections by the AI every week, up to 8 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in injection site pain score immediately post-injection from week 1 (PFS) to week 3 (AI). Injection site pain after 15–30 min post-injection, overall impression, and preference for PFS and AI were also assessed. Safety was assessed up to 11 weeks after the first injection.
Results
A total of 54 patients were enrolled and 52 patients (96.3%) completed the 8-week treatment period. The mean difference in pain scores between PFS and AI was − 0.057 and the 95% CI of the difference was [− 0.63, 0.51], which was within the equivalence margin of ± 5. Overall impression of the device slightly favored the AI. Overall preference for the AI was more favorable when compared to the PFS in all categories. Adverse events were mild to moderate and found to be generally consistent with those expected for reference etanercept. There were no deaths or serious adverse events reported.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated comparable usability and safety between the PFS and AI when self-administrated by patients with RA.
Trial Registration
ClinicalTrials.gov identifier, NCT03193957.
Funding
Samsung Bioepis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr, et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(1):1–26.
Smolen JS, Landewe R, Bijlsma J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):960–77.
Sylwestrzak G, Liu J, Stephenson JJ, Ruggieri AP, DeVries A. Considering patient preferences when selecting anti-tumor necrosis factor therapeutic options. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2014;7(2):71–81.
Johnsson PM, Eberhardt K. Hand deformities are important signs of disease severity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2009;48(11):1398–401.
European Medicines Agency. Enbrel summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/product-information/enbrel-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Accessed 6 Dec 2018.
European Medicines Agency. Humira summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/product-information/humira-epar-product-information_en.pdf. Accessed 5 Dec 2018.
Curtis JR, Singh JA. The use of biologics in rheumatoid arthritis: current and emerging paradigms of care. Clin Ther. 2011;33(6):679–707.
Putrik P, Ramiro S, Kvien TK, et al. Inequities in access to biologic and synthetic DMARDs across 46 European countries. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(1):198–206.
Cho IH, Lee N, Song D, et al. Evaluation of the structural, physicochemical, and biological characteristics of SB4, a biosimilar of etanercept. mAbs. 2016;8(6):1136–55.
Lee YJ, Shin D, Kim Y, Kang J, Gauliard A, Fuhr R. A randomized phase l pharmacokinetic study comparing SB4 and etanercept reference product (Enbrel®) in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;82(1):64–73.
Emery P, Vencovsky J, Sylwestrzak A, et al. A phase III randomised, double-blind, parallel-group study comparing SB4 with etanercept reference product in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(1):51–7.
Emery P, Vencovsky J, Sylwestrzak A, et al. 52-week results of the phase 3 randomized study comparing SB4 with reference etanercept in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2017;56(12):2093–101.
Emery P, Vencovsky J, Sylwestrzak A, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety in patients with rheumatoid arthritis continuing on SB4 or switching from reference etanercept to SB4. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211591.
Egeth M, Soosaar J, Nash P, et al. Patient and healthcare professionals preference for Brenzys vs. Enbrel autoinjector for rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized crossover simulated-use study. Adv Ther. 2017;34(5):1157–72.
Thakur K, Biberger A, Handrich A, Rezk MF. Patient perceptions and preferences of two etanercept autoinjectors for rheumatoid arthritis: findings from a patient survey in Europe. Rheumatol Ther. 2016;3(2):245–56.
Thakur K, Biberger A, Handrich A, Rezk MF. Perceptions and preferences of two etanercept autoinjectors for rheumatoid arthritis: a new European union-approved etanercept biosimilar (Benepali(®)) versus etanercept (Enbrel(®))—findings from a nurse survey in Europe. Rheumatol Ther. 2016;3(1):77–89.
U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Draft Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff: technical considerations for pen, jet and related injectors intended for use with drugs and biological products. 2009. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/RegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM147095.pdf. Accessed 6 Dec 2018.
Kivitz A, Cohen S, Dowd JE, et al. Clinical assessment of pain, tolerability, and preference of an autoinjection pen versus a prefilled syringe for patient self-administration of the fully human, monoclonal antibody adalimumab: the TOUCH trial. Clin Ther. 2006;28(10):1619–29.
Muller-Ladner U, Flipo RM, Vincendon P, Brault Y, Kielar D. Comparison of patient satisfaction with two different etanercept delivery systems. A randomised controlled study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Z Rheumatol. 2012;71(10):890–9.
Kivitz A, Baret-Cormel L, van Hoogstraten H, et al. Usability and patient preference phase 3 study of the sarilumab pen in patients with active moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Ther. 2018;5(1):231–42.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the patients who were involved in this study and the study personnel who made this work possible.
Funding
This study and the journal’s Rapid Service Fee were supported by Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd. All authors had full access to all of the data in this study and take complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Editorial Assistance
Editorial assistance in the preparation of this article was provided by Jung Won Keum, PhD of Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd. Editorial assistance was funded by the study sponsor.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Authorship Contributions
YHR and THK were involved in the conception and design of the study and acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. ARH was involved in acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. BS was involved in acquisition of data. All named authors critically revised the manuscript for intellectual content, have approved the final version to be published, and take responsibility for the integrity of the work.
Disclosures
Young Hee Rho is an employee of Samsung Bioepis and owns stocks in Samsung Biologics. Tae Hyung Kim is an employee of Samsung Bioepis. Anna Rychlewska-Hańczewska received funding for clinical research from Samsung Bioepis. Beata Śliwowska received funding for clinical research from Samsung Bioepis.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This study was conducted in compliance with International Council for Harmonisation Good Clinical Practice guidelines and the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was approved by the ethics committee Komisja Bioetyczna przy Okręgowej Radzie Lekarskiej Wielkopolskiej Izby Lekarskiej w Poznaniu. Written and informed consent was obtained from all patients before any study-related procedures were performed.
Data Availability
Upon request, and subject to certain criteria, conditions, and exceptions, Samsung Bioepis will provide access to individual de-identified participant data. The de-identified participant data will be made available to researchers whose proposals meet the research criteria and other conditions, and for which an exception does not apply. The proposals should be directed to the corresponding author. To gain access, data requestors must enter into a data access agreement with Samsung Bioepis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced Digital Features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.8427593.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rho, Y.H., Rychlewska-Hańczewska, A., Śliwowska, B. et al. Usability of Prefilled Syringe and Autoinjector for SB4 (An Etanercept Biosimilar) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Adv Ther 36, 2287–2295 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-019-01027-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-019-01027-z