Abstract
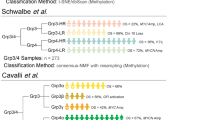
Using publically available datasets on gene expression in medulloblastoma (MB) subtypes, we selected genes for ubiquitin ligases and identified statistically those that best predicted each of the four major MB subgroups as separate disease entities. We identify a gene coding for an ubiquitin ligase, ZNRF3, whose overexpression alone can predict the WNT subgroup for 100% in the Pfister dataset. For the SHH subgroup, we identify a gene for a regulatory subunit of the protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), PPP2R2C, as the major predictor among the E3 ligases genes. The ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like conjugation database (UUCD) lists PPP2R2C as coding for a Cullin Ring ubiquitin ligase adaptor. For group 3 MBs, the best ubiquitin ligase predictor was PPP2R2B, a gene which codes for another regulatory subunit of the PP2A holoenzyme. For group 4, the best E3 gene predictors were MID2, ZBTB18, and PPP2R2A, which codes for a third PP2A regulatory subunit. Heatmap analysis of the E3 gene data shows that expression of ten genes for ubiquitin ligases can be used to classify MBs into the four major consensus subgroups. This was illustrated by analysis of gene expression of ubiquitin ligases of the Pfister dataset and confirmed in the dataset of Cavalli. We conclude that genes for ubiquitin ligases can be used as genetic markers for MB subtypes and that the proteins coded for by these genes should be investigated as subtype specific therapeutic targets for MB.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor MD, Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Remke M, Cho YJ, Clifford SC, et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;123(4):465–72.
Kool M, Korshunov A, Remke M, Jones DT, Schlanstein M, Northcott PA, et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: an international meta-analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, group 3, and group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;123(4):473–84.
Koo BK, Spit M, Jordens I, Low TY, Stange DE, van de Wetering M, et al. Tumour suppressor RNF43 is a stem-cell E3 ligase that induces endocytosis of Wnt receptors. Nature. 2012;488(7413):665–9.
Hsia EY, Gui Y, Zheng X. Regulation of hedgehog signaling by ubiquitination. Front Biol (Beijing). 2015;10(3):203–20.
Roussel MF, Robinson GW. Role of MYC in Medulloblastoma. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013;3(11). https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a014308.
Hammond-Martel I, Yu H, el Affar B. Roles of ubiquitin signaling in transcription regulation. Cell Signal. 2012;24(2):410–21.
Sengupta S, Pomeranz Krummel D, Pomeroy S. The evolution of medulloblastoma therapy to personalized medicine. F1000Res. 2017;6:490.
DeSouza RM, Jones BR, Lowis SP, Kurian KM. Pediatric medulloblastoma - update on molecular classification driving targeted therapies. Front Oncol. 2014;4:176.
Bielskiene K, Bagdoniene L, Mozuraitiene J, Kazbariene B, Janulionis E. E3 ubiquitin ligases as drug targets and prognostic biomarkers in melanoma. Medicina (Kaunas). 2015;51(1):1–9.
Clifford SC, Lusher ME, Lindsey JC, Langdon JA, Gilbertson RJ, Straughton D, et al. Wnt/wingless pathway activation and chromosome 6 loss characterize a distinct molecular sub-group of medulloblastomas associated with a favorable prognosis. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(22):2666–70.
Thom CS, Traxler EA, Khandros E, Nickas JM, Zhou OY, Lazarus JE, et al. Trim58 degrades dynein and regulates terminal erythropoiesis. Dev Cell. 2014;30(6):688–700.
Bedford L, Lowe J, Dick LR, Mayer RJ, Brownell JE. Ubiquitin-like protein conjugation and the ubiquitin-proteasome system as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10(1):29–46.
Shen M, Schmitt S, Buac D, Dou QP. Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome system for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013;17(9):1091–108.
Wang L, Wu J, Yuan J, Zhu X, Wu H, Li M. Midline2 is overexpressed and a prognostic indicator in human breast cancer and promotes breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Front Med. 2016;10(1):41–51.
Mayer RE, Hendrix P, Cron P, Matthies R, Stone SR, Goris J, et al. Structure of the 55-kDa regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A: evidence for a neuronal-specific isoform. Biochemistry. 1991;30(15):3589–97.
Huang HC, Klein PS. The frizzled family: receptors for multiple signal transduction pathways. Genome Biol. 2004;5(7):234.
Chen PH, Chen X, Lin Z, Fang D, He X. The structural basis of R-spondin recognition by LGR5 and RNF43. Genes Dev. 2013;27(12):1345–50.
Kahn M. Can we safely target the WNT pathway? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13(7):513–32.
Hao HX, Jiang X, Cong F. Control of Wnt receptor turnover by R-spondin-ZNRF3/RNF43 signaling module and its dysregulation in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2016;8(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers8060054.
de Lau W, Peng WC, Gros P, Clevers H. The R-spondin/Lgr5/Rnf43 module: regulator of Wnt signal strength. Genes Dev. 2014;28(4):305–16.
Blitzer JT, Nusse R. A critical role for endocytosis in Wnt signaling. BMC Cell Biol. 2006;7:28.
Jin YR, Yoon JK. The R-spondin family of proteins: emerging regulators of WNT signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(12):2278–87.
Mishra SK, Funair L, Cressley A, Gittes GK, Burns RC. High-affinity Dkk1 receptor Kremen1 is internalized by clathrin-mediated endocytosis. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52190.
Malinauskas T, Aricescu AR, Lu W, Siebold C, Jones EY. Modular mechanism of Wnt signaling inhibition by Wnt inhibitory factor 1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18(8):886–93.
Surmann-Schmitt C, Widmann N, Dietz U, Saeger B, Eitzinger N, Nakamura Y, et al. Wif-1 is expressed at cartilage-mesenchyme interfaces and impedes Wnt3a-mediated inhibition of chondrogenesis. J Cell Sci. 2009;122(Pt 20):3627–37.
Mazieres J, He B, You L, Xu Z, Lee AY, Mikami I, et al. Wnt inhibitory factor-1 is silenced by promoter hypermethylation in human lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64(14):4717–20.
Callow MG, Tran H, Phu L, Lau T, Lee J, Sandoval WN, et al. Ubiquitin ligase RNF146 regulates tankyrase and Axin to promote Wnt signaling. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22595.
Jho EH, Zhang T, Domon C, Joo CK, Freund JN, Costantini F. Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(4):1172–83.
Northcott PA, Buchhalter I, Morrissy AS, Hovestadt V, Weischenfeldt J, Ehrenberger T, et al. The whole-genome landscape of medulloblastoma subtypes. Nature. 2017;547(7663):311–7.
Yu J, Virshup DM. Updating the Wnt pathways. Biosci Rep. 2014;34(5). https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20140119.
Chen G, Courey AJ. Groucho/TLE family proteins and transcriptional repression. Gene. 2000;249(1–2):1–16.
Coon TA, Glasser JR, Mallampalli RK, Chen BB. Novel E3 ligase component FBXL7 ubiquitinates and degrades Aurora A, causing mitotic arrest. Cell Cycle. 2012;11(4):721–9.
Liu Y, Lear T, Zhao Y, Zhao J, Zou C, Chen BB, et al. F-box protein Fbxl18 mediates polyubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of the pro-apoptotic SCF subunit Fbxl7. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1630.
Liu Y, Lear T, Iannone O, Shiva S, Corey C, Rajbhandari S, et al. The proapoptotic F-box protein Fbxl7 regulates mitochondrial function by mediating the ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation of survivin. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(19):11843–52.
Wheatley SP, McNeish IA. Survivin: a protein with dual roles in mitosis and apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 2005;247:35–88.
Kamran M, Long ZJ, Xu D, Lv SS, Liu B, Wang CL, et al. Aurora kinase a regulates survivin stability through targeting FBXL7 in gastric cancer drug resistance and prognosis. Oncogene. 2017;6(2):e298.
Kim S, Kon M, DeLisi C. Pathway-based classification of cancer subtypes. Biol Direct. 2012;7:21.
Kool M, Koster J, Bunt J, Hasselt NE, Lakeman A, van Sluis P, et al. Integrated genomics identifies five medulloblastoma subtypes with distinct genetic profiles, pathway signatures and clinicopathological features. PLoS One. 2008;3(8):e3088.
Lee RT, Zhao Z, Ingham PW. Hedgehog signalling. Development. 2016;143(3):367–72.
Brennan D, Chen X, Cheng L, Mahoney M, Riobo NA. Noncanonical hedgehog signaling. Vitam Horm. 2012;88:55–72.
Frappart PO, Lee Y, Russell HR, Chalhoub N, Wang YD, Orii KE, et al. Recurrent genomic alterations characterize medulloblastoma arising from DNA double-strand break repair deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(6):1880–5.
Mille F, Tamayo-Orrego L, Levesque M, Remke M, Korshunov A, Cardin J, et al. The Shh receptor Boc promotes progression of early medulloblastoma to advanced tumors. Dev Cell. 2014;31(1):34–47.
Chen W, Wang Z, Jiang C, Ding Y. PP2A-mediated anticancer therapy. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013;2013:675429.
Perrotti D, Neviani P. Protein phosphatase 2A: a target for anticancer therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(6):e229–38.
Hu P, Yu L, Zhang M, Zheng L, Zhao Y, Fu Q, et al. Molecular cloning and mapping of the brain-abundant B1gamma subunit of protein phosphatase 2A, PPP2R2C, to human chromosome 4p16. Genomics. 2000;67(1):83–6.
Cundell MJ, Hutter LH, Nunes Bastos R, Poser E, Holder J, Mohammed S, et al. A PP2A-B55 recognition signal controls substrate dephosphorylation kinetics during mitotic exit. J Cell Biol. 2016;214(5):539–54.
Pereira G, Schiebel E. Mitotic exit: determining the PP2A dephosphorylation program. J Cell Biol. 2016;214(5):499–501.
Ruvolo PP. The broken "off" switch in cancer signaling: PP2A as a regulator of tumorigenesis, drug resistance, and immune surveillance. BBA Clin. 2016;6:87–99.
Sablina AA, Hahn WC. The role of PP2A A subunits in tumor suppression. Cell Adhes Migr. 2007;1(3):140–1.
Wlodarchak N, Xing Y. PP2A as a master regulator of the cell cycle. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016;51(3):162–84.
Kaur A, Westermarck J. Regulation of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) tumor suppressor function by PME-1. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016;44(6):1683–93.
Devilder MC, Cadoret E, Cherel M, Moreau I, Rondeau G, Bezieau S, et al. cDNA cloning, gene characterization and 13q14.3 chromosomal assignment of CHC1-L, a chromosome condensation regulator-like guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Genomics. 1998;54(1):99–106.
Latil A, Morant P, Fournier G, Mangin P, Berthon P, Cussenot O. CHC1-L, a candidate gene for prostate carcinogenesis at 13q14.2, is frequently affected by loss of heterozygosity and underexpressed in human prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2002;99(5):689–96.
Latil A, Chene L, Mangin P, Fournier G, Berthon P, Cussenot O. Extensive analysis of the 13q14 region in human prostate tumors: DNA analysis and quantitative expression of genes lying in the interval of deletion. Prostate. 2003;57(1):39–50.
Ross-Adams H, Lamb AD, Dunning MJ, Halim S, Lindberg J, Massie CM, et al. Integration of copy number and transcriptomics provides risk stratification in prostate cancer: a discovery and validation cohort study. EBioMedicine. 2015;2(9):1133–44.
Maezawa S, Hayano T, Koiwai K, Fukushima R, Kouda K, Kubota T, et al. Bood POZ containing gene type 2 is a human counterpart of yeast Btb3p and promotes the degradation of terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase. Genes Cells. 2008;13(5):439–57.
Janssens V, Goris J. Protein phosphatase 2A: a highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochem J. 2001;353(Pt 3):417–39.
Pham TT, Angus SP, Johnson GL. MAP3K1: genomic alterations in cancer and function in promoting cell survival or apoptosis. Genes Cancer. 2013;4(11–12):419–26.
Junttila MR, Li SP, Westermarck J. Phosphatase-mediated crosstalk between MAPK signaling pathways in the regulation of cell survival. FASEB J. 2008;22(4):954–65.
Pearson CG, Osborn DP, Giddings TH Jr, Beales PL, Winey M. Basal body stability and ciliogenesis requires the conserved component Poc1. J Cell Biol. 2009;187(6):905–20.
Huang S, Zhang Z, Zhang C, Lv X, Zheng X, Chen Z, et al. Activation of Smurf E3 ligase promoted by smoothened regulates hedgehog signaling through targeting patched turnover. PLoS Biol. 2013;11(11):e1001721.
Farooqi AA, Waseem MS, Riaz AM, Bhatti S. SMURF and NEDD4: sharp shooters monitor the gate keepers and ion traffic controllers of lead astray cell. J Membr Biol. 2011;244(1):1–8.
Cui Y, He S, Xing C, Lu K, Wang J, Xing G, et al. SCFFBXL(1)(5) regulates BMP signalling by directing the degradation of HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf1. EMBO J. 2011;30(13):2675–89.
Malatesta M, Steinhauer C, Mohammad F, Pandey DP, Squatrito M, Helin K. Histone acetyltransferase PCAF is required for hedgehog-Gli-dependent transcription and cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2013;73(20):6323–33.
Zuhlke KA, Johnson AM, Tomlins SA, Palanisamy N, Carpten JD, Lange EM, et al. Identification of a novel germline SPOP mutation in a family with hereditary prostate cancer. Prostate. 2014;74(9):983–90.
Cai H, Liu A. Spop regulates Gli3 activity and Shh signaling in dorsoventral patterning of the mouse spinal cord. Dev Biol. 2017;432:72–85.
Wen X, Lai CK, Evangelista M, Hongo JA, de Sauvage FJ, Scales SJ. Kinetics of hedgehog-dependent full-length Gli3 accumulation in primary cilia and subsequent degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(8):1910–22.
Zhang Q, Shi Q, Chen Y, Yue T, Li S, Wang B, et al. Multiple Ser/Thr-rich degrons mediate the degradation of ci/Gli by the Cul3-HIB/SPOP E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(50):21191–6.
Gan W, Dai X, Lunardi A, Li Z, Inuzuka H, Liu P, et al. SPOP promotes ubiquitination and degradation of the ERG oncoprotein to suppress prostate cancer progression. Mol Cell. 2015;59(6):917–30.
De Smaele E, Di Marcotullio L, Moretti M, Pelloni M, Occhione MA, Infante P, et al. Identification and characterization of KCASH2 and KCASH3, 2 novel Cullin3 adaptors suppressing histone deacetylase and hedgehog activity in medulloblastoma. Neoplasia. 2011;13(4):374–85.
Canettieri G, Di Marcotullio L, Greco A, Coni S, Antonucci L, Infante P, et al. Histone deacetylase and Cullin3-REN(KCTD11) ubiquitin ligase interplay regulates hedgehog signalling through Gli acetylation. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(2):132–42.
Gulino A, Di Marcotullio L, Canettieri G, De Smaele E, Screpanti I. Hedgehog/Gli control by ubiquitination/acetylation interplay. Vitam Horm. 2012;88:211–27.
Canettieri G, Di Marcotullio L, Coni S, Greco A, Gulino A. Turning off the switch in medulloblastoma: the inhibitory acetylation of an oncogene. Cell Cycle. 2010;9(11):2047–8.
Korshunov A, Remke M, Kool M, Hielscher T, Northcott PA, Williamson D, et al. Biological and clinical heterogeneity of MYCN-amplified medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;123(4):515–27.
Ciechanover A, DiGiuseppe JA, Schwartz AL, Brodeur GM. Degradation of MYCN oncoprotein by the ubiquitin system. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1991;366:37–43.
Otto T, Horn S, Brockmann M, Eilers U, Schuttrumpf L, Popov N, et al. Stabilization of N-Myc is a critical function of Aurora A in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2009;15(1):67–78.
Zhao X, Heng JI, Guardavaccaro D, Jiang R, Pagano M, Guillemot F, et al. The HECT-domain ubiquitin ligase Huwe1 controls neural differentiation and proliferation by destabilizing the N-Myc oncoprotein. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(6):643–53.
King B, Boccalatte F, Moran-Crusio K, Wolf E, Wang J, Kayembe C, et al. The ubiquitin ligase Huwe1 regulates the maintenance and lymphoid commitment of hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Immunol. 2016;17(11):1312–21.
Faisal A, Vaughan L, Bavetsias V, Sun C, Atrash B, Avery S, et al. The aurora kinase inhibitor CCT137690 downregulates MYCN and sensitizes MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10(11):2115–23.
Tavana O, Li D, Dai C, Lopez G, Banerjee D, Kon N, et al. HAUSP deubiquitinates and stabilizes N-Myc in neuroblastoma. Nat Med. 2016;22(10):1180–6.
Rodriguez-Blanco J, Pednekar L, Penas C, Li B, Martin V, Long J, et al. Inhibition of WNT signaling attenuates self-renewal of SHH-subgroup medulloblastoma. Oncogene. 2017;36(45):6306–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.232.
Poschl J, Bartels M, Ohli J, Bianchi E, Kuteykin-Teplyakov K, Grammel D, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling inhibits the Shh pathway and impairs tumor growth in Shh-dependent medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;127(4):605–7.
Blaess S, Stephen D, Joyner AL. Gli3 coordinates three-dimensional patterning and growth of the tectum and cerebellum by integrating Shh and Fgf8 signaling. Development. 2008;135(12):2093–103.
Schweiger S, Dorn S, Fuchs M, Kohler A, Matthes F, Muller EC, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase MID1 catalyzes ubiquitination and cleavage of Fu. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(46):31805–17.
Du H, Huang Y, Zaghlula M, Walters E, Cox TC, Massiah MA. The MID1 E3 ligase catalyzes the polyubiquitination of Alpha4 (alpha4), a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A): novel insights into MID1-mediated regulation of PP2A. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(29):21341–50.
Lee EY, Ji H, Ouyang Z, Zhou B, Ma W, Vokes SA, et al. Hedgehog pathway-regulated gene networks in cerebellum development and tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(21):9736–41.
Vuong TA, Leem YE, Kim BG, Cho H, Lee SJ, Bae GU, et al. A sonic hedgehog coreceptor, BOC regulates neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth via interaction with ABL and JNK activation. Cell Signal. 2017;30:30–40.
Shahi MH, Afzal M, Sinha S, Eberhart CG, Rey JA, Fan X, et al. Human hedgehog interacting protein expression and promoter methylation in medulloblastoma cell lines and primary tumor samples. J Neuro-Oncol. 2011;103(2):287–96.
Tan J, Lee PL, Li Z, Jiang X, Lim YC, Hooi SC, et al. B55beta-associated PP2A complex controls PDK1-directed myc signaling and modulates rapamycin sensitivity in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(5):459–71.
Tan Y, Sun D, Jiang W, Klotz-Noack K, Vashisht AA, Wohlschlegel J, et al. PP2A-B55beta antagonizes cyclin E1 proteolysis and promotes its dysregulation in cancer. Cancer Res. 2014;74(7):2006–14.
Oberg EA, Nifoussi SK, Gingras AC, Strack S. Selective proteasomal degradation of the B’beta subunit of protein phosphatase 2A by the E3 ubiquitin ligase adaptor Kelch-like 15. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(52):43378–89.
De Simone A, Gonczy P. Computer simulations reveal mechanisms that organize nuclear dynein forces to separate centrosomes. Mol Biol Cell. 2017;28(23):3165–70.
Mahale SP, Sharma A, Mylavarapu SV. Dynein light intermediate chain 2 facilitates the metaphase to anaphase transition by inactivating the spindle assembly checkpoint. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0159646.
Qiu X, Huang Y, Zhou Y, Zheng F. Aberrant methylation of TRIM58 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its potential clinical implication. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(2):811–8.
Kajiura K, Masuda K, Naruto T, Kohmoto T, Watabnabe M, Tsuboi M, et al. Frequent silencing of the candidate tumor suppressor TRIM58 by promoter methylation in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(2):2890–905.
Zhang W, Mi J, Li N, Sui L, Wan T, Zhang J, et al. Identification and characterization of DPZF, a novel human BTB/POZ zinc finger protein sharing homology to BCL-6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;282(4):1067–73.
Tonchev AB, Tuoc TC, Rosenthal EH, Studer M, Stoykova A. Zbtb20 modulates the sequential generation of neuronal layers in developing cortex. Mol Brain. 2016;9(1):65.
Groisman R, Kuraoka I, Chevallier O, Gaye N, Magnaldo T, Tanaka K, et al. CSA-dependent degradation of CSB by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway establishes a link between complementation factors of the Cockayne syndrome. Genes Dev. 2006;20(11):1429–34.
Felsher DW. MYC inactivation elicits oncogene addiction through both tumor cell-intrinsic and host-dependent mechanisms. Genes Cancer. 2010;1(6):597–604.
Suryo Rahmanto A, Savov V, Brunner A, Bolin S, Weishaupt H, Malyukova A, et al. FBW7 suppression leads to SOX9 stabilization and increased malignancy in medulloblastoma. EMBO J. 2016;35(20):2192–212.
Kim SY, Herbst A, Tworkowski KA, Salghetti SE, Tansey WP. Skp2 regulates Myc protein stability and activity. Mol Cell. 2003;11(5):1177–88.
von der Lehr N, Johansson S, Wu S, Bahram F, Castell A, Cetinkaya C, et al. The F-box protein Skp2 participates in c-Myc proteosomal degradation and acts as a cofactor for c-Myc-regulated transcription. Mol Cell. 2003;11(5):1189–200.
Tansey WP. Transcriptional activation: risky business. Genes Dev. 2001;15(9):1045–50.
Kalev P, Simicek M, Vazquez I, Munck S, Chen L, Soin T, et al. Loss of PPP2R2A inhibits homologous recombination DNA repair and predicts tumor sensitivity to PARP inhibition. Cancer Res. 2012;72(24):6414–24.
Zhang H, Cao D, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Guo X, Li H, et al. ZBTB20 is a sequence-specific transcriptional repressor of alpha-fetoprotein gene. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11979.
Fedele V, Dai F, Masilamani AP, Heiland DH, Kling E, Gatjens-Sanchez AM, et al. Epigenetic regulation of ZBTB18 promotes glioblastoma progression. Mol Cancer Res. 2017;15(8):998–1011.
Link LA, Howley BV, Hussey GS, Howe PH. PCBP1/HNRNP E1 protects chromosomal integrity by translational regulation of CDC27. Mol Cancer Res. 2016;14(7):634–46.
Stewart S, Fang G. Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome controls the stability of TPX2 during mitotic exit. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(23):10516–27.
Song L, Rape M. Regulated degradation of spindle assembly factors by the anaphase-promoting complex. Mol Cell. 2010;38(3):369–82.
Manic G, Corradi F, Sistigu A, Siteni S, Vitale I. Molecular regulation of the spindle assembly checkpoint by kinases and phosphatases. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2017;328:105–61.
Sansregret L, Patterson JO, Dewhurst S, Lopez-Garcia C, Koch A, McGranahan N, et al. APC/C dysfunction limits excessive cancer chromosomal instability. Cancer Discov. 2017;7(2):218–33.
Schwarz TL. Mitochondrial trafficking in neurons. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(6). https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a011304.
Hagting A, Den Elzen N, Vodermaier HC, Waizenegger IC, Peters JM, Pines J. Human securin proteolysis is controlled by the spindle checkpoint and reveals when the APC/C switches from activation by Cdc20 to Cdh1. J Cell Biol. 2002;157(7):1125–37.
Sivakumar S, Gorbsky GJ. Spatiotemporal regulation of the anaphase-promoting complex in mitosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16(2):82–94.
Hein JB, Hertz EPT, Garvanska DH, Kruse T, Nilsson J. Distinct kinetics of serine and threonine dephosphorylation are essential for mitosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(12):1433–40.
Manchado E, Guillamot M, de Carcer G, Eguren M, Trickey M, Garcia-Higuera I, et al. Targeting mitotic exit leads to tumor regression in vivo: modulation by Cdk1, Mastl, and the PP2A/B55alpha,delta phosphatase. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(6):641–54.
Densham RM, Garvin AJ, Stone HR, Strachan J, Baldock RA, Daza-Martin M, et al. Human BRCA1-BARD1 ubiquitin ligase activity counteracts chromatin barriers to DNA resection. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016;23(7):647–55.
Hao Z, Zhang H, Cowell J. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2C: molecular biology, role in tumorigenesis, and potential as a biomarker. Tumour Biol. 2012;33(3):723–30.
Alshalalfa M, Schliekelman M, Shin H, Erho N, Davicioni E. Evolving transcriptomic fingerprint based on genome-wide data as prognostic tools in prostate cancer. Biol Cell. 2015;107(7):232–44.
Liu Z, Yuan F, Ren J, Cao J, Zhou Y, Yang Q, et al. GPS-ARM: computational analysis of the APC/C recognition motif by predicting D-boxes and KEN-boxes. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34370.
Fuchsberger T, Lloret A, Vina J. New functions of APC/C ubiquitin ligase in the nervous system and its role in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051057.
Li W, Bengtson MH, Ulbrich A, Matsuda A, Reddy VA, Orth A, et al. Genome-wide and functional annotation of human E3 ubiquitin ligases identifies MULAN, a mitochondrial E3 that regulates the organelle’s dynamics and signaling. PLoS One. 2008;3(1):e1487.
Lehmann G, Udasin RG, Ciechanover A. On the linkage between the ubiquitin-proteasome system and the mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;473(1):80–6.
Cho YJ, Tsherniak A, Tamayo P, Santagata S, Ligon A, Greulich H, et al. Integrative genomic analysis of medulloblastoma identifies a molecular subgroup that drives poor clinical outcome. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(11):1424–30.
Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T, Eberhart CG, Mack S, et al. Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(11):1408–14.
Remke M, Hielscher T, Northcott PA, Witt H, Ryzhova M, Wittmann A, et al. Adult medulloblastoma comprises three major molecular variants. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(19):2717–23.
Huang X, Jan LY. Targeting potassium channels in cancer. J Cell Biol. 2014;206(2):151–62.
Mochida S, Ikeo S, Gannon J, Hunt T. Regulated activity of PP2A-B55 delta is crucial for controlling entry into and exit from mitosis in Xenopus egg extracts. EMBO J. 2009;28(18):2777–85.
Seshacharyulu P, Pandey P, Datta K, Batra SK. Phosphatase: PP2A structural importance, regulation and its aberrant expression in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013;335(1):9–18.
Nanahoshi M, Tsujishita Y, Tokunaga C, Inui S, Sakaguchi N, Hara K, et al. Alpha4 protein as a common regulator of type 2A-related serine/threonine protein phosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1999;446(1):108–12.
Kong M, Ditsworth D, Lindsten T, Thompson CB. Alpha4 is an essential regulator of PP2A phosphatase activity. Mol Cell. 2009;36(1):51–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no of conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vriend, J., Tate, R.B. Differential Expression of Genes for Ubiquitin Ligases in Medulloblastoma Subtypes. Cerebellum 18, 469–488 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-019-1009-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-019-1009-y