Abstract
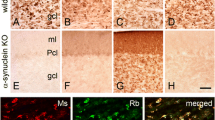
Unipolar brush cells (UBCs) are glutamatergic cerebellar interneurons of the granular layer. Previous studies have shown that there are two distinct subsets of UBCs present in the mice cerebellar cortex: calcium-binding protein calretinin (CR) positive and metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR)1α positive. In this study, we identify phospholipase C (PLC) β4 as an antigenic marker of a novel subset of UBCs. Double immunolabeling reveals that none of the CR+ subset expresses PLCβ4. In contrast, most members of the mGluR1α subset also express PLCβ4. In addition, 65% of the PLCβ4+ subset does not express mGluR1α. Thus, there are three distinct UBC subsets in the mouse cerebellum: CR+/PLCβ4−/mGluR1α−, PLCβ4+/mGluR1α−/CR−, and mGluR1α+/PLCβ4+/CR−. Each has a different topographical distribution, both between lobules and mediolaterally within the vermis. The development of PLCβ4 expression in UBCs is exclusively postnatal—first seen only at P12 and mature at about 3 weeks. A distinct subset of PLCβ4+ UBCs is also present in primary cerebellar cultures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J, Bayer SA (1977) Time of origin and distribution of a new cell type in the rat cerebellar cortex. Exp Brain Res 29:265–274
Mugnaini E, Floris A (1994) The unipolar brush cell: a neglected neuron of the mammalian cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol 339:174–180
Dino MR, Nunzi MG, Anelli R, Mugnaini E (2000) Unipolar brush cells of the vestibulocerebellum: afferents and targets. Prog Brain Res 124:123–137
Nunzi MG, Mugnaini E (2000) Unipolar brush cell axons form a large system of intrinsic mossy fibers in the postnatal vestibulocerebellum. J Comp Neurol 422:55–65
Nunzi MG, Birnstiel S, Bhattacharyya BJ, Slater NT, Mugnaini E (2001) Unipolar brush cells form a glutamatergic projection system within the mouse cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol 434:329–341
Floris A, Dino M, Jacobowitz DM, Mugnaini E (1994) The unipolar brush cells of the rat cerebellar cortex and cochlear nucleus are calretinin-positive: a study by light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Anat Embryol Berl 189:495–520
Nunzi MG, Shigemoto R, Mugnaini E (2002) Differential expression of calretinin and metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR1 alpha defines subsets of unipolar brush cells in mouse cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 451:189–199
Sekerková G, Ilijic E, Mugnaini E (2004) Time of origin of unipolar brush cells in the rat cerebellum as observed by prenatal bromodeoxyuridine labeling. Neuroscience 127:845–858
Nunzi MG, Russo M, Mugnaini E (2003) Vesicular glutamate transporters VGLUT1 and VGLUT2 define two subsets of unipolar brush cells in organotypic cultures of mouse vestibulocerebellum. Neuroscience 122:359–371
Nakamura M, Sato K, Fukaya M, Araishi K, Aiba A, Kano M et al (2004) Signaling complex formation of phospholipase Cβ4 with metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1alpha and 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor at the perisynapse and endoplasmic reticulum in the mouse brain. Eur J Neurosci 20:2929–2944
Zeilhofer HU, Studler B, Arabadzisz D, Schweizer C, Ahmadi S, Layh B et al (2005) Glycinergic neurons expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein in bacterial artificial chromosome transgenic mice. J Comp Neurol 482:123–141
Feng G, Mellor RH, Bernstein M, Keller-Peck C, Nguyen QT, Wallace M et al (2000) Imaging neuronal subsets in transgenic mice expressing multiple spectral variants of GFP. Neuron 28:41–51
Brochu G, Maler L, Hawkes R (1990) Zebrin II: a polypeptide antigen expressed selectively by Purkinje cells reveals compartments in rat and fish cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 291:538–552
Abo T, Balch CM (1981) A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody. J Immunol 127:1024–1029
Eisenman LM, Hawkes R (1993) Antigenic compartmentation in the mouse cerebellar cortex: zebrin and HNK-1 reveal a complex, overlapping molecular topography. J Comp Neurol 335:586–605
Marzban H, Sillitoe RV, Hoy M, Chung SH, Rafuse VR, Hawkes R (2004) Abnormal HNK-1 expression in the cerebellum of an N-CAM null mouse. J Neurocytol 33:117–130
Schwaller B, Buchwald P, Blümcke I, Celio MR, Hunziker W (1994) Characterization of a polyclonal antiserum against the purified recombinant calcium-binding protein calretinin. Cell Calcium 14:639–648
Tanaka J, Nakagawa S, Kushiya E, Yamasaki M, Fukaya M, Iwanaga T et al (2000) Gq protein α subunits Gαq and Gα11 are localized at postsynaptic extra-junctional membrane of cerebellar Purkinje cells and hippocampal pyramidal cells. Eur J Neurosci 12:781–792
Sarna JR, Marzban H, Watanabe M, Hawkes R (2006) Complementary stripes of phospholipase Cβ3 and Cβ4 expression by Purkinje cell subsets in the mouse cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 496:303–313
Jiang H, Lyubarsky A, Dodd R, Vardi N, Pugh E, Baylor D et al (1996) Phospholipase C β4 is involved in modulating the visual response in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:14598–14601
Sillitoe RV, Benson MA, Blake DJ, Hawkes R (2003) Abnormal dysbindin expression in cerebellar mossy fiber synapses in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Neurosci 23:6576–6585
Furuya S, Makino A, Hirabayashi Y (1998) An improved method for culturing cerebellar Purkinje cells with differentiated dendrites under a mixed monolayer setting. Brain Res Prot 3:192–198
Tabata T, Sawada S, Araki K, Bono Y, Furuya S, Kano M (2000) A reliable method for culture of dissociated mouse cerebellar cells enriched for Purkinje neurons. J Neurosci Meth 104:45–53
Marzban H, Khanzada U, Shabir S, Hawkes R, Langnaese K, Smalla K et al (2003) Expression of the immunoglobulin superfamily neuroplastin adhesion molecules in adult and developing mouse cerebellum and their location to parasagittal stripes. J Comp Neurol 462:286–301
Ozol K, Hayden JM, Oberdick J, Hawkes R (1999) Transverse zones in the vermis of the mouse cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 412:95–111
Armstrong C, Krueger-Naug AM, Currie WC, Hawkes R (2000) Constitutive expression of the 25 kDa heat shock protein Hsp25 reveals novel parasagittal bands of Purkinje cells in the adult mouse cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol 416:383–397
Sillitoe RV, Hawkes R (2002) Whole-mount immunohistochemistry: a high-throughput screen for patterning defects in the mouse cerebellum. J Histochem Cytochem 50:235–244
Hawkes R, Brochu G, Doré L, Gravel C, Leclerc N (1992) Zebrins: molecular markers of compartmentation in the cerebellum. In: Llinás R, Sotelo C (eds) The cerebellum revisited. Springer, New York, NY, pp 22–55
Hawkes R (1997) An anatomical model of cerebellar modules. Prog Brain Res 114:39–52
Herrup K, Kuemerle B (1997) The compartmentalization of the cerebellum. Ann Rev Neurosci 20:61–90
Oberdick J, Baader SL, Schilling K (1998) From zebra stripes to postal zones: deciphering patterns of gene expression in the cerebellum. Trends Neurosci 21:383–390
Ji Z, Hawkes R (1994) Topography of Purkinje cell compartments and mossy fiber terminal fields in lobules II and III of the rat cerebellar cortex: spinocerebellar and cuneocerebellar projections. Neuroscience 61:935–954
Akintunde A, Eisenman LM (1994) External cuneocerebellar projections and Purkinje cell zebrin II bands: a direct comparison of parasagittal banding in the mouse cerebellum. J Chem Neuroanat 7:75–86
Voogd J, Gerrits NM, Ruigrok TJ (1996) Organization of the vestibulocerebellum. Ann N Y Acad Sci 781:553–579
Yan XX, Yen LS, Garey LJ (1993) Parasagittal patches in the granular layer of the developing and adult rat cerebellum as demonstrated by NADPH-diaphorase histochemistry. NeuroReport 4:1227–1230
Hawkes R, Turner RW (1994) Compartmentation of NADPH-diaphorase activity in the mouse cerebellar cortex. J Comp Neurol 346:499–516
Schilling K, Schmidt HH, Baader SL (1994) Nitric oxide synthase expression reveals compartments of cerebellar granule cells and suggests a role for mossy fibers in their development. Neuroscience 59:893–903
Ozol KO, Hawkes R (1997) The compartmentation of the granular layer of the cerebellum. Histol Histopathol 12:171–184
Ahn AH, Dziennis S, Hawkes R, Herrup K (1994) The cloning of zebrin II reveals its identity with aldolase C. Development 120:2081–2090
Hawkes R, Herrup K (1996) Aldolase C/zebrin II and the regionalization of the cerebellum. J Mol Neurobiol 6:147–158
Abbott LC, Jacobowitz DM (1995) Development of calretinin-immunoreactive unipolar brush-like cells and an afferent pathway to the embryonic and early postnatal mouse cerebellum. Anat Embryol Berl 191:541–559
Marzban H, Chung S, Watanabe M, Hawkes R (2007) Phospholipase Cβ4 expression reveals the continuity of cerebellar topography through development. J Comp Neurol 502:857–871
Anelli R, Mugnaini E (2001) Enrichment of unipolar brush cell-like neurons in primary rat cerebellar cultures. Anat Embryol (Berl) 203:283–292
Acknowledgments
These studies were supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (RH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, SH., Marzban, H., Watanabe, M. et al. Phospholipase Cβ4 Expression Identifies a Novel Subset of Unipolar Brush Cells in the Adult Mouse Cerebellum. Cerebellum 8, 267–276 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-009-0092-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12311-009-0092-x