Abstract
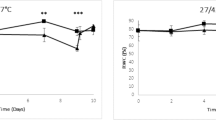
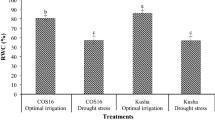
The high costs of N fertilizers in the coffee production emphasizes the need to optimize fertilization practices and improve nitrogen use efficiency. Urea is widespread in nature, characterizing itself as a significant source of nitrogen for the growth and development of several organisms. Thus, the characterization of genes involved in urea transport in coffee plants is an important research topic for the sustainable production of this valuable cash crop. In the current study, we evaluated the expression of the DUR3 gene under abiotic and biotic stresses in coffee plants. Here, we show that the expression of a high-affinity urea transporter gene (CaDUR3) was up-regulated by N starvation in leaves and roots of two out of three C. arabica cultivars examined. Moreover, the CaDUR3 gene was differentially expressed in coffee plants under different abiotic and biotic stresses. In plants of cv. IAPAR59, CaDUR3 showed an increased expression in leaves after exposure to water deficit and heat stress, while it was downregulated in plants under salinity. Upon infection with H. vastatrix (coffee rust), the CaDUR3 was markedly up-regulated at the beginning of the infection process in the disease susceptible Catuaí Vermelho 99 in comparison with the resistant cultivar. These results indicate that besides urea acquisition and N-remobilization, CaDUR3 gene may be closely involved in the response to various stresses.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402
Arnhold E (2013) Package in the R environment for analysis of variance and complementary analyses. Braz J Vet Res Anim Sci 50(6):488–492
Baba VY, Braghini MT, dos Santos TB, de Carvalho K, Soares JDM, Ivamoto-Suzuki ST, Maluf MP, Padilha L, Paccola-Meirelles LD, Pereira LF, Domingues DS (2020) Transcriptional patterns of Coffea arabica L. nitrate reductase, glutamine and asparagine synthetase genes are modulated under nitrogen suppression and coffee leaf rust. PeerJ 8:e8320
Bawin Y, Ruttink T, Staelens A, Haegeman A, Stoffelen P, Mwanga JCIM, Roldán-Ruiz I, Honnay O, Janssens SB (2020) Phylogenomic analysis clarifies the evolutionary origin of Coffea arabica L. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1111/jse.12694
Beier MP, Fujita T, Sasaki K, Kanno K, Ohashi M, Tamura W, Konishi N, Saito M, Imagawa F, Ishiyama K, Miyao A, Yamaya T, Kojima S (2019) The urea transporter DUR3 contributes to rice production under nitrogen-deficient and field conditions. Physiol Plant 167(1):75–89
Bohner A, Kojima S, Hajirezaei M, Melzer M, von Wirén N (2015) Urea retranslocation from senescing Arabidopsis leaves is promoted by DUR3-mediated urea retrieval from leaf apoplast. Plant J 81:377–387
Box GEP, Cox DR (1964) An analysis of transformations (with discussion). R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 26:211–252
Bloom AJ (2015) The increasing importance of distinguishing among plant nitrogen sources. Curr Opin Plant Biol 25:10–16
Chaumont F, Tyerman SD (2017) Plant aquaporins from transport to signaling. Springer, Cham
Clark RB (1975) Characterization of phosphatase of intact maize roots. J Agr Food Chem 23:458–460
Davis AP, Tosh J, Ruch N, Fay MF (2011) Growing coffee: Psilanthus (Rubiaceae) subsumed on the basis of molecular and morphological data; implications for the size, morphology, distribution and evolutionary history of Coffea. Bot J Linn Soc 167:357–377
de Carvalho K, Bespalhok Filho JC, dos Santos TB, de Souza SGH, Vieira LGE, Pereira LFP, Domingues DS (2013) Nitrogen starvation, salt and heat stress in coffee (Coffea arabica L.): identification and validation of new genes for qPCR normalization. Mol Biotechnol 53:315–325
De Michele R, Loqué D, Lalonde S, Frommer WB (2012) Ammonium and urea transporter inventory of the Selaginella and Pyscomitrella genomes Front. Plant Sci 3:62
dos Santos TB, Budzinski IG, Marur CJ, Petkowicz CL, Pereira LF, Vieira LG (2011) Expression of three galactinol synthase isoforms in Coffea arabica L. and accumulation of raffinose and stachyose in response to abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:441–448
dos Santos TB, Lima JE, Felicio MS, Soares JDM, Domingues DS (2017) Genome-wide identification, classification and transcriptional analysis of nitrate and ammonium transporters in Coffea. Genet Mol Biol 40:346–359
dos Santos TB, Lima RBD, Nagashima GT, Petkowicz CLDO, Carpentieri-Pípolo V, Pereira LFP, Domingues DS, Vieira LGE (2015) Galactinol synthase transcriptional profile in two genotypes of Coffea canephora with contrasting tolerance to drought. Genet Mol Biol 38(2):182–190
dos Santos TB, Soares JDM, Lima JE, Silva JC, Ivamoto ST, Baba VY, Souza SGH, Lorenzetti APR, Paschoal AR, Meda AR, Nishiyama Júnior MY, De Oliveira ÚC, Mokochinski JB, Guyot R, Junqueira-de-Azevedo ILM, Figueira AVO, Mazzafera P, Júnior OR, Vieira LGE, Pereira LFP, Domingues DS (2019) An integrated analysis of mRNA and sRNA transcriptional profiles in Coffea arabica L. roots: insights on nitrogen starvation responses. Funct Integr Genom 19(1):151–169
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Elberry HM, Majumdar ML, Cunningham TS, Sumrada RA, Cooper TG (1993) Regulation of the urea active transporter gene (DUR3) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 175(15):4688–4698
Fan X, Naz M, Fan X, Xuan W, Miller AJ, Xu G (2017) Plant nitrate transporters: from gene function to application. J Exp Bot 68:2463–2475
Fridell G (2014) Coffee. Wiley, New York
Gerendás J, Zhu Z, Sttelmacher B (1998) Influence of nitrogen and Ni supply on nitrogen metabolism and urease activity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot 49:1545–1554
Gupta KJ, Brotman Y, Segu S, Zeier T, Zeier J, Persijn ST, Cristescu SM, Harren FJM, Bauwe H, Fernie AR, Kaiser WM, Mur LAJ (2013) The form of nitrogen nutrition affects resistance against Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola in tobacco. J Exp Bot 64:553–568
Karamos RE, Hanson K, Stevenson FC (2014) Nitrogen form, time and rate of application, and nitrification inhibitor effects on crop production. Can J Plant Sci 94:425–432
Kojima S, Bohner A, Gassert B, Yuan L, von Wirén N (2007) AtDUR3 represents the major transporter for high-affinity urea transport across the plasma membrane of nitrogen-deficient Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 52:30–40
Lashermes P, Combes MC, Robert J, Trouslot P, D’Hont A, Charrier A (1999) Molecular characterisation and origin of the Coffea arabica L. genome. Mol Gen Genet 261:259–266
Lashermes P, Paczek V, Trouslot P, Combes MC, Couturon E, Charrier A (2000) Single-locus inheritance in the allotetraploid Coffea arabica L. and interspecific hybrid C. arabica x C. canephora. J Hered 91:81–85
Liu LH, Ludewig U, Frommer WB, von Wirén N (2003a) AtDUR3 encodes a new type of high-affinity urea/H + symporter in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:790-800***
Liu GW, Sun AL, Li DQ, Athman A, Gilliham M, Liu LH (2015) Molecular identification and functional analysis of a maize (Zea mays) DUR3 homolog that transports urea with high affinity. Planta 241:861–874
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Masclaux-Daubresse C, Daniel-Vedele F, Dechorgnat J, Chardon F, Gaufichon L, Suzuki A (2010) Nitrogen uptake, assimilation and remobilization in plants: challenges for sustainable and productive agriculture. Ann Bot 105:1141–1157
Matiz A, Mioto PT, Mercier H (2019) Urea in plants: metabolic aspects and ecological implications 1–31. In: Progress in botany. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Mérigout P, Lelandais M, Bitton F, Renou JP, Briand X, Meyer C, Daniel-Vedele F (2008) Physiological and transcriptomic aspects of urea uptake and assimilation in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol 147:1225–1238
Mondego JMC, Vidal RO, CarazzolleMF TEK, Parizzi LP, Costa GGL (2011) An EST-based analysis identifies new genes and reveals distinctive gene expression features of Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora. BMC Plant Biol 11:30
Pageau K, Reisdorf-Cren M, Morot-Gaudry JF, Masclaux-Daubress C (2006) The two senescence-related markers, GS1 (cytosolic glutamine synthetase) and GDH (glutamate dehydrogenase), involved in nitrogen mobilization, are differentially regulated during pathogen attack and by stress hormones and reactive oxygen species in Nicotiana tabacum L. leaves. J Exp Bot 57:547–557
R Core Team (2019) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. https://www.R-project.org/
Roca LF, Romero J, Bohórquez JM, Alcántara E, Fernández-Escobar R, Trapero A (2018) Nitrogen status affects growth, chlorophyll content and infection by Fusicladium oleagineum in olive. Crop Prot 109:80–85
Ruijter JM, Ramakers C, Hoogaars WMH, Karlen Y, Bakker O, van den Hoff MJB, Moorman AFM (2009) Amplification efficiency: linking baseline and bias in the analysis of quantitative PCR data. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e45
Scalabrin S, Toniutti L, Di Gaspero G, Scaglione D, Magris G, Vidotto M, Pinosio S, Cattonaro F, Magni F, Jurman I, Cerutti M, Liverani FS, Navarini L, Del Terra L, Pellegrino G, Ruosi MR, Vitulo N, Valle G, Pallavicini A, Graziosi G, Klein PE, Bentley N, Murray S, Solano W, Al Hakimi A, Schilling T, Montagnon C, Morgante M, Bertrand B (2020) A single polyploidization event at the origin of the tetraploid genome of Coffea arabica is responsible for the extremely low genetic variation in wild and cultivated germplasm. Sci Rep 10(1):4642
Tegeder M, Masclaux-Daubresse C (2018) Source and sink mechanisms of nitrogen transport and use. New Phytol 217:35–53
Tucker C (2017) Coffee culture, 2nd edn. Routledge, New York, p 188
Thalineau E, Fournier C, Gravot A, Wendehenne D, Jeandroz S, Truong H-N (2018) Nitrogen modulation of Medicago truncatula resistance to Aphanomyces euteiches depends on plant genotype. Mol Plant Pathol 19(3):664–676
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern applied statistics with S, 4th edn. Springer, New York (ISBN 0-387-95457-0)
Vidal EA, Araus V, Lu C, Parry G, Green PJ, Coruzzi GM, Gutiérrez RA (2010) Nitrate-responsive miR393/AFB3 regulatory module controls root system architecture in Arabidopsis thaliana. P Natl Acad Sci 107:4477–4482
Vieira LGE, Andrade AC, Colombo CA, Moraes AHDA, Metha Â, Oliveira ACD, Labate CA, Marino CL, Monteiro-Vitorello CB, Monte DC, Giglioti E, Kimura ET, Romano E, Kuramae EE, Lemos EGM, Almeira ERP, Jorge EC, Albuquerque EVS, Silva FR, Vinecky F, Sawazaki HE, Dorry HFA, Carrer H, Abreu IN, Batista JAN, Teixeira JB, Kitajima JP, Xavier KG, Lima LM, Camargo LEA, Pereira LFP, Coutinho LL, Lemos MVF, Romano MR, Machado MA, Costa MMC, Sá MFG, Goldman MHS, Ferro MIT, Tinoco MLP, Oliveira MC, Sluys MAV, Shimizu MM, Maluf MP, Eira MTS, Filho OG, Arruda P, Mazzafera P, Mariani PDSC, Oliveira RLBC, Harakava R, Balbao SF, Tsai SM, Mauro SMZ, Santos SN, Siqueira WJ, Costa GGL, Formighieri EF, Carazzolle MF, Pereira GAG (2006) Brazilian coffee genome project: an ESTbased genomic resource. Braz J Plant Physiol 18:95–108
Wang WH, Köhler B, Cao FQ, Liu LH (2008) Molecular and physiological aspects of urea transport in higher plants. Plant Sci 175:467–477
Wang WH, Köhler B, Cao FQ, Liu GW, Gong YY, Sheng S, Song QC, Cheng XY, Garnett T, Okamoto M, Qin R, Mueller-Roeber B, Tester M, Liu LH (2012) Rice DUR3 mediates high-affinity urea transport and plays an effective role in improvement of urea acquisition and utilization when expressed in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 193:432–444
Wang WH, Liu GW, Cao FQ, Cheng XY, Liu BW, Liu LH (2013) Inadequate root uptake may represent a major component limiting rice to use urea as sole nitrogen source for growth. Plant Soil 363(1–2):191–200
Weatherburn MW (1967) Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal Chem 39:971–974
Witte CP (2011) Urea metabolism in plants. Plant Sci 180:431–438
Yang H, Menz J, Haussermann I, Benz M, Fujiwara T, Ludewig U (2015) High and low affinity urea root uptake: involvement of NIP5;1. Plant Cell Physiol 56(8):1588–1597
Yu Q, Guyot R, de Kochko A, Byers A, Navajas-Pérez R, Langston BJ, Dubreuil-Tranchant C, Paterson AH, Poncet V, Nagai C, Ming R (2011) Microcolinearity and genome evolution in the vicinity of an ethylene receptor gene of cultivated diploid and allotetraploid coffee species (Coffea). Plant J 67:305–317
Zanin L, Tomasi N, Wirdnam C, Meier S, Komarova NY, Mimmo T, Cesco S, Rentsch D, Pinton R (2014) Isolation and functional characterization of a high affinity urea transporter from roots of Zea mays. BMC Plant Biol 14:222
Zhang L, Yan J, Vatamaniuk OK, Du X (2016) CsNIP2;1 is a plasma membrane transporter from Cucumis sativus that facilitates urea uptake when expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 57(3):616–629
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by of the Brazilian Coffee Research Consortium and National Council of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq). Special acknowledge to Dr. Anderson Rotter Meda for participating in the beginning of these studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos, T.B., Baba, V.Y., Vieira, L.G.E. et al. The urea transporter DUR3 is differentially regulated by abiotic and biotic stresses in coffee plants. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27, 203–212 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-00930-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-00930-6