Abstract
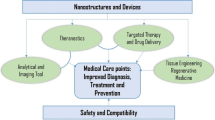
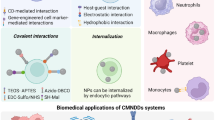
Nanotechnology has brought revolution in cancer detection and treatment. It has capability to detect even a single cancerous cell in vivo and deliver the highly toxic drugs to the cancerous cells. Nanoshells, carbon nanotubes, quantum dots, supermagnetic nanoparticles, nano wires, nanodiamonds, dandrimers, and recently synthesized nanosponges are some of the materials used for cancer detection. Using specific cross linkers, such as specific antibodies against cancer cells individual cancer cells can be located. With the aid of a novel set of lipid-coated, targeted quantum dots a method for quantifying multiple specific biomarkers on the surfaces of individual cancer cells was also developed. This approach to quantitative biomarker detection stands to improve the histopathology methods used to diagnosis pancreatic and other cancers and enable the development of methods to spot cancer cells circulating in the blood stream. Certain nano materials can also deliver cancer drugs at the site so the drug toxicity can also be reduced.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mousa SA, Bharali DJ, Armstrong D. From nutraceuticals to pharmaceuticals to nanopharmaceuticals: a case study in angiogenesis modulation during oxidative stress. Mol Biotechnol. 2007;37:72–80.
Davis ME, Chen ZG, Shin DM. Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:771–82.
Frank A, June-Wha R, Jerome PR, Radovic-Moreno AF, Robert L, Omid CF. New frontiers in nanotechnology for cancer treatment. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Invest. 2008;26:74–85.
Koning GA, Krijger GC. Targeted multifunctional lipid-based nanocarriers for image-guided drug delivery. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007;7:425–40.
Ranjita M, Sarbari A, Sanjeeb KS. Cancer nanotechnology: application of nanotechnology in cancer therapy. Drug Discovery Today. 2010;15:19–20.
Kewal K, Jain T. Nanotechnology in clinical laboratory diagnostics, review. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;358:37–54.
Hirsch LR, Gobin AM, Lowery AR, et al. Metal nanoshells. Ann Biomed Eng. 2006;34:15–22.
Loo C, Lowery A, Halas N, West J, Drezek R. Immunotargeted nanoshells for integrated cancer imaging and therapy. Nano Lett. 2005;5(4):709–11.
Avouris P, Chen Z, Perebeinos V. Carbon-based electronics. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2(10):605–15.
Bakry R, Vallant RM, Najam-ul-Haq M, Rainer M, Szabo Z, Huck CW, Bonn GK. Medicinal applications of fullerenes. Int J Nanomed. 2007;2(4):639–49.
Bosi S, Da Ros T, Spalluto G, Prato M. Fullerene derivatives: an attractive tool for biological applications. Eur J Med Chem. 2003;38:913–23.
Guldi DM, Prato M. Excited-state properties of C(60) fullerene derivatives. Acc Chem Res. 2000;33(10):695–703.
Ji SR, Liu C, Zhang B, Yang F, Xu J, Long J, Jin C, Fu DL, Ni QX, Yu XJ. Carbon nanotubes in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1806:29–35.
Kam NW, O’Connell M, Wisdom JA, Dai H. Carbon nanotubes as multifunctional biological transporters and near-infrared agents for selective cancer cell destruction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(33):11600–5.
Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alivisatos AP. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science. 1998;281:2013–6.
Schroeder JE, Shweky I, Shmeeda H, Banin U, Gabizon A. Folate-mediated tumor cell uptake of quantum dots entrapped in lipid nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2007;124:2834.
Jayagopal A, Yan RS, Blakemore JL, Linton MF, Fazio S, Haselton FR. Quantum dot mediated imaging of atherosclerosis. Nanotechnology. 2009;20:165102.
Maysinger D. Nanoparticles and cells: good companions and doomed relationships. Org Biomol Chem. 2007;5:2335–42.
Jiang W, Singhal A, Kim BYS, Zheng J, Rutka JT, Wang C, Chan WCW. Assessing near-infrared quantum dots for deep tissue, organ, and animal imaging applications. J Assoc Lab Autom. 2008;13:6–12.
Zimmer JP, Kim SW, Ohnishi S, Tanaka E, Frangioni JV, Bawendi MG. Size series of small indium arsenide-zinc selenide core-shell nanocrystals and their application to in vivo imaging. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:2526–7.
Cai W, Chen X. Preparation of peptide-conjugated quantum dots for tumor vasculature-targeted imaging. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(1):89–96.
Smith AM, Dave S, Nie S, True L, Gao X. Multicolor quantum dots for molecular diagnostics of cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2006;6:231–44.
Tada H, Higuchi H, Wanatabe TM, Ohuchi N. In vivo real-time tracking of single quantum dots conjugated with monoclonal anti-HER2 antibody in tumors of mice. Cancer Res. 2007;67(3):1138–44.
Wust P, Hildebrandt B, Sreenivasa G, Rau B, Gellermann J, Riess H, et al. Hyperthermia in combined treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3(8):487–97.
Harris JM, Martin NE, Modi M. Pegylation: a novel process for modifying pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmcokinetics. 2001;40:539–51.
Kubo T, Sugita T, Shimose S, Nitta Y, Ikuta Y, Murakami T. Targeted delivery of anticancer drugs with intravenously administered magnetic liposomes in osteosarcoma-bearing hamsters. Int J Oncol. 2000;17(2):309–15.
Johannsen M, Gneveckow U, Thiesen B, Taymoorian K, Cho CH, Waldofner N, Scholz R, Jordan A, Loening SA, Wust P. Thermotherapy of prostate cancer using magnetic nanoparticles: feasibility, imaging, and three-dimensional temperature distribution. Eur Urol. 2007;52:1653–61.
Neuwelt E, Varallyay P, Bago A, Muldoon L, Nesbit G, Nixon R. Imaging of iron oxide nanoparticles by MR and light microscopy in patients with malignant brain tumours. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2004;30(5):456–71.
Kupsch A, Earl C. Neurosurgical interventions in the treatment of idiopathic Parkinson disease: neurostimulation and neural implantation. J Mol Med. 1999;77(1):178–84.
Lee Min-Ho, Lee Dong-Ho, Jung Suk-Won, Lee Kuk-Nyung, Park YoungSoo, Seong Woo-Kyeong. Measurements of serum C-reactive protein levels in patients with gastric cancer and quantification using silicon nanowire arrays. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2010;6:78–83.
Krueger A. New carbon materials: biological applications of functionalized nanodiamond materials. Chemistry. 2008;14:1382–90.
Enoki T, Takai K, Osipov V, Baidakova M, Vul A. Nanographene and nanodiamond; new members in the nanocarbon family. Chem Asian J. 2009;4:796–804.
Holt KB. Diamond at the nanoscale: applications of diamond nanoparticles from cellular biomarkers to quantum computing. Philos Transact A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2007;365:2845–61.
Vaijayanthimala V, Chang HC. Functionalized fluorescent nanodiamonds for biomedical applications. Nanomed. 2009;4(1):47–55.
Fu CC, Lee HY, Chen K, Lim TS, Wu HY, Lin PK, et al. Characterization and application of single flourescent ananodiamonds as cellular biomarkers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:727–32.
Chang YP, Pinaud F, Antelman J, Weiss S. Tracking bio-molecules in live cells using quantum dots. J Biophotonics. 2008;1:287–98.
Chang YR, Lee HY, Chen K, Chang CC, Tsai DS, Fu CC, et al. Mass production and dynamic imaging of fluorescent nanodiamonds. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008;3(5):284–8.
Cavalli R, Trotta F, Tumiatti V. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for drug delivery. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2006;56:209–13.
Guo L, Gao G, Liu X, Liu F. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 nanosponge. Mater Chem Phys. 2008;111:322–5.
Swaminathan S, Vavia PR, Trotta F, Torne S. Formulation of betacyclodextrin based nanosponges of itraconazole. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2007;57:337–41.
Sampathkumar SG, Yarema KJ. Targeting cancer cells with dendrimers. Chem Biol. 2005;12:5–6.
Lee CC, MacKay JA, Frechet JM, Szoka FC. Designing dendrimers for biological applications. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:1517–26.
Gillies ER, Frechet JMJ. Dendrimers and dendritic polymers in drug delivery. Drug Discov Today. 2005;10:35–43.
Shi X, Wang S, Meshinchi S, Van Antwerp ME, Bi X, Lee I, et al. Dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles as a platform for cancer-cell targeting and imaging. Small. 2007;3:1245–52.
Link S, El-Sayed MA. Shape and size dependence of radiative, non-radiative and photothermal properties of gold nanocrystals. Int Rev Phys Chem. 2000;19:409–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaishree, V., Gupta, P.D. Nanotechnology: A Revolution in Cancer Diagnosis. Ind J Clin Biochem 27, 214–220 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-012-0221-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-012-0221-z