Abstract
Background
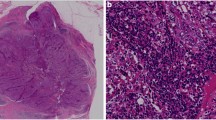
The status of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) is a prognostic factor for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Recent studies have shown that programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) or programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is expressed on T lymphocytes or tumor cells modulating antitumor immunity. The regulation of immune checkpoints between tumor cells and T lymphocytes may serve as a target for improvement of TNBC prognosis. We investigated TILs and PD-L1 status in TNBCs before or after preoperative systemic therapy (PST) to elucidate the clinical significance of PD-L1 expression.
Methods
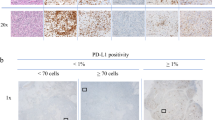
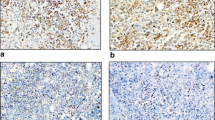
Ninety patients received PST, and materials of core needle biopsies (CNB) taken before PST were available for 32 patients. TILs were scored as “% stromal”, and tumors were defined as High-TILs (≥30%) or Low-TILs (<30%). The expression of PD-L1 was assessed by immunohistochemistry.
Results
TILs status in CNB is significant in pathological therapeutic grade: 1 vs. 2 or 3 (p = 0.0359). Disease-free survival (DFS) in patients with Low-TIL tumors were significantly worse than those with High-TIL tumors (p = 0.0383), but overall survival (OS) showed no significance (p = 0.0772). However, in patients with Low-TIL tumors, both DFS and OS in patients with High-PD-L1 expression were extremely unfavorable than in patients with Low-PD-L1 expression (p = 0.0032, p = 0.0002).
Conclusion
The patients with TNBCs with combined Low-TILs and High-PD-L1 status in pre-PST situation showed unfavorable prognosis. The subset of TNBCs with Low-TILs and High-PD-L1 status could be the therapeutic target for immune checkpoint inhibitor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, André F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1275–81.
Mohammed ZM, Going JJ, Edwards J, Elsberger B, McMillan DC. The relationship between lymphocyte subsets and clinico-pathological determinants of survival in patients with primary operable invasive ductal breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:1676–84.
Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F, Salgado R, Viale G, Van Eenoo F, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG 02–98. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:860–7.
Loi S, Michiels S, Salgado R, Sirtaine N, Jose V, Fumagalli D, et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: results from the FinHER trial. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1544–50.
Adams S, Gray RJ, Demaria S, Goldstein L, Perez EA, Shulman LN, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers from two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG 1199. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:2959–66.
Denkert C, Loibl S, Noske A, Roller M, Müller BM, Komor M, et al. Tumor-associated lymphocytes as an independent predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:105–13.
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, Sinn BV, Gade S, Kronenwett R, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without carboplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive and triple-negative primary breast cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:983–91.
Miyashita M, Sasano H, Tamaki K, Chan M, Hirakawa H, Suzuki A, et al. Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ and FOXP3+ lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer: its correlation with pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;148:525–34.
Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C, Leek RD, Garcia JF, Harris AL, et al. Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5373–80.
Mahmoud SM, Paish EC, Powe DG, Macmillan RD, Grainge MJ, Lee AH, et al. Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes predict clinical outcome in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1949–55.
Liu S, Lachapelle J, Leung S, Gao D, Foulkes WD, Nielsen TO. CD8+ lymphocyte infiltration is an independent favorable prognostic indicator in basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2012;14:R48.
Droeser R, Zlobec I, Kilic E, Güth U, Heberer M, Spagnoli G, et al. Differential pattern and prognostic significance of CD4+ , FOXP3+ , and IL-17+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in ductal and lobular breast cancers. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:134.
Cimino-Mathews A, Ye X, Meeker A, Argani P, Emens LA. Metastatic triple-negative breast cancers at first relapse have fewer tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes than their matched primary breast tumors: a pilot study. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:2055–63.
Takenaka M, Seki N, Toh U, Hattori S, Kawahara A, Yamaguchi T, et al. FOXP3 expression in tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with breast cancer prognosis. Mol Clin Oncol. 2013;1:625–32.
Seo AN, Lee HJ, Kim EJ, Kim HJ, Jang MH, Lee HE, et al. Tumour-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes as an independent predictive factor for pathological complete response to primary systemic therapy in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2705–13.
Miyashita M, Sasano H, Tamaki K, Hirakawa H, Takahashi Y, Nakagawa S, et al. Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ and FOXP3+ lymphocytes in residual tumors and alterations in these parameters after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multicenter study. Breast Cancer Res. 2015;17:124.
Soliman H, Khalil F, Antonia S. PD-L1 expression is increased in a subset of basal type breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2014;9:e88557.
Schalper KA, Velcheti V, Carvajal D, Wimberly H, Brown J, Pusztai L, et al. In situ tumor PD-L1 mRNA expression is associated with increased TILs and better outcome in breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:2773–82.
Schalper KA. PD-L1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: Revisiting the antitumor immune response potential in breast cancer. Oncoimmunology. 2014;3:e29288.
Pardoll DM. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:252–64.
Stagg J, Allard B. Immunotherapeutic approaches in triple-negative breast cancer: latest research and clinical prospects. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2013;5:169–81.
Muenst S, Schaerli AR, Gao F, Daster S, Trella E, Droeser RA, et al. Expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is associated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;46:15–24.
Ahn SG, Jeong J, Hong S. Jung WH (2015) Current issues and clinical evidence in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer. J Pathol Transl Med. 2015;49:355–63.
Salgado R, Denkert C, Demaria S, Sirtaine N, Klauschen F, Pruneri G, et al. The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: recommendations by an International TILs working group 2014. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:259–71.
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N, Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2018–28.
Ménard S, Tomasic G, Casalini P, Balsari A, Pilotti S, Cascinelli N, et al. Lymphoid infiltration as a prognostic variable for early-onset breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:817–9.
Topalian SL, Taube JM, Anders RA, Pardoll DM. Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:275–87.
Taube JM, Ander RA, Young GD, Xu H, Sharma R, McMiller TL, et al. Colocalization of inflammatory response with B7-h1 expression in human melanocytic lesions supports an adaptive resistance mechanism of immune escape. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:127ra37.
Teng MWL, Ngiow TSF, Ribas A, Smyth MJ. Classifying cancers based on T-cell infiltrating and PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2015;75(11):2139–45.
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:711–23.
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ, Topalian SL, Hwu P, et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2455–65.
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu WJ, Kefford R, et al. Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:134–44.
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD, Hamid O, Gordon MS, et al. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 2014;515:563–7.
Ribas A, Puzanov I, Dummer R, Schadendorf D, Hamid O, Robert C, et al. Pembrolizumab versus investigator-choice chemotherapy for ipilimumab-refractory melanoma (KEYNOTE-002): a randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:908–18.
Sunshine J. Taube JM (2015) PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015;23:32–8.
Baras AS, Drake C, Liu JJ, Gandhi N, Kates M, Hoque MO, et al. The ratio of CD8 to Treg tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with response to cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with muscle invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5(5):e1134412.
Postow MA, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, Robert C, Grossmann K, McDermott D, et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(21):2006–17.
Gubin MM, Zhang X, Schuster H, Caron E, Ward JP, Noguchi T, et al. Checkpoint blockade cancer immunotherapy targets tumor-specific mutant antigens. Nature. 2014;515:577–81.
Naing A, Papadopoulos KP, Autio KA, Ott PA, Patel MR, Wong DJ, et al. Safty, antitumor activity, and immune activation of pegylated recombinant human Interleukin-10 (AM0010) in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:3562–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients, their families, and the study personnel across all sites for participating in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors have declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Tomioka, N., Azuma, M., Ikarashi, M. et al. The therapeutic candidate for immune checkpoint inhibitors elucidated by the status of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Breast Cancer 25, 34–42 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0781-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-017-0781-0