Abstract
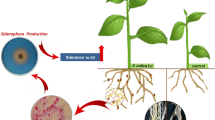
The present study demonstrates the metal toxicity ameliorating and growth promoting abilities of three different bacterial isolates when applied to rice as host plant. The three bacterial strains included a cadmium resistant Ochrobactrum sp., a lead resistant Bacillus sp. and an arsenic resistant Bacillus sp. designated as CdSP9, PbSP6, and AsSP9, respectively. When these isolates were used as inocula applied to metal-treated rice plants of variety Satabdi, the germination percentage, relative root elongation (RRE), amylase and protease activities were increased. The toxic effect of metal was reduced in presence of these bacteria. The overall biomass and root/shoot ratio were also enhanced by bacterial inoculation. Hydroponic studies showed that the superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) level, which had been increased in the presence of metal stress in rice roots, were lowered by the bacterial inoculation. In addition, all three strains were 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase and catalase positive, whereas siderophore producing ability was lacking in PbSP6. However, both PbSP6 and AsSP9 were protease positive and could hydrolyse starch. The data indicate that these bacteria have promise for bioremediation as well as for plant growth promotion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amico, E.D., Cavalca, L., and Andreoni, V. 2008. Improvement of Brassica napus growth under cadmium stress by cadmium-resistant rhizobacteria. Soil Biol. Biochem. 40, 74–84.
Baisak, R., Rana, D., Acharya, P.B.B., and Ka.r, M. 1994. Alterations in the activities of active oxygen scavenging enzymes of weat leaves subjected to water stress. Plant Cell Physiol. 35, 489–495.
Belimov, A.A., Hontzeas, N., Safronova, V.I., Demchinskaya, S.V., Piluzza, G., Bullitta, S., and Glick, B.R. 2005. Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.) Soil Biol. Biochem. 37, 241–250.
Bhattacharya, S. and Mukherjee, A.K. 2002. Salt stree-induced cytosolute accumulation, antioxidant response and membrane deterioration in three rice cultivars during early germination. Seed Sci. Technol. 30, 279–287.
Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Burd, G.I., Dixon, D.G., and Glick, B.R. 1998. A plant growth promoting bacterium that decreases nickel toxicity in seedlings. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 3663–3668.
Burd, G.I., Dixon, D.G., and Glick, B.R. 2000. Plant growth promoting bacteria that decrease heavy metal toxicity in plants. Can. J. Microbiol. 46, 237–245.
Chen, S.Y. 1991. Injury of membrane lipid peroxidation to plant cell. Plant Physiol. Commun. 27, 84–90.
Dell’Amico, E., Cavalca, L., and Andreoni, V. 2005. Analysis of rhizobacterial communities in perennial Graminaceae from polluted water meadow soil, and screening of metal-resistant potentially plant-growth promoting bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 52, 153–162.
Dhindsa, R.H., Plumb-Dhindsa, P., and Thorpe, T.A. 1981. Leaf senescence correlated with increased level of membrane permeability, lipid peroxidation and decreased level of SOD and CAT. J. Exp. Bot. 32, 93–101.
Doelman, P. 1985. Resistance of soil microbial communities to heavy metals, pp. 369–384. In Jensen, V., Kjoelles, A., and Soerensen, L.H. (wds.), Microbial Communities in Soil. Elsevier, London, UK.
Downs, R.J. and Hellmers, H. 1975. Environment and Experimental Control of Plant Growth. Academic Press, New York, N.Y., USA.
Faisal, M. and Hasnain, S. 2006. Growth stimulatory effect of Ochrobactrum intermedium and Bacillus cereus sp. on Vigna radiata plants. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 43, 461–466.
Fick, G.N. and Qualset, C.O. 1975. Genetic control of endosperm amylase activity and gibberellic acid responses in standard-height and short-statured wheats. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 72, 892–895.
Gadd, G.M. 1990. Heavy metal accumulation by bacteria and other microorganisms. Experientia 46, 834–840.
Glick, B.R. 2003. Phytoremediation: synergistic use of plants and bacteria to clean up the environment. Biotechnol. Adv. 21, 383–393.
Glick, B.R., Jacobson, C.B., Schwarze, M.M.K., and Pasternak, J.J. 1994. 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase mutants of the plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR12-2 do not stimulate canola root elongation. Can. J. Microbiol. 40, 911–915.
Glick, B.R., Karaturovíc, D., and Newell, P. 1995. A novel procedure for rapid isolation of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Can. J. Microbiol. 41, 533–536.
Glick, B.R., Penrose, D.M., and Li, J. 1998. A model for lowering of plant ethylene concentrations by plant-growth-promoting bacteria. J. Theor. Biol. 190, 63–68.
Heath, R.L. and Packer, L. 1968. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 125, 189–198.
Honma, M. and Shimomura, T. 1978. Metabolism of 1 aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid. Agri. Biol. Chem. 42, 1825–1831.
Hu, X. and Boyer, G.L. 1996. Siderophore-mediated aluminium uptake by Bacillus megaterium ATCC 19213. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 4044–4048.
John, R., Ahmad, P., Gadgil, K., and Sarma, S. 2009. Heavy metal toxicity: Effect of plant growth, Biochemical parameters and metal accumulation by Brasica juncea, L. Int. J. Plant Prod. 3, 65–75.
Kachout, S. Sai., Leclerc, J.C., BenMansoura, A., Rejeb, M.N., and Ouerghi, Z. 2009. Effect of heavy metals on growth and bioaccumulation of the annual halophytes Atriplex hortensis and A. rosea. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 5, 746–756.
Kanekar, P.P., Nilegaonkar, S.S., Sarnaik, S.S., and Kelkar, A.S. 2002. Optimization of protease activity of alkaliphilic bacteria isolated from an alkaline lake in India. Biores. Technol. 85, 87–93.
Khan, M.A. and Faust, M.A. 1967. Effect of growth retardants on — amylase production in germinating barley seeds. Physiol. Plant 20, 673–681.
Li, J., Ovakim, D.H., Charles, T.C., and Glick, B.R. 2000. An ACC deaminase minus mutant of Enterobacter cloacae UW4 no longer promotes 419 root elongation. Curr. Microbiol. 41, 101–105.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Pandey, S., Gupta, K., and Mukherjee, A.K. 2007. Impact of cadmium and lead on Catharanthus roseus — A phytoremediation study. Indian J. Environ. Biol. 28, 655–662.
Pandey, S. and Maiti, T.K. 2008. Physicochemical and biological characterization of slag disposal site at Burnpur, West Bengal. Poll. Res. 27, 345–348.
Pandey, S., Saha, P., Barai, P.K., and Maiti, T.K. 2010. Characterization of a Cd2+ — resistant strain of Ochrobactrum sp. isolated from slag disposal site of an iron and steel factory. Curr. Microbiol. 61, 106–111.
Pandey, S., Saha, P., Biswas, S., and Maiti, T.K. 2011. Characterization of two heavy metal resistant Bacillus strains isolated from slag disposal site at Burnpur. Indian J. Environ. Biol. 32, 773–779.
Pishchik, V.N., Vorobyev, N.I., Chernyaeva, I.I., Timofeeva, S.V., Kozhemyakov, A.P., Alexeev Y.V., and Lukin, S.M. 2002. Experimental and mathematical simulation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and plant interaction under cadmium stress. Plant Soil 243, 173–186.
Reed, M.L.E. and Glick, B.R. 2005. Growth of canola (Brassica napus) in the presence of plant growth-promoting bacteria and either copper or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Can. J. Microbiol. 51, 1061–1069.
Schwyn, B. and Neilands, J. 1987. Universal assay for detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 160, 47–56.
Snell, F.D. and Snell, C.T. 1971. Colorimetric methods of analysis, Vol. IV IAA, pp. 7–145. Van Nostrand Reinold Co., New York, USA.
Tripathi, A.K., Verma, S.C., and Ron, E.Z. 2002. Molecular characterization of a salt-tolerant bacterial community in the rice rhizosphere. Res. Microbiol. 153, 579–584.
Wu, C.H., Wood, T.K., Mulchandani, A., and Chen, W. 2006. Engineering plant-microbe symbiosis for rhizoremediation of heavy metals. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 1129–1134.
Zaidi, S., Usmani, S., Singh, B.R., and Musarrat, J. 2006. Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 64, 991–997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, S., Ghosh, P.K., Ghosh, S. et al. Role of heavy metal resistant Ochrobactrum sp. and Bacillus spp. strains in bioremediation of a rice cultivar and their PGPR like activities. J Microbiol. 51, 11–17 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2330-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2330-7