Abstract
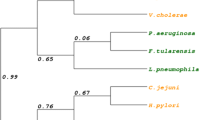
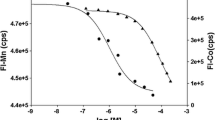
The Ferric uptake regulator (Fur) is a global transcription factor that affects expression of bacterial genes in an iron-dependent fashion. Although the Fur protein and its iron-responsive regulon are well studied, there are still important questions that remain to be answered. For example, the consensus Fur binding site also known as the “Fur box” is under debate, and it is still unclear which Fur residues directly interact with the DNA. Our long-term goal is to dissect the biological roles of Fur in the development of the disease cold-water vibriosis, which is caused by the psychrophilic bacteria Aliivibrio salmonicida (also known as Vibrio salmonicida). Here, we have used experimental and computational methods to characterise the Fur protein from A. salmonicida (AS-Fur). Electrophoretic mobility shift assays show that AS-Fur binds to the recently proposed vibrio Fur box consensus in addition to nine promoter regions that contain Fur boxes. Binding appears to be dependent on the number of Fur boxes, and the predicted “strength” of Fur boxes. Finally, structure modeling and molecular dynamics simulations provide new insights into potential AS-Fur-DNA interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, R., B.O. Brandsdal, I. Michaud-Soret, and N.P. Willassen. 2009a. Ferric uptake regulator protein: Binding free energy calculations and per-residue free energy decomposition. Proteins 75, 373–386.
Ahmad, R., E. Hjerde, G. Hansen, P. Haugen, and N.P. Willassen. 2009b. Prediction and experimental testing of ferric uptake regulator regulons in vibrios. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 16, 159–168.
Baichoo, N., T. Wang, R. Ye, and J.D. Helmann. 2002. Global analysis of the Bacillus subtilis Fur regulon and the iron starvation stimulon. Mol. Microbiol. 45, 1613–1629.
Case, D.A., T.A. Darden, T.E. Cheatham, 3rd, C.L. Simmerling, J. Wang, R.E. Duke, R. Luo, and et al. 2008. AMBER 10, University of California, San Francisco, USA.
Chen, Z., K.A. Lewis, R.K. Shultzaberger, I.G. Lyakhov, M. Zheng, B. Doan, G. Storz, and T.D. Schneider. 2007. Discovery of Fur binding site clusters in Escherichia coli by information theory models. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 6762–6777.
Colquhoun, D.J. and H. Søum. 2001. Temperature dependent siderophore production in Vibrio salmonicida. Microb. Pathog. 31, 213–219.
D’Autréaux, B., L. Pecqueur, A. Gonzalez de Peredo, R.E. Diederix, C. Caux-Thang, L. Tabet, B. Bersch, E. Forest, and I. Michaud-Soret. 2007. Reversible redox- and zinc-dependent dimerization of the Escherichia coli fur protein. Biochemistry 46, 1329–1342.
de Lorenzo, V., S. Wee, M. Herrero, and J.B. Neilands. 1987. Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColV-K30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor. J. Bacteriol. 169, 2624–2630.
Delany, I., R. Rappuoli, and V. Scarlato. 2004. Fur functions as an activator and as a repressor of putative virulence genes in Neisseria meningitidis. Mol. Microbiol. 52, 1081–1090.
Fuangthong, M. and J.D. Helmann. 2003. Recognition of DNA by three ferric uptake regulator (Fur) homologs in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 185, 6348–6357.
Gao, H., D. Zhou, Y. Li, Z. Guo, Y. Han, Y. Song, J. Zhai, Z. Du, X. Wang, J. Lu, and R. Yang. 2008. The iron-responsive Fur regulon in Yersinia pestis. J. Bacteriol. 190, 3063–3075.
Grifantini, R., S. Sebastian, E. Frigimelica, M. Draghi, E. Bartolini, A. Muzzi, R. Rappuoli, G. Grandi, and C.A. Genco. 2003. Identification of iron-activated and -repressed Fur-dependent genes by transcriptome analysis of Neisseria meningitidis group B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 9542–9547.
Hantke, K. 1981. Regulation of ferric iron transport in Escherichia coli K12: isolation of a constitutive mutant. Mol. Gen. Genet. 182, 288–292.
Hjerde, E., M.S. Lorentzen, M.T. Holden, K. Seeger, S. Paulsen, N. Bason, C. Churcher, and et al. 2008. The genome sequence of the fish pathogen Aliivibrio salmonicida strain LFI1238 shows extensive evidence of gene decay. BMC Genomics 9, 616.
Kollman, P.A., I. Massova, C. Reyes, B. Kuhn, S. Huo, L. Chong, M. Lee, and et al. 2000. Calculating structures and free energies of complex molecules: combining molecular mechanics and continuum models. Acc. Chem. Res. 33, 889–897.
Le Cam, E., D. Frechon, M. Barray, A. Fourcade, and E. Delain. 1994. Observation of binding and polymerization of Fur repressor onto operator-containing DNA with electron and atomic force microscopes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 11816–11820.
Lee, H.J., S.H. Bang, K.H. Lee, and S.J. Park. 2007. Positive regulation of fur gene expression via direct interaction of Fur in a pathogenic bacterium, Vibrio vulnificus. J. Bacteriol. 189, 2629–2636.
Liu, Q., P. Wang, Y. Ma, and Y. Zhang. 2007. Characterization of the Vibrio alginolyticus fur gene and localization of essential amino acid sites in fur by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 13, 15–21.
Massé, E., F.E. Escorcia, and S. Gottesman. 2003. Coupled degradation of a small regulatory RNA and its mRNA targets in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 17, 2374–2383.
Massé, E. and S. Gottesman. 2002. A small RNA regulates the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 4620–4625.
Mey, A.R., S.A. Craig, and S.M. Payne. 2005a. Characterization of Vibrio cholerae RyhB: the RyhB regulon and role of ryhB in biofilm formation. Infect. Immun. 73, 5706–5719.
Mey, A.R., E.E. Wyckoff, V. Kanukurthy, C.R. Fisher, and S.M. Payne. 2005b. Iron and Fur regulation in Vibrio cholerae and the role of Fur in virulence. Infect. Immun. 73, 8167–8178.
Pecqueur, L., B. D’Autréaux, J. Dupuy, Y. Nicolet, L. Jacquamet, B. Brutscher, I. Michaud-Soret, and B. Bersch. 2006. Structural changes of Escherichia coli ferric uptake regulator during metaldependent dimerization and activation explored by NMR and X-ray crystallography. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 21286–21295.
Pohl, E., J.C. Haller, A. Mijovilovich, W. Meyer-Klaucke, E. Garman, and M.L. Vasil. 2003. Architecture of a protein central to iron homeostasis: crystal structure and spectroscopic analysis of the ferric uptake regulator. Mol. Microbiol. 47, 903–915.
Sali, A. and T.L. Blundell. 1993. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 234, 779–815.
Sheikh, A. and G.L. Taylor. 2009. Crystal structure of the Vibrio cholerae ferric uptake regulator (Fur) reveals insights into metal co-ordination. Mol. Microbiol. 75, 1208–1220.
Srinivasan, J., T.E. Cheatham, 3rd, P. Cieplak, P.A. Kollman, and D.A. Case. 1998. Continuum solvent studies of the stability of DNA, RNA, and phosphoramidate-DNA helices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 9401–9409.
Stojiljkovic, I., A.J. Bäumler, and K. Hantke. 1994. Fur regulon in Gram-negative bacteria Identification and characterization of new iron-regulated Escherichia coli genes by a fur titration assay. J. Mol. Biol. 236, 531–545. Erratum in: J. Mol. Biol. 1994. 240, 271.
Sun, K., S. Cheng, M. Zhang, F. Wang, and L. Sun. 2008. Cys-92, Cys-95, and the C-terminal 12 residues of the Vibrio harveyi ferric uptake regulator (Fur) are functionally inessential. J. Microbiol. 46, 670–680.
Thompson, C.C., F.L. Thompson, A.C. Vicente, and J. Swings. 2007. Phylogenetic analysis of vibrios and related species by means of atpA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 2480–2484.
Tiss, A., O. Barre, I. Michaud-Soret, and E. Forest. 2005. Characterization of the DNA-binding site in the ferric uptake regulator protein from Escherichia coli by UV crosslinking and mass spectrometry. FEBS Lett. 579, 5454–5460.
Zhou, D., L. Qin, Y. Han, J. Qiu, Z. Chen, B. Li, Y. Song, and et al. 2006. Global analysis of iron assimilation and fur regulation in Yersinia pestis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 258, 9–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedersen, H.L., Ahmad, R., Riise, E.K. et al. Experimental and computational characterization of the ferric uptake regulator from Aliivibrio salmonicida (Vibrio salmonicida). J Microbiol. 48, 174–183 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-9199-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-9199-5