Abstract
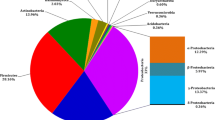
Invasive plants have caused great economic losses and environmental problems worldwide. Eupatorium adenophorum is one of the most invasive weeds in China. To better understand its invasive mechanisms, in the present paper, the microbial communities of healthy and diseased leaves of E. adenophorum were obtained using both culture-independent and -dependent methods and their diversities were compared. The bacteria obtained from culture-independent method belong to Proteobacteria (95.8%), Actinobacteria (2.1%), and Firmicutes (2.1%) and fungi belong to Ascomycota (65.2%) and Basidiomycota (34.8%). Very few overlapped microbial species were found by culture-dependent and -independent methods. Healthy leaves display higher bacterial diversity than diseased leaves. Phylogenetic structures are very different between healthy and diseased phyllosphere microbial communities. Bacteria close to Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas were dominant on healthy leaves, whereas those close to Shigella were dominant on diseased leaves. 52.9% of fungal clones from healthy leaves were Ustilaginomycetes, close to Rhodotorula phylloplana and uncultured basidomycete; by contrast, 60% of clones from diseased leaves were Lecanoromycetes, close to Umbilicaria muehlenbergii. No bacteria but four fungal strains phylogenetically close to Myrothecium sp. and Alternaria alternate were pathogenic to seedlings and detached leaves of the invasive plant. Therefore, this plant may be resistant to pathogens from bacteria but not fungi in its introduced range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamri, S.A. 2008. Epiphytic microflora on the leaves of Juniperus procera from Asser region, Saudi Arabia. J. Biol. Sci. 8, 857–865.
Bordoloi, M.J., V.S. Shakla, and R.P. Sharam. 1985. Absolute stereochemistry of the insect antifeedant cadinene from Eupatorium adenophorum. Tetrahedron Lett. 26, 509–510.
Borneman, J. and R.J. Hartin. 2000. PCR primers that amplify fungal rRNA genes from environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 4356–4360.
Boyer, H.W. and D. Roulland-Dussoix. 1969. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 41, 459–472.
Bunster, L., H.J. Fokkema, and B. Schippers. 1989. Effect of surface activity of Pseudomonas spp. on leaf wettability. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55, 1340–1345.
Ding, J., R.N. Mack, P. Lu, M. Ren, and H. Huang. 2008. China’s booming economy is sparking and accelerating biological invasions. Bioscience 58, 317–324.
Duncan, C.A., J.J. Jachetta, M.L. Brown, V.F. Carrithers, J.K. Clark, J.M. Ditomaso, R.G. Lym, K.C. Mcdaniel, M.J. Renz, and P.M. Rice. 2004. Assessing the economic, environmental, and societal losses from invasive plants on rangeland and wildlands. Weed Technol. 18, 1411–1416.
Felsenstein, J. 1989. PHYLIP-phylogeny inference package (version 3.2). Cladistics 5, 164–166.
Fenn, M.E., P.H. Dunn, and D.M. Durall. 1989. Effects of ozone and sulfur dioxide on phyllosphere fungi from three tree species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55, 412–418.
Filion, M., R.C. Hamelin, L. Bernier, and M. St-Arnaud. 2004. Molecular profiling of rhizosphere microbial communities associated with healthy and diseased black spruce (Picea mariana) seedlings grown in a nursery. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 3541–3551.
Good, I.J. 1953. The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 40, 237–264.
Hughes, J.B., J.J. Hellmann, T.H. Ricketts, and B.J.M. Bohannan. 2001. Counting the uncountable: Statistical approaches to estimating microbial diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 4399–4406.
Keane, R.M. and M.J. Crawley. 2002. Exotic plant invasions and the enemy release hypothesis. Trends Ecol. Evol. 17, 164–170.
Lambais, M.R., D.E. Crowley, J.C. Cury, R.C. Büll, and R.R. Rodrigues. 2006. Bacterial diversity in tree canopies of the Atlantic forest. Science 312, 1917.
Leveti, E. and K. Dorsey. 2006. Contribution of leaf surface fungi to the airspora. Aerobiologia 22, 3–12.
Li, Y., H. Xu, L. Shi, and Z. Li. 2007. Allelopathic effects of Eupatorium adenophorum on five species of the family Gesneriaceae. Biodivers. Sci. 15, 486–491.
Lindow, S.E. and M.T. Brandl. 2003. Microbiology of the phyllosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 1875–1883.
Lu, P., W.G. San, and K.P. Ma. 2005. Advance in the invasive species E. adenophorum. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 29, 1029–1037.
Ma, R., R. Wang, and J. Ding. 2003. Classical biological control of exotic weeds. Acta Ecol. Sin. 23, 2677–2688.
McSpadden Gardener, B.B. 2004. Ecology of Bacillus and Paenibacillus spp. in agricultural systems. Phytopathology 94, 1252–1258.
McSpadden Gardener, B.B. 2007. Diversity and ecology of biocontrol Pseudomonas spp. in agricultural systems. Phytopathology 97, 221–226.
Mitchell, C.E. and A.G. Power. 2003. Release of invasive plants from fungal and viral pathogens. Nature 421, 625–627.
Namasivayam, S.K. and K. Sahayaraj. 2009. Changes in bacterial and actinomycetes diversity of groundnut phyllosphere with reference to plant age, kind of leaves and season adopting culture dependent methods. The Internet J. Microbiol. 6, no. 1.
Nübel, U., B. Engelen, A. Felske, J. Snaidr, A. Wieshuber, R.I. Amann, W. Ludwig, and H. Backhaus. 1996. Sequence heterogeneities of genes encoding 16S rRNAs in Paenibacillus polymyxa detected by temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. J. Bacteriol. 178, 5636–5643.
Pei, Z., E.J. Bini, L. Yang, M. Zhou, F. Francois, and M.J. Blaser. 2004. Bacterial biota in the human distal esophagus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 4250–4255.
Pimentel, D., L. Lach, R. Zuniga, and D. Morrison. 2000. Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. Bioscience 50, 53–65.
Qiang, S. 1998. The history and status of the study on crofton weed (E. adenophorum Spreng), a worst worldwide weed. J. Wuhan Bot. Res. 16, 366–372.
Schloss, P.D. and J. Handelsman. 2005. Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 1501–1506.
Schloss, P.D., B.R. Larget, and J. Handelsman. 2004. Integration of microbial ecology and statistics: a test to compare gene libraries. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 5485–5492.
Thompson, I.P., M.J. Bailey, J.S. Fenlon, T.R. Fermor, A.K. Lilley, J.M. Lynch, P.J. Mccormank, and et al. 1993. Quantitative and qualitative seasonal changes in the microbial community from the phyllosphere of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Plant Soil 150, 177–191.
Wan, Z.X., J.J. Zhu, and S. Qiang. 2001. The pathogenic mechanism of toxin of Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissler to Eupatorium adenophorum. J. Plant Res. Environ. 10, 47–50.
Wang, R. and Y. Wang. 2006. Invasion dynamics and potential spread of the invasive alien plant species Ageratina adenophora (Asteraceae) in China. Divers. Distribut. 12, 397–408.
Weidner, S., W. Arnold, E. Stackebrandt, and A. Pühler. 2000. Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial communities associated with leaves of the seagrass Halophila stipulacea by a culture-independent small-subunit rRNA gene approach. Microb. Ecol. 39, 22–31.
Whipps, J.M., P. Hand, D. Pink, and G.D. Bending. 2008. Phyllosphere microbiology with special reference to diversity and plant genotype. J. Appl. Microbiol. 105, 1744–1755.
White, T.J., S.T. Brun, S. Lee, and J. Taylor. 1990. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics, pp. 315–322. In M.A. Innis, D.H. Gelfand, J.J. Sninsky, and T.J. White (eds.), PCR protocols, a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, New York, N.Y., USA.
Wolfe, L.M. 2002. Why alien invaders succeed: support for the escape-from-enemy hypothesis. Am. Nat. 160, 705–711.
Yang, C.H., D.E. Crowley, J. Borneman, and N.T. Keen. 2001. Microbial phyllosphere populations are more complex than previously realized. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 3889–3894.
Yu, X., D. Yu, and K. MA. 2004. Relationships between allelopathy and invasiveness by Eupatorium adenophorum at different sites. Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 28, 773–780.
Zhang, P., W. Luo, and Y. Yang. 2006. Inhibition effect of leaf juice extracts of Eupatorium adenophorum on Phytophthora infestans. South West China J. Agri. Sci. 19, 246–250.
Zhou, J., M.A. Bruns, and J.M. Tiedje. 1996. DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 316–322.
Zhou, T., M. Yang, and G. Fang. 2003. Antifeeding activity determination of Eupatorium adenophorum extracts on Pieris rapae larvae. J. Yunnan Agri. Uni. 18, 259–263.
Ziedan, E.H.E. 2006. Effect of menno-florades on microflora of grapevine phyllosphere a their antagonistic potential on Plasmopara viticola. Res. J. Agri. Biol. Sci. 2, 262–267.
Zolan, M.E. and P.J. Pukkila. 1986. Inheritance of DNA methylation in Coprinus cinereus. Cell Mol. Biol. 6, 195–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, ZX., Jiang, H., Yang, C. et al. Microbial community on healthy and diseased leaves of an invasive plant Eupatorium adenophorum in Southwest China. J Microbiol. 48, 139–145 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-9185-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-9185-y