Abstract
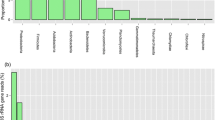
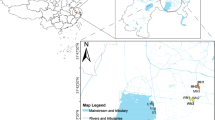
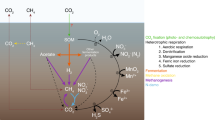
A culture-independent molecular phylogenetic analysis was carried out to study the prokaryotic diversity in two soil samples collected from the subsurface (1.34 km depth) of the former Homestake gold mine, Lead, South Dakota, USA at two sites, the Ross shaft and number 6 Winze. Microbial community analyses were performed by cloning and sequencing of 16S rRNA genes retrieved directly from soil samples. Geochemical characterization of soils revealed high amount of toxic metals such as As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, and U at both the sites. Phylogenetic analyses showed that soil samples were predominantly composed of phylotypes related to phylum Proteobacteria. Other phyla detected in libraries were Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Chloroflexi, Chlorobi, Firmicutes, Gemmatimonadetes, Nitrospirae, Planctomycetes, Verrucomicrobia, and candidate divisions OP10 and TM7. The majority (>95%) of the phylotypes retrieved in the libraries were most closely related to environmental sequences from yet-uncultured bacteria representing a hitherto unidentified diversity. The archaeal communities at both the sites exhibited lower diversity and were most closely affiliated to uncultivated species within the Crenarchaeota. Results showed the existence of diverse microbial populations in deep subsurface environment of the Homestake gold mine. Statistical analyses demonstrated that each site harbored phylogenetically distinct microbial populations that were more diverse at Ross site compare to winze site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akob, D.M., H.J. Mills, and J.E. Kostka. 2007. Metabolically active microbial communities in uranium-contaminated subsurface sediments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 59, 95–107.
Ashelford, K.E., N.A. Chuzhanova, J.C. Fry, A.J. Jones, and A.J. Weightman. 2006. New screening software shows that most recent large 16S rRNA gene clone libraries contain chimeras. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 5734–5741.
Bachman, R.L. and S.W. Caddey. 1990. The Homestake Mine, Lead, South Dakota: an overview, vol. 7, p. 89–94. In C.J. Paterson and A.L. Lisenbee (eds.), Metallogeny of Gold in the Black Hills, South Dakota. Society of Economic Geologists, Guidebook Series.
Baker, B.J., D.P. Moser, B.J. MacGregor, S. Fishbain, M. Wagner, N.K. Fry, B. Jackson, N. Speolstra, S. Loos, K. Takai, B.S. Lollar, J. Fredrickson, D. Balkwill, T.C. Onstott, C.F. Wimpee, and D.A. Stahl. 2003. Related assemblages of sulphate-reducing bacteria associated with ultradeep gold mines of South Africa and deep basalt aquifers of Washington State. Environ. Microbiol. 5, 267–277.
Blowes, D.W., J.L. Jambor, C.J. Hanton-Fong, L. Lortie, and W.D. Gould. 1998. Geochemical, mineralogical and microbiological characterization of a sulphide-bearing carbonate-rich gold-mine tailings impoundment, Joutel, Quebec. Appl. Geochem. 13, 687–705.
Davis, A., W. Roggenthen, L. Stetler, Z. Hladysz, and C. Johnson. 2009. Post-closure flooding of the Homestake mine at Lead, South Dakota. Mining Engineering March p. 43–47.
DeFlaun, M.F., J.K. Fredrickson, H. Dong, S.M. Pfiffner, T.C. Onstott, D.L. Balkwill, S.H. Streger, E. Stackebrandt, S. Knoessen, and E. van Heerden. 2007. Isolation and characterization of a Geobacillus thermoleovorans strain from an ultra-deep South African gold mine. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 30, 152–164.
DeSantis, T.Z., E.L. Brodie, J.P. Moberg, I.X. Zubieta, Y.M. Piceno, and G.L. Andersen. 2007. High-density universal 16S rRNA microarray analysis reveals broader diversity than typical clone library when sampling the environment. Microb. Ecol. 53, 371–383.
Felsenstein, J. 1989. PHYLIP-Phylogeny inference package (version 3.2). Cladistics 5, 164–166.
Henriksen, J.R. 2004. webLIBSHUFF (http://libshuff.mib.uga.edu)
Hirayama, H., K. Takai, F. Inagaki, Y. Yamato, M. Suzuki, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2005. Bacterial community shift along a subsurface geothermal water stream in a Japanese gold mine. Extremophiles 9, 169–184.
Inagaki, F., K. Takai, H. Hirayama, Y. Yamato, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2003. Distribution and phylogenetic diversity of the subsurface microbial community in a Japanese epithermal gold mine. Extremophiles 7, 307–317.
Janssen, P.H. 2006. Identifying the dominant soil bacterial taxa in libraries of 16S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 1719–1728.
Kumar, S., K. Tamura, and M. Nei. 1993. MEGA: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis. Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA.
Lin, Y.T. and W.Y. Shieh. 2006. Zobellella denitrificans gen. nov., sp. nov. and Zobellella taiwanensis sp. nov., denitrifying bacteria capable of fermentative metabolism. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 1209–1215.
Liu, C. and Z. Shao. 2005. Alcanivorax dieselolei sp. nov., a novel alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from sea water and deep-sea sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 1181–1186.
Morillo, J.A., M. Aguilera, A. Ramos-Cormenzana, and M. Monteoliva-Sánchez. 2006. Production of a metal-binding exopolysaccharide by Paenibacillus jamilae using two-phase olive-mill waste as fermentation substrate. Curr. Microbiol. 53, 189–193.
Nemergut, D.R., A.P. Martin, and S.K. Schmidt. 2004. Integron diversity in heavy-metal-contaminated mine tailings and inferences about integron evolution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 1160–1168.
Nunoura, T., H. Hirayama, H. Takami, H. Oida, S. Nishi, S. Shimamura, Y. Suzuki, F. Inagaki, K. Takai, K.H. Nealson, and K. Horikoshi. 2005. Genetic and functional properties of uncultivated thermophilic crenarchaeotes from a subsurface gold mine as revealed by analysis of genome fragments. Environ. Microbiol. 7, 1967–1984.
Onstott, T.C., D.P. Moser, S.M. Pfiffner, J.K. Fredrickson, F.J. Brockman, T.J. Phelps, D.C. White, A. Peacock, D. Balkwill, R. Hoover, L.R. Krumholz, M. Borscik, T.L. Kieft, and R. Wilson. 2003. Indigenous and contaminant microbes in ultra-deep mines. Environ. Microbiol. 5, 1168–1191.
Peters, J. 2007. Wisconsin Procedures for Soil Testing, Plant Analysis and Feed & Forage Analysis, No. 6, Soil Fertility Series. Soil Science Department, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, University of Wisconsin (MD, USA). Available online at http://uwlab.soils.wisc.edu/procedures.htm
Pontes, D.S., C.I. Lima-Bittencourt, E. Chartone-Souza, and A.M. Amaral Nascimento. 2007. Molecular approaches: advantages and artifacts in assessing bacterial diversity. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 34, 463–473.
Rastogi, G., G.L. Muppidi, R.N. Gurram, A. Adhikari, K.M. Bischoff, S.R. Hughes, W.A. Apel, S.S. Bang, D.J. Dixon, and R.K. Sani. 2009. Isolation and characterization of cellulose-degrading bacteria from the deep subsurface of the Homestake gold mine, Lead, South Dakota, USA. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36, 585–598.
Rastogi, G., R.K. Sani, B.M. Peyton, J.G. Moberly, and T.R. Ginn. 2008. Molecular studies on the microbial diversity associated with mining-impacted Coeur d’ Alene river sediments. Microb. Ecol. DOI: 10.1007/s00248-008-9445-0.
Rosado, A.S., G.F. Duarte, L. Seldin, and J.D. Van Elsas. 1998. Genetic diversity of nifH gene sequences in Paenibacillus azotofixans strains and soil samples analyzed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified gene fragments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 2770–2779.
Schloss, P.D. and J. Handelsman. 2005. Introducing DOTUR, a computer grogram for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 1501–1506.
Schloss, P.D. and J. Handelsman. 2006a. Introducing SONS, a tool for operational taxonomic unit-based comparisons of microbial community memberships and structures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 6773–6779.
Schloss, P.D. and J. Handelsman. 2006b. Toward a census of bacteria in soil. PLoS Comput. Biol. e92.
Southham, G. and T.J. Beveridge. 1992. Enumeration of thiobacilli within pH-neutral and acidic mine tailings and their role in the development of secondary mineral soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58, 1904–1912.
Takai, K., D.P. Moser, M. DeFlaun, T.C. Onstott, and J.K. Fredrickson. 2001. Archaeal diversity in waters from deep South African gold mines. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 5750–5760.
Vanparys, B., K. Heylen, L. Lebbe, and P. De Vos. 2005. Devosia limi sp. nov., isolated from a nitrifying inoculum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 1997–2000.
Wang, Q., G.M. Garrity, J.M. Tiedje, and J.R. Cole. 2007. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 5261–5271.
Wang, C.M., C.L. Shyu, S.P. Ho, and S.H. Chiou. 2008. Characterization of a novel thermophilic, cellulose-degrading bacterium Paenibacillus sp. strain B39. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 47, 46–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rastogi, G., Stetler, L.D., Peyton, B.M. et al. Molecular analysis of prokaryotic diversity in the deep subsurface of the former Homestake gold mine, South Dakota, USA. J Microbiol. 47, 371–384 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0249-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0249-1